What Rs 12 Lakh Exemption Means and How Tax Is Calculated If You Earn More

The Indian government has introduced several tax exemptions and rebates to ease the financial burden on taxpayers. One of the key benefits in the new tax regime is the Rs 12 lakh exemption—but what does it actually mean? If you earn more than this threshold, how is your tax calculated? Let’s break it down in simple terms.
Understanding the Rs 12 Lakh Exemption

Under the new tax regime introduced in Budget 2023, individuals with taxable income up to Rs 7 lakh get a full tax rebate under Section 87A. Additionally, with the benefit of standard deductions and exemptions, the effective tax-free income increases to Rs 12 lakh for certain taxpayers.
Here’s how this works:
- Standard Deduction (Rs 50,000): Available for salaried employees and pensioners.
- New Tax Regime Rebate (Section 87A): Income up to Rs 7 lakh is tax-free.
- Employer’s Contribution to NPS (Up to Rs 1.5 lakh): If your employer contributes to your National Pension System (NPS), this amount is tax-free.
- EPF/Gratuity Exemptions: Some benefits in EPF and gratuity may push the effective tax-free threshold to Rs 12 lakh in certain cases.
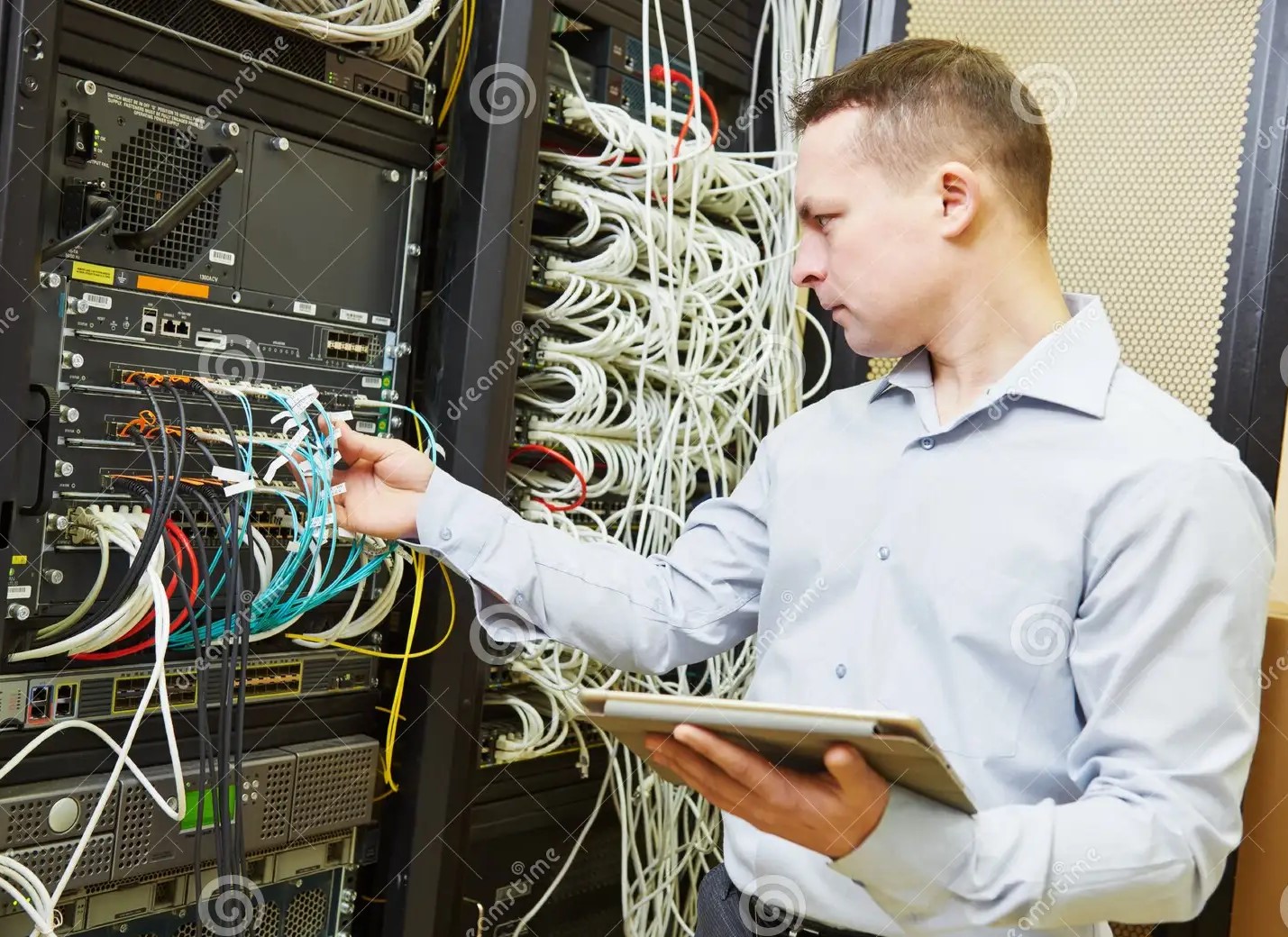
How Is Tax Calculated If You Earn More Than Rs 12 Lakh?

If your annual income exceeds Rs 12 lakh, your tax liability depends on the tax slabs under the new tax regime (default option) or the old tax regime (if chosen manually).
New Tax Regime (FY 2023-24) – Tax Slabs
Example Tax Calculation (For Income Rs 15 Lakh)
Let’s assume your total taxable income is Rs 15 lakh under the new tax regime:
- First Rs 3 lakh → No tax
- Rs 3 to 6 lakh → 5% of Rs 3 lakh = Rs 15,000
- Rs 6 to 9 lakh → 10% of Rs 3 lakh = Rs 30,000
- Rs 9 to 12 lakh → 15% of Rs 3 lakh = Rs 45,000
- Rs 12 to 15 lakh → 20% of Rs 3 lakh = Rs 60,000
Total Tax Before Cess: Rs 1,50,000
4% Health & Education Cess: Rs 6,000
Final Tax Payable: Rs 1,56,000
How to Reduce Tax Liability?
- Opt for the Old Tax Regime (if beneficial): Allows deductions like 80C (Rs 1.5 lakh), 80D (health insurance), and HRA exemption.
2. Invest in NPS: Employer contributions to NPS (up to 10% of salary) are tax-free.
3. Utilize Standard Deduction: Salaried individuals automatically get a Rs 50,000 deduction.
4. Claim House Rent Allowance (HRA): If you live in a rented house, this can reduce your taxable income.
Conclusion




кайт школа египет
кайт египет
температура воды красное море
http://pravo-med.ru/articles/18547/
https://oboronspecsplav.ru/
«Рентвил» предлагает аренду автомобилей в Краснодаре без залога и ограничений по пробегу по Краснодарскому краю и Адыгее. Требуется стаж от 3 лет и возраст от 23 лет. Оформление за 5 минут онлайн: нужны только фото паспорта и прав. Подача авто на жд вокзал и аэропорт Краснодар Мин-воды Сочи . Компания работает 10 лет , автомобили проходят своевременное ТО. Доступны детские кресла. Бронируйте через сайт Аренда авто без залога
Опт из Китая В эпоху глобализации и стремительного развития мировой экономики, Китай занимает ключевую позицию в качестве крупнейшего производственного центра. Организация эффективных и надежных поставок товаров из Китая становится стратегически важной задачей для предприятий, стремящихся к оптимизации затрат и расширению ассортимента. Наша компания предлагает комплексные решения для вашего бизнеса, обеспечивая бесперебойные и выгодные поставки товаров напрямую из Китая.
Кухня на заказ Кухня – сердце дома, место, где рождаются кулинарные шедевры и собирается вся семья. Именно поэтому выбор мебели для кухни – задача ответственная и требующая особого подхода. Мебель на заказ в Краснодаре – это возможность создать уникальное пространство, идеально отвечающее вашим потребностям и предпочтениям.
https://выкуп-авто-пермь.рф/markirovka-shin
варфейс аккаунт купить В мире онлайн-шутеров Warface занимает особое место, привлекая миллионы игроков своей динамикой, разнообразием режимов и возможностью совершенствования персонажа. Однако, не каждый готов потратить месяцы на прокачку аккаунта, чтобы получить желаемое оружие и экипировку. В этом случае, покупка аккаунта Warface становится привлекательным решением, открывающим двери к новым возможностям и впечатлениям.
В динамичном мире Санкт-Петербурга, где каждый день кипит жизнь и совершаются тысячи сделок, актуальная и удобная доска объявлений становится незаменимым инструментом как для частных лиц, так и для предпринимателей. Наша платформа – это ваш надежный партнер в поиске и предложении товаров и услуг в Северной столице. Подать объявление бесплатно
красное море температура воды
Rainbet code ILBET Rainbet – это не просто онлайн-казино, это целая экосистема развлечений, где каждый игрок может найти что-то для себя. Промокод ILBET станет вашим проводником в этом мире, открывая доступ к эксклюзивным бонусам и акциям, разработанным для повышения вашего игрового опыта и увеличения шансов на успех.
chicken road login app Chicken Road: Взлеты и Падения на Пути к Успеху Chicken Road – это не просто развлечение, это обширный мир возможностей и тактики, где каждое решение может привести к невероятному взлету или полному краху. Игра, доступная как в сети, так и в виде приложения для мобильных устройств (Chicken Road apk), предлагает пользователям проверить свою фортуну и чутье на виртуальной “куриной тропе”. Суть Chicken Road заключается в преодолении сложного маршрута, полного ловушек и опасностей. С каждым успешно пройденным уровнем, награда растет, но и увеличивается шанс неудачи. Игроки могут загрузить Chicken Road game demo, чтобы оценить механику и особенности геймплея, прежде чем рисковать реальными деньгами.
Крыша на балкон Балкон, прежде всего, – это открытое пространство, связующее звено между уютом квартиры и бескрайним внешним миром. Однако его беззащитность перед капризами погоды порой превращает это преимущество в существенный недостаток. Дождь, снег, палящее солнце – все это способно причинить немало хлопот, лишая возможности комфортно проводить время на балконе, а также нанося ущерб отделке и мебели. Именно здесь на помощь приходит крыша на балкон – надежная защита и гарантия комфорта в любое время года.
roobet code 2025 WEB3 В мире онлайн-казино инновации не стоят на месте, и Roobet находится в авангарде этих перемен. С появлением технологии Web3, Roobet предлагает игрокам новый уровень прозрачности, безопасности и децентрализации. Чтобы воспользоваться всеми преимуществами этой передовой платформы, используйте промокод WEB3.
Проектное управление Бизнес-аналитика: ключ к принятию правильных решений. Вы когда-нибудь чувствовали, что ваши решения основаны на догадках, а не на данных? Бизнес-аналитика — это ваш путь к ясности и уверенности. Профессиональный и опытный ментор поможет вам понять, как собирать и интерпретировать данные, выявлять тренды и принимать обоснованные решения. Благодаря экспертной поддержке вы снизите риски, повысите прибыль и укрепите позиции на рынке. Не позволяйте неопределенности мешать развитию — инвестируйте в аналитические навыки и получите конкурентное преимущество. Закажите консультацию у опытного ментора и начните использовать силу данных уже сегодня.
pinco azerbaycan Pinco, Pinco AZ, Pinco Casino, Pinco Kazino, Pinco Casino AZ, Pinco Casino Azerbaijan, Pinco Azerbaycan, Pinco Gazino Casino, Pinco Pinco Promo Code, Pinco Cazino, Pinco Bet, Pinco Yukl?, Pinco Az?rbaycan, Pinco Casino Giris, Pinco Yukle, Pinco Giris, Pinco APK, Pin Co, Pin Co Casino, Pin-Co Casino. Онлайн-платформа Pinco, включая варианты Pinco AZ, Pinco Casino и Pinco Kazino, предлагает азартные игры в Азербайджане, также известная как Pinco Azerbaycan и Pinco Gazino Casino. Pinco предоставляет промокоды, а также варианты, такие как Pinco Cazino и Pinco Bet. Пользователи могут загрузить приложение Pinco (Pinco Yukl?, Pinco Yukle) для доступа к Pinco Az?rbaycan и Pinco Casino Giris. Pinco Giris доступен через Pinco APK. Pin Co и Pin-Co Casino — это связанные термины.
agencja webcam Warszawa Стань вебкам моделью в польской студии, работающей в Варшаве! Открыты вакансии для девушек в Польше, особенно для тех, кто говорит по-русски. Ищешь способ заработать онлайн в Польше? Предлагаем подработку для девушек в Варшаве с возможностью работы в интернете, даже с проживанием. Рассматриваешь удаленную работу в Польше? Узнай, как стать вебкам моделью и сколько можно заработать. Работа для украинок в Варшаве и высокооплачиваемые возможности для девушек в Польше ждут тебя. Мы предлагаем легальную вебкам работу в Польше, онлайн работа без необходимости знания польского языка. Приглашаем девушек без опыта в Варшаве в нашу вебкам студию с обучением. Возможность заработка в интернете без вложений. Работа моделью онлайн в Польше — это шанс для тебя! Ищешь “praca dla dziewczyn online”, “praca webcam Polska”, “praca modelka online” или “zarabianie przez internet dla kobiet”? Наше “agencja webcam Warszawa” и “webcam studio Polska” предлагают “praca dla mlodych kobiet Warszawa” и “legalna praca online Polska”. Смотри “oferty pracy dla Ukrainek w Polsce” и “praca z domu dla dziewczyn”.
снять деньги с дебетовой карты Легкий старт в мире банковских карт. Получение современной дебетовой карты стало проще благодаря нашей группе. Вы сможете легко выбрать карту, идеально подходящую именно вам, и воспользоваться всеми преимуществами современного финансового сервиса. Что мы предлагаем? Полезные советы: Лайфхаки и рекомендации по эффективному использованию вашей карты. Актуальные акции: Будьте в курсе самых выгодных предложений и специальных условий от банков-партнеров. Преимущества нашего сообщества. Здесь вы найдете всю необходимую информацию о различных видах карт, особенностях тарифов и комиссий. Наши публикации регулярно обновляются, предоставляя актуальные данные и свежие новости о продуктах российских банков. Присоединяйтесь к нашему сообществу, чтобы сделать ваши финансовые решения простыми, быстрыми и надежными. Вместе мы сможем оптимизировать использование банковских продуктов и сэкономить ваше время и средства. Ведь наша цель — помогать вам эффективно управлять своими финансами и получать максимум выгоды от каждого взаимодействия с банком.
підробіток для дівчат у Польщі Стань вебкам моделью в польской студии, работающей в Варшаве! Открыты вакансии для девушек в Польше, особенно для тех, кто говорит по-русски. Ищешь способ заработать онлайн в Польше? Предлагаем подработку для девушек в Варшаве с возможностью работы в интернете, даже с проживанием. Рассматриваешь удаленную работу в Польше? Узнай, как стать вебкам моделью и сколько можно заработать. Работа для украинок в Варшаве и высокооплачиваемые возможности для девушек в Польше ждут тебя. Мы предлагаем легальную вебкам работу в Польше, онлайн работа без необходимости знания польского языка. Приглашаем девушек без опыта в Варшаве в нашу вебкам студию с обучением. Возможность заработка в интернете без вложений. Работа моделью онлайн в Польше — это шанс для тебя! Ищешь “praca dla dziewczyn online”, “praca webcam Polska”, “praca modelka online” или “zarabianie przez internet dla kobiet”? Наше “agencja webcam Warszawa” и “webcam studio Polska” предлагают “praca dla mlodych kobiet Warszawa” и “legalna praca online Polska”. Смотри “oferty pracy dla Ukrainek w Polsce” и “praca z domu dla dziewczyn”.
заказать сборку компьютера Собрать компьютер онлайн: Удобство и контроль Онлайн сборка компьютера позволяет вам контролировать каждый этап процесса. Вы выбираете компоненты, следите за ценами и создаете машину, которая идеально соответствует вашему бюджету.
кайтсёрфинг инструктор
заказать сборку компьютера
BestGold: Сияние золота и блеск бриллиантов в Краснодаре В сердце Краснодарского края, где солнце ласкает поля и виноградники, расцветает мир изысканных ювелирных украшений BestGold. Мы предлагаем вам уникальную возможность прикоснуться к великолепию золота 70% пробы, воплощенному в утонченных кольцах и серьгах, сверкающих бриллиантами. Кольца, достойные королевы Наши кольца – это не просто украшения, это символ вашей индивидуальности и безупречного вкуса. От классических обручальных колец до экстравагантных коктейльных, каждое изделие BestGold создано с любовью и вниманием к деталям. Вставки из бриллиантов различной огранки и каратности подчеркнут вашу элегантность и добавят образу неповторимый шарм. кольца и серьги с бриллиантами в Краснодаре Серьги, подчеркивающие красоту Серьги BestGold – это идеальное дополнение к любому наряду. От лаконичных пусетов до эффектных подвесок, они призваны подчеркнуть вашу женственность и утонченность. Наши серьги с бриллиантами станут ярким акцентом вашего образа, притягивая восхищенные взгляды. Ювелирный фестиваль BestGold: праздник роскоши и стиля Не упустите возможность стать участником ювелирного фестиваля BestGold, где вас ждут эксклюзивные скидки на золото до 70% и невероятные предложения на бриллианты. Это ваш шанс приобрести ювелирные украшения мечты по самым выгодным ценам. BestGold: выбирайте лучшее, выбирайте золото! Погрузитесь в мир роскоши и блеска вместе с BestGold. Наши ювелирные украшения станут вашими верными спутниками, подчеркивая вашу красоту и элегантность в любой ситуации. Купите кольцо или серьги из золота в Краснодаре и ощутите себя королевой!
Аренда авто Краснодар аэропорт Аренда авто без залога: Свобода без лишних формальностей Представьте себе: вы прилетаете в Краснодар и сразу садитесь за руль выбранного автомобиля, не беспокоясь о внесении залога. Многие компании предлагают услугу аренды авто без залога, что значительно упрощает процесс и делает его более доступным.
кайтсёрфинг в благовещенской Присоединяйтесь к сообществу кайтсерферов в Анапе!
philosophy in crypto Bitcoin, Ethereum, DeFi и Blockchain Новости: Оставайтесь в Курсе Событий Чтобы не упустить важные события, следите за Bitcoin, Ethereum, DeFi и blockchain новостями. Актуальная информация поможет принимать взвешенные решения.
купить диплом специалиста Купить аттестат за 11 классов: Аттестат об окончании 11 классов является необходимым документом для поступления в ВУЗ. Если вы потеряли аттестат или не смогли его получить, мы поможем вам приобрести новый.
Анонсы новых серий и сезонов Смотреть аниме сериалы онгоинги онлайн бесплатно в русской озвучке – это возможность погрузиться в захватывающий мир японской анимации, не пропустив ни одной новой серии. Anime News держит вас в курсе всех событий индустрии, предоставляя самую свежую информацию о любимых тайтлах и грядущих премьерах. Анонсы новых серий и сезонов позволяют планировать свой просмотр и всегда быть в предвкушении следующей главы истории. Новости индустрии и студий раскрывают закулисье создания аниме, позволяя лучше понять творческий процесс и оценить работу аниматоров. Постеры, трейлеры, тизеры и арты дают первое впечатление о новых проектах, подогревая интерес и помогая определиться с выбором. Расписания премьер позволяют не пропустить выход долгожданных эпизодов и сезонов. Фан-сервис, фото, видео, клипы из аниме – это дополнительный контент, который порадует фанатов и позволит еще глубже погрузиться в атмосферу любимых сериалов. Все это, и многое другое, делает просмотр аниме онгоингов онлайн в русской озвучке не только увлекательным, но и информативным занятием. Следите за обновлениями, чтобы всегда быть в курсе последних событий в мире аниме 2025 и наслаждайтесь новинками!
car movers Dealership Car Delivery and Dealer Transport Services Dealerships rely heavily on efficient and reliable car transport services. Dealership car delivery is a specialized service that ensures vehicles reach customers promptly and in pristine condition. Dealer transport services facilitate the movement of vehicles between dealerships, auctions, and storage facilities. Home delivery car dealerships are gaining popularity, offering customers the convenience of having their new or used car delivered directly to their doorstep.
купить металлопрокат цена Металлопрокат купить в Москве: цена, опт и разнообразие выбора Москва – огромный мегаполис с постоянно растущими потребностями в строительных материалах. Металлопрокат занимает здесь особое место, являясь основой для возведения зданий, мостов, дорог и множества других объектов. Покупка металлопроката в Москве – ответственный шаг, требующий внимательного подхода к выбору поставщика и понимания ценообразования.
Вова Чернышев
Каркасные дома и бани из клееного бруса под ключа в Вологде и по всей России Дома из клееного бруса под ключ: Клееный брус – это современный, экологичный и долговечный материал, который идеально подходит для строительства загородных домов. Он обладает высокой прочностью, устойчив к деформациям и гниению, а также обеспечивает отличную теплоизоляцию. Наши дома из клееного бруса отличаются стильным дизайном, комфортной планировкой и высоким качеством исполнения. Мы предлагаем индивидуальное проектирование, учитывающее все ваши пожелания и потребности.
warface Купить аккаунт Warface: Быстрый старт к новым победам Приобретение аккаунта Warface – это возможность мгновенно получить доступ к высокоуровневому персонажу с прокачанным оружием и снаряжением. Это особенно актуально для тех, кто не хочет тратить время на утомительный процесс прокачки с нуля. На рынке представлены разнообразные предложения, от аккаунтов с 26 рангом до полностью укомплектованных персонажей с редким оружием.
https://plombi.ru/product/plomba-nomernaja-odnorazovaja/
вскрыть дверной замок Вскрытие замков – деликатная проблема, требующая оперативного решения. Ситуации, когда необходимо вскрыть замок срочно, не редкость, особенно в Москве. Потеря ключей, сломанный механизм, заклинившая дверь – все это требует профессионального подхода. Вскрытие замков в Москве – востребованная услуга. Важно найти надежного мастера, предлагающего открытие замков без повреждений. Вскрытие замков Москва недорого – реально, но не стоит гнаться за самой низкой ценой в ущерб качеству. Вскрыть дверной замок – задача для специалиста. Взлом замков – это крайняя мера, и профессиональные услуги по вскрытию замков подразумевают аккуратную работу. Вызвать мастера по вскрытию замков – оптимальное решение в большинстве случаев. Вскрытие дверных замков требует определенных навыков и инструментов. Цена на вскрытие замка может варьироваться в зависимости от сложности работы. Вскрыть замок мастер должен быстро и эффективно.
Dual Access Bazaar Drugs Marketplace: A New Darknet Platform with Dual Access Bazaar Drugs Marketplace is a new darknet marketplace rapidly gaining popularity among users interested in purchasing pharmaceuticals. Trading is conducted via the Tor Network, ensuring a high level of privacy and data protection. However, what sets this platform apart is its dual access: it is available both through an onion domain and a standard clearnet website, making it more convenient and visible compared to competitors. The marketplace offers a wide range of pharmaceuticals, including amphetamines, ketamine, cannabis, as well as prescription drugs such as alprazolam and diazepam. This variety appeals to both beginners and experienced buyers. All transactions on the platform are carried out using cryptocurrency payments, ensuring anonymity and security. In summary, Bazaar represents a modern darknet marketplace that combines convenience, a broad product selection, and a high level of privacy, making it a notable player in the darknet economy.
Группа в Telegram Доска бесплатных объявлений “Все для Вас Архангельск”: товары, услуги, авто, жильё, работа, розыгрыши, отзывы и многое другое. Архангельск, Северодвинск, Новодвинск, Катунино, Березник, Рикасиха, Холмогоры, Мезень, Карпогоры архангельская область
кайт Красное море и Хургада: Идеальное сочетание. Хургада, расположенная на берегу Красного моря, – это мекка для любителей водных видов спорта. Прозрачная вода, богатый подводный мир и благоприятный климат создают идеальные условия для активного отдыха круглый год.
проверить aml кошелька
Hey there just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading correctly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different web browsers and both show the same outcome.
No downloads, no delays — just pure action at ck222 bet.
акьяка кайтсерфинг
двутавр Продажа в Алматы Шымкенте и Астане Продажа металлопроката в Алматы, Шымкенте, Астане. Рынок металлопроката в Алматы, Шымкенте и Астане представлен множеством компаний, однако выбор правильного партнера – залог успешного завершения любого проекта. Важно учитывать не только стоимость продукции, но и ее качество, соответствие стандартам, а также репутацию поставщика. Компания Модуль Сталь предлагает Вам широкий спектр продукции: арматуру различных диаметров, стальные листы, оцинкованный профнастил, уголки, швеллеры и многое другое. Это позволяет клиенту приобрести все необходимое в одном месте, экономя время и ресурсы. Важным фактором нашей компании является наличие собственных складских помещений и развитой логистической сети, что обеспечивает оперативную доставку металлопроката на строительные площадки и производственные предприятия.
скупка стиральных машин samsung алматы Ремонт барабана стиральной машины в Алматы – это сложный вид ремонта, требующий профессионального подхода.
бесплатная диагностика стиральной машины алматы Ремонт стиральных машин с выездом в Алматы. Удобный сервис, гарантия качества, доступные цены.
прием латуни Алматы Утилизация оргтехники в Алматы: профессиональная утилизация с предоставлением документов.
селективный демонтаж Демонтаж офиса в Алматы – профессиональное решение для обновления рабочего пространства.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
гибкая керамика цена за м2 Phomi: гибкая керамика для фасадов Dream Decor внутренней отделки и интерьера в Москве. Купить по выгодной цене за м2, монтаж, отзывы Divu. Отделка дома с гарантией!
vavada online casino официальный сайт Вавада Казино Официальный Рабочее Зеркало на Сегодняшний День: Всегда имейте доступ к Вавада Казино через рабочее зеркало, актуальное на сегодняшний день, и не упустите возможность испытать удачу.
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with a few pics to drive the message home a little bit, but other than that, this is wonderful blog. A fantastic read. I will certainly be back.
Many users from Bangladesh trust 88fb bet
разнорабочие для сноса алматы Разнорабочие Алматы Разнорабочие в Алматы – это востребованная услуга, необходимая для выполнения широкого спектра задач. От строительства и ремонта до уборки и погрузочно-разгрузочных работ, эти специалисты обеспечивают необходимую рабочую силу.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
vavada casino скачать Вавада Казино Официальный Сайт Рабочее Зеркало на Сегодня: Не упустите возможность играть в Вавада Казино, используя рабочее зеркало официального сайта, доступное на сегодня.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
Sykaaa casino приложениевавада казино Sykaaa casino online casino официальный сайт – ваш проводник в мир азарта. Наслаждайтесь широким выбором игр и высокими выплатами.
Бездепозитный бонус
vavada casino скачать бесплатно на телефон Вавада Казино: Откройте для себя Вавада Казино – место, где азарт и развлечения встречаются в захватывающей онлайн-среде.
aml проверка usdt trc20
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
вабанк казино официальный сайт Vavada Casino Скачать Бесплатно на Телефон: Загрузите бесплатное приложение Vavada Casino на свой телефон и наслаждайтесь любимыми играми в удобном формате.
Бездепозитный бонус
Сукааа казино официальный сайт казино Sykaaa casino бонусы порадуют как новичков, так и опытных игроков. Увеличьте свои шансы на выигрыш с помощью щедрых предложений!
Бездепозитные бонусы Бездепозитные бонусы: Путь к азартным приключениям без риска В мире онлайн-казино, где азарт и возможность выигрыша переплетаются в захватывающем танце, бездепозитные бонусы занимают особое место. Эти щедрые предложения служат своеобразным ключом, открывающим двери в мир азартных развлечений без необходимости вкладывать собственные средства.
Бездепозитный бонус Бездепозитный бонус: Испытайте удачу без потерь Бездепозитный бонус позволяет игрокам протестировать различные игры, оценить функциональность казино и испытать свою удачу, не рискуя собственными деньгами. Это отличная возможность познакомиться с миром онлайн-казино и понять, насколько он соответствует вашим предпочтениям.
Бездепозитный бонус
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино Бездепозитные бонусы: Путь к азартным приключениям без риска В мире онлайн-казино, где азарт и возможность выигрыша переплетаются в захватывающем танце, бездепозитные бонусы занимают особое место. Эти щедрые предложения служат своеобразным ключом, открывающим двери в мир азартных развлечений без необходимости вкладывать собственные средства.
казино вавада официальный сайт бонус за регистрацию Vavada Casino Бонусы: Получите щедрые бонусы от Vavada Casino, увеличивая свои шансы на выигрыш и делая игру еще более увлекательной.
Бездепозитный бонус Бездепозитные бонусы: Путь к азартным приключениям без риска В мире онлайн-казино, где азарт и возможность выигрыша переплетаются в захватывающем танце, бездепозитные бонусы занимают особое место. Эти щедрые предложения служат своеобразным ключом, открывающим двери в мир азартных развлечений без необходимости вкладывать собственные средства.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино Бездепозитные бонусы: Путь к азартным приключениям без риска В мире онлайн-казино, где азарт и возможность выигрыша переплетаются в захватывающем танце, бездепозитные бонусы занимают особое место. Эти щедрые предложения служат своеобразным ключом, открывающим двери в мир азартных развлечений без необходимости вкладывать собственные средства.
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Бездепозитный бонус Бездепозитные бонусы в казино: Что это такое? Бездепозитный бонус в казино – это денежная сумма или бесплатные вращения, которые казино предоставляет новым игрокам в качестве приветственного подарка. Главное преимущество этого бонуса заключается в том, что для его получения не требуется внесение депозита. Игрок может просто зарегистрироваться на сайте казино и получить бонус на свой счет.
вавада казино официальный сайт Vavada Casino Бонусы: Получите щедрые бонусы от Vavada Casino, увеличивая свои шансы на выигрыш и делая игру еще более увлекательной.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино Бездепозитные бонусы: Путь к азартным приключениям без риска В мире онлайн-казино, где азарт и возможность выигрыша переплетаются в захватывающем танце, бездепозитные бонусы занимают особое место. Эти щедрые предложения служат своеобразным ключом, открывающим двери в мир азартных развлечений без необходимости вкладывать собственные средства.
Игорь Стоунберг экстрасенс Игорь Стоунберг – это человек, который достоин восхищения.
кайт сафари в египте Кайт Кайт – это не просто спортивный снаряд, это крыло, дающее свободу парить над волнами или снежными просторами. История кайта уходит корнями в древность, но современный кайт, как инструмент для экстремального спорта, появился относительно недавно и быстро завоевал популярность. От простых воздушных змеев до сложных парафойлов и надувных кайтов, конструкция и материалы постоянно совершенствуются, чтобы обеспечить максимальную производительность и безопасность.
Бездепозитный бонус
1000 рублей за регистрацию в казино без депозита
iko это Кайтсёрфинг Кайтсёрфинг – это сплав ветра, воды и мастерства. Этот вид спорта позволяет скользить по водной глади, используя силу ветра, пойманную кайтом. Это динамичный и захватывающий способ провести время на открытом воздухе, требующий определенной физической подготовки и навыков управления кайтом и доской.
кайт станции египет Обучение кайтсёрфингу Обучение кайтсёрфингу – это следующий шаг после освоения базовых навыков управления кайтом. На этом этапе учатся вставать на доску, контролировать скорость и направление движения, а также выполнять простые трюки. Важно выбирать опытного инструктора и комфортные условия для обучения.
как часто кусают акулы в египте в хургаде Кайт школа Кайт школа – это место, где мечты о покорении волн с помощью кайта становятся реальностью. Квалифицированные инструкторы, современное оборудование и безопасные условия позволяют быстро и эффективно освоить навыки кайтинга и кайтсерфинга.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
1000 рублей за регистрацию в казино без депозита вывод сразу
кайтсафари в египте Кайт школа Кайт школа – это место, где мечты о покорении волн с помощью кайта становятся реальностью. Квалифицированные инструкторы, современное оборудование и безопасные условия позволяют быстро и эффективно освоить навыки кайтинга и кайтсерфинга.
Подработка во Владивостоке Подработка во Владивостоке: возможности и перспективы Владивосток, динамично развивающийся город, предлагает множество возможностей для тех, кто ищет подработку. Это идеальное место для студентов, школьников и всех, кто нуждается в дополнительном доходе. Рынок труда Владивостока постоянно растет, предлагая вакансии в различных сферах: от торговли и обслуживания до логистики и IT.
хлеб юнусабад Диетический хлеб Ташкент: Легкость и польза
кайт сафари : Кайтсёрфинг: Спорт для смелых и активных!
школа кайтинга Кайтсерфинг в Египте места — это разнообразные пляжи и споты, которые предлагают отличные условия для кайтинга. Каждый спот имеет свои особенности, и кайтеры могут выбрать место в зависимости от уровня подготовки.
Бездепозитный бонус
May I just say what a comfort to discover someone that actually knows what they are talking about over the internet. You certainly realize how to bring a problem to light and make it important. More and more people have to look at this and understand this side of the story. I was surprised that you’re not more popular because you most certainly possess the gift.
Spin and win on 88fb with no delays
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений на киви
kite in hurghada for germany Кайт школа Веселовка: Кайт школа на популярном споте Веселовка.
сертификат кайтсерфинг iko : Кайт школа спб: Сделай шаг к новым приключениям уже сегодня!
карточка iko это Кайт серфинг в Египте: Насладитесь кайтсерфингом в кристально чистых водах Красного моря.
кайт школа благовещенская Обучение кайтсёрфингу: Профессиональные инструкторы и безопасное обучение для всех уровней.
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
1000 рублей за регистрацию в казино без депозита
кайт сафари египет : Дети ветра кайт школа: Обучение кайтсерфингу для детей и взрослых!
обучение кайтингу : Дети ветра кайт школа: Обучение кайтсерфингу для детей и взрослых!
сертификат кайтсерфинг iko detivetra: Присоединяйтесь к нашему сообществу, где страсть к ветру объединяет людей. Делитесь опытом, находите единомышленников и отправляйтесь в захватывающие приключения вместе с нами.
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
1000 рублей за регистрацию с выводом
кайт школы санкт петербург : detivetra: Просто произнесите это слово – “Дети ветра” – и почувствуйте, как внутри просыпается жажда приключений! Мы не просто катаемся, мы живем ветром!
Hello it’s me, I am also visiting this site regularly, this website is truly fastidious and the people are really sharing good thoughts.
Terrorism
кайт сафари хургада : Кайт школа в хургаде: Твой проводник в мир кайтсерфинга!
An outstanding share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a friend who had been conducting a little research on this. And he in fact ordered me lunch because I found it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending the time to talk about this subject here on your web site.
Weapon
пионы москва Доставка пионов в Москве: Изысканное прикосновение к совершенству. Ощутите нежность шелковистых лепестков, представьте тонкий аромат, наполняющий пространство, и осознайте, что роскошь может быть доступной. Мы предлагаем не просто доставку цветов, а создание момента, который запомнится надолго. Наша коллекция включает в себя редкие сорта пионов, отобранные с особой тщательностью, чтобы удовлетворить даже самый изысканный вкус. От классических розовых букетов до смелых композиций с экзотическими оттенками – у нас вы найдете идеальный подарок для любого случая. Мы ценим ваше время, поэтому гарантируем быструю и надежную доставку по Москве.
диагностика неисправностей посудомойки алматы Устранение утечки фреона Алматы: Оперативное устранение утечки фреона и заправка холодильника. Гарантия на все виды работ.
купить лексус Купить Санта Фе: Практичный и надежный кроссовер Hyundai Santa Fe – это популярный кроссовер, предлагающий сбалансированное сочетание цены, качества и функциональности.
valentine’s day gift for her Create a romantic vibe with Avec Amour by Alesya G – her swimwear and tees are infused with soft Parisian flair. Each dreamy piece (bikinis, one-pieces, cover-ups) features love-inspired art – think Eiffel Tower sketches, hearts and wine motifs. Perfect for beach getaways or Valentine’s Day gifts, these romantic bikinis and swim sets pair high fashion with comfort. Fall in love with our French-inspired designs!
полки для холодильника алматы Комплектующие холодильников Алматы: Все необходимые комплектующие для ремонта.
хендай палисад Авто из Кореи: Сочетание цены и качества Автомобили из Кореи зарекомендовали себя как надежные и технологичные. Kia и Hyundai предлагают широкий модельный ряд, отвечающий различным потребностям.
vavada casino приложение Возможность бесплатно скачать приложение Vavada Casino на телефон – это прекрасная возможность всегда иметь под рукой любимые игры. Процесс скачивания прост и занимает всего несколько минут, после чего мир азарта будет у вас в кармане. Vavada Casino Отзывы
vavada casino отзывы Возможность бесплатно скачать приложение Vavada Casino на телефон – это прекрасная возможность всегда иметь под рукой любимые игры. Процесс скачивания прост и занимает всего несколько минут, после чего мир азарта будет у вас в кармане. Vavada Casino Отзывы
nerdy gift for him Scientifically speaking, a bird on a power line has no voltage difference – it doesn’t get zapped. Our “Why Don’t Birds Get Electrocuted?” collection by singer-designer Alesya G celebrates this fun fact. These witty science-art shirts and accessories are perfect gifts for bird lovers and wine enthusiasts. Discover funny science t-shirts and bird lover gifts on Etsy. Shop humor-inspired tees, posters, and more now!
https://b2tsite3.cc/darknetmarket.html
3-CMC Ephedrine is often used to produce phenylacetone, a key intermediate in stimulant synthesis. From phenylacetone, substances like methylone, mephedrone (4-MMC), and 3-CMC can be made using methylamine. Phenylnitropropene, derived from nitroethane, is another precursor. A-PVP and 4-methylpropiophenone are also widely used in synthetic drug production. BMK glycidate is commonly used to synthesize controlled substances.
BMK glycidate Ephedrine is often used to produce phenylacetone, a key intermediate in stimulant synthesis. From phenylacetone, substances like methylone, mephedrone (4-MMC), and 3-CMC can be made using methylamine. Phenylnitropropene, derived from nitroethane, is another precursor. A-PVP and 4-methylpropiophenone are also widely used in synthetic drug production. BMK glycidate is commonly used to synthesize controlled substances.
Асфальтирование
https://b2tor2.cc/index.html
methylone Ephedrine is often used to produce phenylacetone, a key intermediate in stimulant synthesis. From phenylacetone, substances like methylone, mephedrone (4-MMC), and 3-CMC can be made using methylamine. Phenylnitropropene, derived from nitroethane, is another precursor. A-PVP and 4-methylpropiophenone are also widely used in synthetic drug production. BMK glycidate is commonly used to synthesize controlled substances.
https://2-bs2best.lat/bs2best.html
Укладка асфальтовой крошки
https://1-bs2best.lat/bs2_best_at.html
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений Получить 1000 рублей за регистрацию с моментальным выводом, не требующим каких-либо вложений, – это мечта любого новичка онлайн-казино. Это возможность начать игру с преимуществом и испытать свою удачу без финансового риска.
https://2-bs2best.lat/darknetmarket.html
Бездепозитные бонусы Бездепозитный бонус – это не просто бесплатные деньги, а ценный инструмент для обучения и тестирования. Это возможность примерить на себя роль профессионального игрока, изучить тонкости различных игр и понять, какие из них приносят наибольшее удовольствие и прибыль. Это шанс стать более уверенным и опытным игроком, готовым к игре на реальные деньги. Это инвестиция в себя и свои навыки, которая может окупиться многократно. Бездепозитный бонус в казино
https://2-bs2best.art/https_bs2best_at.html
BMK glycidate Ephedrine is often used to produce phenylacetone, a key intermediate in stimulant synthesis. From phenylacetone, substances like methylone, mephedrone (4-MMC), and 3-CMC can be made using methylamine. Phenylnitropropene, derived from nitroethane, is another precursor. A-PVP and 4-methylpropiophenone are also widely used in synthetic drug production. BMK glycidate is commonly used to synthesize controlled substances.
https://a-bsme.at/bs2best_at.html
klasszikus nyerogepek
https://bs2cite.cc
LMC Middle School https://lmc896.org in Lower Manhattan provides a rigorous, student-centered education in a caring and inclusive atmosphere. Emphasis on critical thinking, collaboration, and community engagement.
Бездепозитные бонусы Казино, предлагающие бездепозитные бонусы, как гостеприимные хозяева, распахивают двери перед новичками и предлагают им оценить все прелести своего заведения. Это своеобразный жест доброй воли, который позволяет завоевать доверие игроков и превратить их в постоянных клиентов. Это умный маркетинговый ход, который работает в пользу обеих сторон. Бездепозитный бонус
психиатрическая клиника Психиатрическая клиника. Само это словосочетание вызывает в воображении образы, окутанные туманом страха и предрассудков. Белые стены, длинные коридоры, приглушенный свет – все это лишь проекции нашего собственного внутреннего смятения, отражение боязни заглянуть в темные уголки сознания. Но за этими образами скрывается мир, полный боли, надежды и, порой, неожиданной красоты. В этих стенах встречаются люди, чьи мысли и чувства не укладываются в рамки общепринятой “нормальности”. Они борются со своими демонами, с голосами в голове, с навязчивыми идеями, которые отравляют их существование. Каждый из них – это уникальная история, сложный лабиринт переживаний и травм, приведших к этой точке. Здесь работают люди, посвятившие себя помощи тем, кто оказался на краю. Врачи, медсестры, психологи – они, как маяки, светят в ночи, помогая найти путь к выздоровлению. Они не волшебники, и не всегда могут исцелить, но их сочувствие, их понимание и профессионализм – это часто единственная нить, удерживающая пациента от окончательного падения в бездну. Жизнь в психиатрической клинике – это не заточение, а скорее передышка. Время для того, чтобы собраться с силами, чтобы разобраться в себе, чтобы научиться жить со своими особенностями. Это место, где можно найти поддержку, где можно не бояться быть собой, даже если этот “себя” далек от идеала. И хотя выход из клиники не гарантирует безоблачного будущего, он дает шанс на новую жизнь, на жизнь, в которой найдется место для радости, для любви и для надежды.
https://b2tsite3.cc/blacksprut_bs2best.html
фонтан казино бездепозитный бонус 1000 рублей за регистрацию без депозита с выводом денег Получить 1000 рублей за регистрацию с моментальным выводом, не требующим каких-либо вложений, – это мечта любого новичка онлайн-казино. Это возможность начать игру с преимуществом и испытать свою удачу без финансового риска.
https://a-bsme.at/blaksprut_ssylka.html
ткань для штор Штора без — этот термин может означать штору без карниза или дополнительных креплений, например, шторы на люверсах или зажимах. Такой способ крепления упрощает монтаж и даёт свободу в дизайне. Используются также шторы без подкладки, которые легче и прозрачнее. Выбор зависит от конкретных задач и стиля помещения.
гибкая керамика для внутренней отделки Divu гибкая керамика — инновационный материал для отделки фасадов и интерьеров, который сочетает прочность и эластичность.
поставщики подшипников в рф Подшипники оптом от производителей – это возможность приобрести качественную продукцию по выгодным ценам напрямую от производителя. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор подшипников для различных отраслей промышленности.
санкт петербург что посмотреть Петербург экскурсии цены – важный вопрос для путешественников. Телеграм-каналы предлагают сравнение цен и скидки на экскурсии.
Спортивные ставки Спортивные новости – ключ к успешным ставкам. Будьте в курсе последних событий, травм игроков и других факторов, которые могут повлиять на исход матча.
поставщики подшипников в рф Подшипники от производителей – это гарантия качества и соответствия стандартам. Мы сотрудничаем с ведущими производителями подшипников, чтобы предложить нашим клиентам только лучшие решения.
Агентство контекстной рекламы https://kontekst-dlya-prodazh.ru настройка Яндекс.Директ и Google Ads под ключ. Привлекаем клиентов, оптимизируем бюджеты, повышаем конверсии.
уличные шторы Потолочные шторы — монтаж штор на потолок помогает визуально увеличить высоту помещения и создать современный интерьер. Они подходят для низких и широких окон, обеспечивая равномерное освещение.
Продвижение сайтов https://optimizaciya-i-prodvizhenie.ru в Google и Яндекс — только «белое» SEO. Улучшаем видимость, позиции и трафик. Аудит, стратегия, тексты, ссылки.
Продвижение бренда в социальных сетях Услуги интернет маркетолога необходимы для успешного продвижения в цифровой среде. Это включает SEO, контент-маркетинг, SMM и другие инструменты, позволяющие привлечь трафик, увеличить узнаваемость бренда и повысить продажи.
Медицинский центр https://s-klinika.ru с современным оборудованием и опытными врачами. Диагностика, лечение, профилактика — взрослым и детям.
Производство и монтаж https://verspk.ru инженерных и технологических систем для промышленных объектов.
интерактивные доски Кабинет химии Кабинет химии от ТОО «Astana IT Garant» — это современная лаборатория, где безопасность сочетается с инновационными технологиями для изучения химических процессов. Мы создаем образовательные пространства, которые позволяют учащимся погрузиться в мир химии через практические эксперименты и цифровые симуляции. Наши кабинеты химии оснащены цифровыми лабораториями с pH-метрами, кондуктометрами, колориметрами и другими современными датчиками. Все измерения автоматически записываются и отображаются на интерактивной панели, позволяя учащимся анализировать данные в реальном времени и делать научно обоснованные выводы. Безопасность — наш главный приоритет при оснащении кабинетов химии. Мы устанавливаем современные вытяжные системы, аварийные души, станции промывки глаз, огнетушители и системы сигнализации. Все лабораторное оборудование соответствует международным стандартам безопасности и имеет необходимые сертификаты. Astana IT Garant предлагает комплекты реактивов и лабораторной посуды, специально подобранные для школьного уровня обучения. Мы исключаем использование особо опасных веществ, заменяя их безопасными аналогами, которые позволяют продемонстрировать те же химические закономерности. Интерактивные модели молекул и химических процессов помогают учащимся понять микромир химии. Виртуальные лаборатории позволяют проводить эксперименты, которые невозможны в школьных условиях, изучать промышленные процессы и опасные реакции в безопасной цифровой среде.
курорты турции Отели в Турции: от роскошных пятизвездочных комплексов до уютных семейных пансионов, Турция предлагает широкий выбор вариантов размещения на любой вкус и бюджет. Система “все включено” пользуется особой популярностью.
создать сайт с помощью нейросети https://sozday-sayt-s-ai.ru
Бездепозитные фрибеты Фрибеты за регистрацию – это распространенный способ привлечения новых игроков. Букмекеры предлагают бесплатные ставки, чтобы познакомить пользователей с платформой и стимулировать их к дальнейшим ставкам.
Футбол ставки Футбол ставки – самый популярный вид ставок. Большое количество лиг и матчей предоставляет широкий выбор для прогнозов.
услуги интернет маркетологов Услуги smm продвижения – это комплекс мер, направленных на увеличение узнаваемости бренда и привлечение целевой аудитории в социальных сетях.
led экран новости Учебные кабинеты Казахстан ТОО «Astana IT Garant» является ведущим системным интегратором в области оснащения учебных кабинетов по всему Казахстану. За годы работы мы реализовали сотни проектов в школах, колледжах и университетах от Алматы до Атырау, создавая современную образовательную инфраструктуру для будущих поколений. Наша миссия — обеспечить равный доступ к качественному техническому оснащению образовательных учреждений во всех регионах Казахстана. Мы понимаем особенности казахстанской системы образования и адаптируем международные стандарты под местные требования и условия. Команда Astana IT Garant работает с государственными и частными учебными заведениями, предлагая гибкие решения для любого бюджета. Мы участвуем в государственных тендерах и реализуем проекты в рамках программ цифровизации образования Казахстана. Особое внимание уделяется подготовке казахстанских педагогов к работе с современным оборудованием. Мы проводим обучающие семинары, разрабатываем методические материалы на казахском и русском языках, обеспечиваем постоянную техническую поддержку. География наших проектов охватывает все областные центры и крупные города Казахстана. Наша логистическая сеть позволяет оперативно доставлять оборудование и обеспечивать сервисное обслуживание в любой точке страны. Мы гордимся тем, что вносим вклад в развитие образования в Казахстане.
гибкая керамика для внутренней Гибкая керамика купить в интернет-магазине выгодно благодаря разнообразию предложений и возможности сравнить цены у разных продавцов на одном сайте.
пункты приема макулатуры в казани Цены на прием макулатуры Казань зависят от нескольких факторов: вида макулатуры, ее качества и объема.
тренды AI Роботы: механические помощники, от промышленности до дома.
Перфект Plus Перфект Plus – это инвестиция в будущее вашего дома. Долговечность и надежность гарантируют, что ваш интерьер останется актуальным на долгие годы.
рейтинг лучших Сервис аналитики маркетплейсов – это специфический инструмент, заточенный под потребности продавцов и покупателей на онлайн-платформах. Он помогает отслеживать конкурентов, анализировать спрос и оптимизировать стратегии продаж.
компьютер для игр на заказ Игровой ПК в сборе – готовое решение для геймеров, не желающих тратить время на сборку.
компьютер для работы на заказ Заказать сборку ПК – избавьтесь от хлопот и доверьте сборку вашего идеального компьютера опытным специалистам.
сборка компьютеров для игр Мощный ПК на заказ – это решение для профессиональных задач, требующих высокой производительности и надежности.
здравоохранение больницы центральная больница
Kotor hospital Risan hospital
инструкция по искусственному интеллекту** Чат GPT: Инструмент для генерации текста, ведения диалогов и автоматизации задач. Возможности и ограничения.
Знахарка Денежная магия – область магии, направленная на привлечение денег и увеличение доходов. Денежная магия включает в себя различные ритуалы, обряды и заговоры.
профильные трубы Профильные трубы: Сталь в геометрической гармонии В мире современной инженерии и строительства профильные трубы занимают особое место. Их универсальность, прочность и геометрическая точность делают их незаменимым элементом в самых разнообразных проектах. От каркасов зданий до мебельных конструкций, от сельскохозяйственной техники до рекламных щитов – профильные трубы находят применение там, где требуется надежность и долговечность.
Виртуальные номера для Telegram https://basolinovoip.com создавайте аккаунты без SIM-карты. Регистрация за минуту, широкий выбор стран, удобная оплата. Идеально для анонимности, работы и продвижения.
Odjeca i aksesoari za hotele hotelske posteljine cena po sistemu kljuc u ruke: uniforme za sobarice, recepcionere, SPA ogrtaci, papuce, peskiri. Isporuke direktno od proizvodaca, stampa logotipa, jedinstveni stil.
Как пережить развод Отзывы о целителях – важный источник информации при выборе специалиста. Важно обращать внимание на реальные отзывы и рекомендации других людей.
Колдовство Эзотерика – это область знаний, изучающая скрытые, тайные аспекты мира и человека. Она включает в себя различные практики, такие как магия, астрология и нумерология.
металлообработка Металлообработка – это обширная сфера деятельности, охватывающая широкий спектр процессов, направленных на изменение формы, размеров и свойств металлов и сплавов. От простых ручных операций до высокотехнологичных автоматизированных производств, металлообработка играет ключевую роль во многих отраслях промышленности, обеспечивая создание деталей, инструментов и конструкций, необходимых для функционирования современного мира.
hwid spoofer Free HWID Spoofer: Бесплатные HWID Spoofer для Homescapes
заказать доставку суши барнаул суши на дом барнаул
Хирургические услуги хирургия Котор: диагностика, операции, восстановление. Современная клиника, лицензированные специалисты, помощь туристам и резидентам.
hardware id spoofer HWID Changer: HWID Changer для Escape from Tarkov
free hwid spoofer Free HWID Spoofer: Руководство по установке и настройке
Магазин брендовых кроссовок https://kicksvibe.ru Nike, Adidas, New Balance, Puma и другие. 100% оригинал, новые коллекции, быстрая доставка, удобная оплата. Стильно, комфортно, доступно!
суши барнаул суши роллы барнаул
ecole de theatre Apprendre l’art theatral Maitriser le jeu d’acteur Realisation de films Etudier le theatre Decouvrir le theatre Le monde du cinema Le metier d’acteur Formation d’acteur Cours de theatre a Paris Le cinema
Онлайн казино России Онлайн казино России: Надежность и Честность Игры В динамичном мире азартных игр онлайн, выбор надежного и честного казино становится ключевым фактором для успешного и приятного времяпровождения. Российский рынок онлайн казино предлагает множество вариантов, но как среди них найти те, которые действительно заслуживают доверия? Тщательный анализ и оценка различных аспектов позволяют составить рейтинг онлайн казино, ориентированный на потребности российских игроков. Критерии оценки включают лицензирование, репутацию, разнообразие игр, бонусные предложения, качество обслуживания клиентов и скорость выплат. Лицензирование является одним из важнейших факторов. Казино, имеющие лицензии от авторитетных регуляторов, таких как Malta Gaming Authority (MGA) или UK Gambling Commission, обычно придерживаются строгих правил и стандартов. Репутация казино формируется на основе отзывов игроков и экспертных оценок. Положительные отзывы, отсутствие жалоб на невыплаты и честность игры свидетельствуют о надежности казино. Разнообразие игр также играет важную роль. Широкий выбор слотов, настольных игр, видеопокера и игр с живыми дилерами позволяет удовлетворить вкусы разных игроков. Бонусные предложения могут быть привлекательными, но важно обращать внимание на условия их получения и отыгрыша. Честные и прозрачные условия говорят о добросовестности казино. Качество обслуживания клиентов также является важным показателем. Быстрая и профессиональная поддержка поможет решить любые возникающие вопросы. Скорость выплат является одним из ключевых факторов, определяющих надежность казино. Быстрые и беспроблемные выплаты свидетельствуют о финансовой стабильности и добросовестности казино. На основе этих критериев формируется рейтинг онлайн казино России, который позволяет игрокам сделать осознанный выбор и наслаждаться азартными играми в безопасной и надежной среде.
Детство и музыка известных исполнителей Рецензии на новые фильмы: Оценка киноновинок.
лицензия онлайн казино казино россии
https://stroidom36.ru/dom-iz-penoblokov-pod-klyuch/
работа военным Работа военным: служение Родине Работа военным – это не просто профессия, это призвание. Это служение Родине, защита ее интересов и обеспечение безопасности граждан. Военные – это люди, готовые рисковать своей жизнью ради мира и спокойствия в стране. Служба в армии – это школа жизни, которая закаляет характер, учит дисциплине и ответственности. Военные приобретают навыки, необходимые не только на поле боя, но и в обычной жизни. Они умеют работать в команде, быстро принимать решения в сложных ситуациях и нести ответственность за свои действия. Военная служба – это возможность получить образование и профессию. Армия предоставляет широкий выбор специальностей, от технических до гуманитарных. Военные могут получить высшее образование за счет государства и стать высококвалифицированными специалистами. Работа военным – это стабильность и социальные гарантии. Военнослужащие получают достойную зарплату, жилье, медицинское обслуживание и другие льготы. Они уверены в завтрашнем дне и могут планировать свое будущее. Служба в армии – это возможность проявить себя и сделать карьеру. Военные могут расти по служебной лестнице, занимать высокие должности и участвовать в принятии важных решений. Они вносят свой вклад в развитие страны и укрепление ее обороноспособности. Работа военным – это почет и уважение. Военные – это герои, которыми гордится страна. Их подвиги и заслуги отмечаются государственными наградами и званиями. Они являются примером для подражания и вдохновляют молодежь на служение Родине. Служба в армии – это нелегкий труд, требующий мужества, силы и выносливости. Но это также возможность реализовать себя, принести пользу обществу и оставить свой след в истории. Работа военным – это выбор сильных и ответственных людей, готовых посвятить свою жизнь защите Родины.
работа военным Работа военным: служение Родине Работа военным – это не просто профессия, это призвание. Это служение Родине, защита ее интересов и обеспечение безопасности граждан. Военные – это люди, готовые рисковать своей жизнью ради мира и спокойствия в стране. Служба в армии – это школа жизни, которая закаляет характер, учит дисциплине и ответственности. Военные приобретают навыки, необходимые не только на поле боя, но и в обычной жизни. Они умеют работать в команде, быстро принимать решения в сложных ситуациях и нести ответственность за свои действия. Военная служба – это возможность получить образование и профессию. Армия предоставляет широкий выбор специальностей, от технических до гуманитарных. Военные могут получить высшее образование за счет государства и стать высококвалифицированными специалистами. Работа военным – это стабильность и социальные гарантии. Военнослужащие получают достойную зарплату, жилье, медицинское обслуживание и другие льготы. Они уверены в завтрашнем дне и могут планировать свое будущее. Служба в армии – это возможность проявить себя и сделать карьеру. Военные могут расти по служебной лестнице, занимать высокие должности и участвовать в принятии важных решений. Они вносят свой вклад в развитие страны и укрепление ее обороноспособности. Работа военным – это почет и уважение. Военные – это герои, которыми гордится страна. Их подвиги и заслуги отмечаются государственными наградами и званиями. Они являются примером для подражания и вдохновляют молодежь на служение Родине. Служба в армии – это нелегкий труд, требующий мужества, силы и выносливости. Но это также возможность реализовать себя, принести пользу обществу и оставить свой след в истории. Работа военным – это выбор сильных и ответственных людей, готовых посвятить свою жизнь защите Родины.
ecole de theatre Arts du spectacle
amoxicillin pills – https://combamoxi.com/ buy amoxicillin pills
работа военным Работа военным: защита Отечества Работа военным – это защита Отечества. Это священный долг каждого гражданина, готового встать на защиту своей Родины в трудную минуту. Военная служба – это не просто работа, это призвание, требующее мужества, отваги и самоотверженности. Военные – это люди, которые прошли специальную подготовку, владеют современным оружием и техникой, готовы выполнить любой приказ, защитить свою страну от внешних угроз. Они стоят на страже мира и спокойствия, обеспечивая безопасность граждан. Военная служба – это возможность получить уникальный опыт, развить свои физические и моральные качества, научиться преодолевать трудности и нести ответственность за свои действия. Военные – это сильные и уверенные в себе люди, способные принимать решения в сложных ситуациях. Армия – это школа жизни, которая воспитывает патриотизм, дисциплину и уважение к старшим. Военные – это пример для подражания, люди, которые своим примером вдохновляют молодежь на служение Родине. Государство заботится о своих защитниках, предоставляя им достойное денежное довольствие, жилье, медицинское обслуживание и другие социальные гарантии. Военная служба – это стабильность и уверенность в завтрашнем дне. Работа военным – это возможность внести свой вклад в развитие страны, в укрепление ее обороноспособности и международного авторитета. Военные участвуют в научных исследованиях, разрабатывают новые виды вооружения и техники, повышают боеготовность армии. Военная служба – это нелегкий труд, требующий постоянного совершенствования, физической и моральной подготовки. Но это также возможность почувствовать себя частью сильной и сплоченной команды, гордиться своей профессией и служением Родине. Работа военным – это выбор настоящих героев, готовых отдать свою жизнь за свободу и независимость своей страны.
jouer au cinema Etudes de realisation de films
https://stroidom36.ru/catalog/doma/ Натяжные потолки в Воронеже: установка и выбор дизайна
Modern operations https://www.surgery-montenegro.me innovative technologies, precision and safety. Minimal risk, short recovery period. Plastic surgery, ophthalmology, dermatology, vascular procedures.
Профессиональное https://prp-expert.ru: PRP, Plasmolifting, протоколы и нюансы проведения процедур. Онлайн курс обучения плазмотерапии.
работа военным Работа военным: служение Родине Работа военным – это не просто профессия, это призвание. Это служение Родине, защита ее интересов и обеспечение безопасности граждан. Военные – это люди, готовые рисковать своей жизнью ради мира и спокойствия в стране. Служба в армии – это школа жизни, которая закаляет характер, учит дисциплине и ответственности. Военные приобретают навыки, необходимые не только на поле боя, но и в обычной жизни. Они умеют работать в команде, быстро принимать решения в сложных ситуациях и нести ответственность за свои действия. Военная служба – это возможность получить образование и профессию. Армия предоставляет широкий выбор специальностей, от технических до гуманитарных. Военные могут получить высшее образование за счет государства и стать высококвалифицированными специалистами. Работа военным – это стабильность и социальные гарантии. Военнослужащие получают достойную зарплату, жилье, медицинское обслуживание и другие льготы. Они уверены в завтрашнем дне и могут планировать свое будущее. Служба в армии – это возможность проявить себя и сделать карьеру. Военные могут расти по служебной лестнице, занимать высокие должности и участвовать в принятии важных решений. Они вносят свой вклад в развитие страны и укрепление ее обороноспособности. Работа военным – это почет и уважение. Военные – это герои, которыми гордится страна. Их подвиги и заслуги отмечаются государственными наградами и званиями. Они являются примером для подражания и вдохновляют молодежь на служение Родине. Служба в армии – это нелегкий труд, требующий мужества, силы и выносливости. Но это также возможность реализовать себя, принести пользу обществу и оставить свой след в истории. Работа военным – это выбор сильных и ответственных людей, готовых посвятить свою жизнь защите Родины.
Онлайн-курсы https://obuchenie-plasmoterapii.ru: теория, видеоуроки, разбор техник. Обучение с нуля и для практикующих. Доступ к материалам 24/7, сертификат после прохождения, поддержка преподавателя.
психотерапия онлайн Тёмная ночь души: Переживание кризиса и поиск нового смысла в жизни. Преодоление трудностей и рост над собой.
Почему в жизни черная полоса Приворот: опасная игра с чувствами. Приворот – это магический ритуал, направленный на насильственное привлечение любви другого человека.
amoxil for sale – order amoxicillin sale amoxicillin for sale online
Все о беременности Как пережить схватки: Эффективные методы облегчения боли и дискомфорта во время схваток. Дыхательные упражнения, массаж и альтернативные техники.
Эфирные масла и медитация: как достичь гармонии Эфирные масла для духовного роста и самосовершенствования: Углубите свою духовную практику с помощью эфирных масел, открывающих новые горизонты осознанности и помогающих найти свой путь.
Грузоперевозки Луганск Грузоперевозки Луганск: Аренда грузового транспорта с водителем. Различные модели автомобилей, гибкие условия аренды, профессиональные водители. Оптимальное решение для ваших транспортных задач.
плазменное поле Гиперчувствительность – особенность, связанная с повышенной восприимчивостью к внешним и внутренним стимулам.
плазменное поле Психология будущего: Исследование трендов и возможностей будущего с точки зрения психологии.
Грузоперевозки Луганск Упаковка грузов Луганск: Профессиональная упаковка грузов для обеспечения их сохранности при транспортировке.
Грузоперевозки Луганск Аренда грузового автомобиля Луганск: Выгодные условия аренды грузовых автомобилей для бизнеса и частных нужд.
Обряд на любовь Как пережить измену
гайнулин эмиль нилович Эмиль Гайнулин: психология инвестиций. Как принимать взвешенные решения, избегать эмоциональных ошибок и сохранять спокойствие в кризисных ситуациях.
the best and interesting https://lusitanohorsefinder.com
interesting and new https://www.greenwichodeum.com
purchase fluconazole – click diflucan 200mg us
visit the site online https://www.amakmeble.pl
best site online https://pvslabs.com
макросы варфейс Поднимите свой скилл в Warface с помощью макросы варфейс! Улучшите свою стрельбу, контролируйте отдачу и станьте настоящим профессионалом. Доминируйте в каждом бою и наслаждайтесь игрой!
правильное питание Пищеварение – сложный процесс расщепления пищи на компоненты, которые могут быть усвоены организмом. Нарушения пищеварения приводят к дискомфорту и различным заболеваниям.
завьялов илья поинт пей PointPay: Образовательные инициативы Ильи Завьялова для повышения финансовой грамотности в сфере криптовалют
Замена открывания с простого на сложное в Алматы В Алматы компания Okna Service оказывает полный спектр услуг по восстановлению окон из ПВХ, используя только высококачественные компоненты. Сюда входит замена уплотнителей, гарантирующих отличную изоляцию и защиту от продувания, а также специальной фурнитуры: ручек, петель для различных типов открывания, которые заменяются при необходимости. Восстановление и замена москитных сеток, подверженных повреждениям, также включены в список услуг. Для повышения удобства пользования окнами профессионалы Okna Service рекомендуют установку дополнительных устройств: дверных доводчиков, ограничителей открывания (важно для семей с малышами), а также монтаж пластиковых откосов как внутри, так и снаружи, что улучшает эстетику окон. В сервисном центре в Алматы можно заказать и приобрести все необходимые детали для ремонта окон с доставкой и профессиональным монтажом. Мы тщательно отбираем материалы, подходящие именно для ваших окон, обеспечивая надежность и долговечность ремонта. Замена изношенных частей позволяет вернуть окну прежние характеристики, сохранение тепла и уют в доме.
рулонные шторы блэкаут пятигорск Рулонные шторы Пятигорск: Практичность и Стиль Рулонные шторы – это современное и практичное решение для оформления окон. Они идеально подходят для любого интерьера, обеспечивая надежную защиту от солнца и посторонних взглядов. В Пятигорске можно найти рулонные шторы различных цветов, фактур и размеров.
visit the site https://puntera.com
go to the site https://petitedanse.com.br
cost forcan – click cheap fluconazole 200mg
реставрация поддона смеситель врезной на борт ванной
Removing free ai clothes remover from images is an advanced tool for creative tasks. Neural networks, accurate generation, confidentiality. For legal and professional use only.
завьялов илья поинт пей Илья Завьялов: PointPay – платформа для эффективного управления крипто-портфелем
завьялов илья поинт пей Point Pay: Платформа Возможностей благодаря Илье Завьялову
макрос варфейс x7 Для игроков Warface! Хотите улучшить свою стрельбу? Попробуйте макрос варфейс bloody! Он поможет вам контролировать отдачу и повысить точность. Не упустите шанс стать настоящим профи!
макрос на отдачу варфейс Затрудняетесь с установкой макроса? Узнайте, как установить макрос на варфейс правильно! Следуйте инструкциям, и вы сможете наслаждаться улучшенной стрельбой и контролем отдачи. Удачи!
Профессиональная платная наркологическая клиника. Лечение зависимостей, капельницы, вывод из запоя, реабилитация. Анонимно, круглосуточно, с поддержкой врачей и психологов.
Рефрижераторные перевозки https://camper4x4.ru/czeny-na-refrizheratornye-perevozki-sravnenie-predlozhenij-na-rynke/ по России и СНГ. Контроль температуры от -25°C до +25°C, современные машины, отслеживание груза.
накрутка пф рост трафика яндекс Накрутка ПФ услуга: Быстрый результат или временный эффект? Услуги накрутки ПФ обещают быстрый рост позиций в поисковой выдаче. Но так ли это на самом деле? Разберемся, какие методы используют сервисы и какие риски несет накрутка для сайта.
Счетчик с пультом Умные электросчетчики: Эффективность, точность и прозрачность Умные электросчетчики – это приборы учета нового поколения, позволяющие дистанционно контролировать потребление электроэнергии и автоматически передавать данные поставщику.
Ev!us Archivecore: Архивкор – это увлечение прошлым, запечатленным в старых фотографиях, выцветших документах и винтажных журналах. Он создает атмосферу ушедших эпох, где каждая деталь хранит историю и тайны. Это эстетика, которая ценит подлинность и неповторимость.
реальные мистические истории Мистические истории: За гранью реальности. В мире, где наука пытается объяснить все, мистика остается неизведанной территорией, манящей своей загадочностью. Мистические истории – это отражение нашего подсознательного страха перед неизвестным, переплетенные с надеждой на чудо. От старинных преданий до современных городских легенд, они продолжают волновать сердца и умы.
https://vavada-sign-up.online Регистрация в Vavada Casino открывает доступ к 4000+ игровым автоматам и бонусу 100% на первый депозит. Быстрая процедура sign-up, верификация за 5 минут, стартовый пакет 1000€ + 100 фриспинов. Играйте в лицензионном казино с 2016 года.
нотариальный перевод документов Перевод с английского на русский язык – это не просто передача смысла, но и адаптация текста к культурным особенностям. Наши переводчики обладают безупречным знанием обоих языков.
Dual Access Bazaar Drugs Marketplace: A New Darknet Platform with Dual Access Bazaar Drugs Marketplace is a new darknet marketplace rapidly gaining popularity among users interested in purchasing pharmaceuticals. Trading is conducted via the Tor Network, ensuring a high level of privacy and data protection. However, what sets this platform apart is its dual access: it is available both through an onion domain and a standard clearnet website, making it more convenient and visible compared to competitors. The marketplace offers a wide range of pharmaceuticals, including amphetamines, ketamine, cannabis, as well as prescription drugs such as alprazolam and diazepam. This variety appeals to both beginners and experienced buyers. All transactions on the platform are carried out using cryptocurrency payments, ensuring anonymity and security. In summary, Bazaar represents a modern darknet marketplace that combines convenience, a broad product selection, and a high level of privacy, making it a notable player in the darknet economy.
военная служба по контракту Служба по контракту: обучение, тренировки и совершенствование профессиональных навыков
Ищете казино https://sbpcasino.ru? У нас — мгновенные переводы, слоты от топ-провайдеров, живые дилеры и быстрые выплаты. Безопасность, анонимность и мобильный доступ!
Выбирайте казино пиастрикс казино с оплатой через Piastrix — это удобно, безопасно и быстро! Топ-игры, лицензия, круглосуточная поддержка.
purchase escitalopram pills – buy escitalopram 10mg generic buy escitalopram without a prescription
Служба по контракту Служба по контракту: Стабильная работа, социальные гарантии и уверенность в завтрашнем дне
Играйте в онлайн-покер покерок легальный с игроками со всего мира. МТТ, спины, VIP-программа, акции.
Хотите https://motoreuro.ru ДВС с гарантией? Б большой выбор моторов из Японии, Европы и Кореи. Проверенные ДВС с небольшим пробегом. Подбор по VIN, доставка по РФ, помощь с установкой.
Хирurgija u Crnoj Gori https://www.hirurgija-crna-gora.me savremena klinika, iskusni ljekari, evropski standardi. Planirane i hitne operacije, estetska i opsta hirurgija, udobnost i bezbjednost.
военная служба по контракту Военная служба по контракту: как найти свое место В этом разделе рассматриваются различные варианты трудоустройства после окончания военной службы по контракту.
cenforce over the counter – https://cenforcers.com/ purchase cenforce generic
военная служба по контракту Военный контракт: возможность обеспечить стабильное будущее для себя и своей семьи
Элитная недвижимость https://real-estate-rich.ru в России и за границей — квартиры, виллы, пентхаусы, дома. Где купить, как оформить, во что вложиться.
Служба по контракту Военнослужащий по контракту: физическая подготовка на высшем уровне, участие в спортивных мероприятиях и соревнованиях
Служба по контракту Служба по контракту: Возможность проявить свои лучшие качества, внести свой вклад в укрепление обороноспособности страны и защиту национальных интересов
Tor Network Bazaar Drugs Marketplace: A New Darknet Platform with Dual Access Bazaar Drugs Marketplace is a new darknet marketplace rapidly gaining popularity among users interested in purchasing pharmaceuticals. Trading is conducted via the Tor Network, ensuring a high level of privacy and data protection. However, what sets this platform apart is its dual access: it is available both through an onion domain and a standard clearnet website, making it more convenient and visible compared to competitors. The marketplace offers a wide range of pharmaceuticals, including amphetamines, ketamine, cannabis, as well as prescription drugs such as alprazolam and diazepam. This variety appeals to both beginners and experienced buyers. All transactions on the platform are carried out using cryptocurrency payments, ensuring anonymity and security. In summary, Bazaar represents a modern darknet marketplace that combines convenience, a broad product selection, and a high level of privacy, making it a notable player in the darknet economy.
Смотреть фильмы kinobadi.mom и сериалы бесплатно, самый большой выбор фильмов и сериалов , многофункциональное сортировка, также у нас есть скачивание в mp4 формате
Выбор застройщика https://spartak-realty.ru важный шаг при покупке квартиры. Расскажем, как проверить репутацию, сроки сдачи, проектную документацию и избежать проблем с новостройкой.
cenforce 100mg us – buy cenforce generic cenforce 100mg brand
Недвижимость в Балашихе https://balashihabest.ru комфорт рядом с Москвой. Современные жилые комплексы, школы, парки, транспорт. Объекты в наличии, консультации, юридическое сопровождение сделки.
Поставка нерудных материалов https://sr-sb.ru песок, щебень, гравий, отсев. Прямые поставки на стройплощадки, карьерный материал, доставка самосвалами.
Лайфхаки для ремонта https://stroibud.ru квартиры и дома: нестандартные решения, экономия бюджета, удобные инструменты.
Женский журнал https://e-times.com.ua о красоте, моде, отношениях, здоровье и саморазвитии. Советы, тренды, рецепты, вдохновение на каждый день. Будь в курсе самого интересного!
мистические детективы Бесплатный мистический контент позволяет каждому прикоснуться к миру тайн и загадок, не тратя на это деньги. В интернете можно найти множество мистических рассказов, сериалов и фильмов, которые помогут вам скоротать время и испытать острые ощущения.
Туристический портал https://atrium.if.ua всё для путешественников: путеводители, маршруты, советы, отели, билеты и отзывы. Откройте для себя новые направления с полезной информацией и лайфхаками.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://socvirus.com.ua мода, макияж, карьера, семья, тренды. Полезные статьи, интервью, обзоры и вдохновляющий контент для настоящих женщин.
Портал про ремонт https://prezent-house.com.ua полезные советы, инструкции, дизайн-идеи и лайфхаки. От черновой отделки до декора. Всё о ремонте квартир, домов и офисов — просто, понятно и по делу.
Всё о ремонте https://sevgr.org.ua на одном портале: полезные статьи, видеоуроки, проекты, ошибки и решения. Интерьерные идеи, советы мастеров, выбор стройматериалов.
Бюро дизайна https://sinega.com.ua интерьеров: функциональность, стиль и комфорт в каждой детали. Предлагаем современные решения, индивидуальный подход и поддержку на всех этапах проекта.
Портал про ремонт https://techproduct.com.ua для тех, кто строит, переделывает и обустраивает. Рекомендации, калькуляторы, фото до и после, инструкции по всем этапам ремонта.
Всё о строительстве https://kinoranok.org.ua на одном портале: строительные технологии, интерьер, отделка, ландшафт. Советы экспертов, фото до и после, инструкции и реальные кейсы.
Портал о строительстве https://bms-soft.com.ua от фундамента до кровли. Технологии, лайфхаки, выбор инструментов и материалов. Честные обзоры, проекты, сметы, помощь в выборе подрядчиков.
Ремонт и строительство https://mtbo.org.ua всё в одном месте. Сайт с советами, схемами, расчетами, обзорами и фотоидееями. Дом, дача, квартира — строй легко, качественно и с умом.
военная служба по контракту Военная служба по контракту: как сохранить здоровье В этом разделе рассматриваются советы по сохранению здоровья во время военной службы по контракту.
Сайт о ремонте https://sota-servis.com.ua и строительстве: от черновых работ до декора. Технологии, материалы, пошаговые инструкции и проекты.
Онлайн-журнал https://elektrod.com.ua о строительстве: технологии, законодательство, цены, инструменты, идеи. Для строителей, архитекторов, дизайнеров и владельцев недвижимости.
Женский сайт https://7krasotok.com о моде, красоте, здоровье, отношениях и саморазвитии. Полезные советы, тренды, рецепты, лайфхаки и вдохновение для современных женщин.
Полезный сайт https://quickstudio.com.ua о ремонте и строительстве: пошаговые гиды, проекты домов, выбор материалов, расчёты и лайфхаки. Для начинающих и профессионалов.
Журнал о строительстве https://tfsm.com.ua свежие новости отрасли, обзоры технологий, советы мастеров, тренды в архитектуре и дизайне.
Женские новости https://biglib.com.ua каждый день: мода, красота, здоровье, отношения, семья, карьера. Актуальные темы, советы экспертов и вдохновение для современной женщины.
Все главные женские https://pic.lg.ua новости в одном месте! Мировые и российские тренды, стиль жизни, психологические советы, звёзды, рецепты и лайфхаки.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://bestwoman.kyiv.ua для тех, кто ценит себя. Мода, уход, питание, мотивация и женская энергия в каждой статье.
Сайт для женщин https://angela.org.ua любого возраста — статьи о жизни, любви, стиле, здоровье и успехе. Полезно, искренне и с заботой.
Путеводитель по Греции https://cpcfpu.org.ua города, курорты, пляжи, достопримечательности и кухня. Советы туристам, маршруты, лайфхаки и лучшие места для отдыха.
how long does cialis last 20 mg – https://ciltadgn.com/ what happens when you mix cialis with grapefruit?
Портал о строительстве https://ateku.org.ua и ремонте: от фундамента до крыши. Пошаговые инструкции, лайфхаки, подбор материалов, идеи для интерьера.
Строительный портал https://avian.org.ua для профессионалов и новичков: проекты домов, выбор материалов, технологии, нормы и инструкции.
кайт египет Кайт Египет: Лучшие споты и незабываемые впечатления
Ваш онлайн-гид https://inhotel.com.ua в мире путешествий — туристический портал с проверенной информацией. Куда поехать, что посмотреть, где остановиться.
Туристический портал https://deluxtour.com.ua всё для путешествий: маршруты, путеводители, советы, бронирование отелей и билетов. Информация о странах, визах, отдыхе и достопримечательностях.
Открой мир https://hotel-atlantika.com.ua с нашим туристическим порталом! Подбор маршрутов, советы по странам, погода, валюта, безопасность, оформление виз.
Химчистка мебели ростов Сухая химчистка мебели Ростов – бережный уход за деликатными тканями.
приемка домов Полный комплекс услуг по приемке квартир и ИЖС: от визуального осмотра до экспертного заключения.
где продать неиспользованные лекарства Где можно продать лекарственные препараты? Важно помнить, что продажа лекарственных препаратов без лицензии запрещена и может повлечь за собой юридическую ответственность.
аренда инструментов Получение компенсации от застройщика за обнаруженные недостатки – верните свои деньги!
Журнал о строительстве https://kennan.kiev.ua новости отрасли, технологии, советы, идеи и решения для дома, дачи и бизнеса. Фото-проекты, сметы, лайфхаки, рекомендации специалистов.
Строительный сайт https://diasoft.kiev.ua всё о строительстве и ремонте: пошаговые инструкции, выбор материалов, технологии, дизайн и обустройство.
На строительном сайте https://eeu-a.kiev.ua вы найдёте всё: от выбора кирпича до дизайна спальни. Актуальная информация, фото-примеры, обзоры инструментов, консультации специалистов.
Сайт о строительстве https://domtut.com.ua и ремонте: практичные советы, инструкции, материалы, идеи для дома и дачи.
Строительный журнал https://inter-biz.com.ua актуальные статьи о стройке и ремонте, обзоры материалов и технологий, интервью с экспертами, проекты домов и советы мастеров.
кайт египет Кайтсерфинг и друзья: Кайтсерфинг и друзья
Сайт о ремонте https://mia.km.ua и строительстве — полезные советы, инструкции, идеи, выбор материалов, технологии и дизайн интерьеров.
Сайт о ремонте https://rusproekt.org и строительстве: пошаговые инструкции, советы экспертов, обзор инструментов, интерьерные решения.
Всё для ремонта https://zip.org.ua и строительства — в одном месте! Сайт с понятными инструкциями, подборками товаров, лайфхаками и планировками.
Автомобильный портал https://just-forum.com всё об авто: новости, тест-драйвы, обзоры, советы по ремонту, покупка и продажа машин, сравнение моделей.
Полезный сайт для ремонта https://rvps.kiev.ua и строительства: от черновых работ до отделки и декора. Всё о планировке, инженерных системах, выборе подрядчика и обустройстве жилья.
кайт хургада : Кайт Школа Хургада: От новичка до профи под чутким руководством инструкторов. Если вы мечтаете покорить волны на кайте, кайт школы Хургады – это лучший выбор. Опытные инструкторы с международными сертификатами помогут вам освоить азы кайтсерфинга и научат сложным трюкам. Безопасность – главный приоритет, поэтому обучение проводится с использованием современного оборудования и соблюдением всех необходимых мер предосторожности.
how many mg of cialis should i take – https://ciltadgn.com/ where to get generic cialis without prescription
Онлайн-портал https://spkokna.com.ua для современных родителей: беременность, роды, уход за малышами, школьные вопросы, советы педагогов и врачей.
Сайт для женщин https://ww2planes.com.ua идеи для красоты, здоровья, быта и отдыха. Тренды, рецепты, уход за собой, отношения и стиль.
Современный женский журнал https://superwoman.kyiv.ua стиль, успех, любовь, уют. Новости, идеи, лайфхаки и мотивация для тех, кто ценит себя и своё время.
Онлайн-журнал https://eternaltown.com.ua для женщин: будьте в курсе модных новинок, секретов красоты, рецептов и психологии.
Сайт для женщин https://womanfashion.com.ua которые ценят себя и своё время. Мода, косметика, вдохновение, мотивация, здоровье и гармония.
приемка квартир от застройщика Представление ваших интересов в суде.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://abuki.info мода, красота, здоровье, психология, отношения и вдохновение. Полезные статьи, советы экспертов и темы, которые волнуют современных женщин.
Современный авто портал https://simpsonsua.com.ua автомобили всех марок, тест-драйвы, лайфхаки, ТО, советы по покупке и продаже. Для тех, кто водит, ремонтирует и просто любит машины.
Актуальные новости https://uapress.kyiv.ua на одном портале: события России и мира, интервью, обзоры, репортажи. Объективно, оперативно, профессионально. Будьте в курсе главного!
Онлайн авто портал https://sedan.kyiv.ua для автолюбителей и профессионалов. Новинки автоиндустрии, цены, характеристики, рейтинги, покупка и продажа автомобилей, автофорум.
Информационный портал https://mediateam.com.ua актуальные новости, аналитика, статьи, интервью и обзоры. Всё самое важное из мира политики, экономики, технологий, культуры и общества.
тепловизионное обследование Снижение расходов на отопление и кондиционирование.
Современный мужской портал https://kompanion.com.ua полезный контент на каждый день. Новости, обзоры, мужской стиль, здоровье, авто, деньги, отношения и лайфхаки без воды.
Сайт для женщин https://storinka.com.ua всё о моде, красоте, здоровье, психологии, семье и саморазвитии. Полезные советы, вдохновляющие статьи и тренды для гармоничной жизни.
Следите за событиями https://kiev-pravda.kiev.ua дня на новостном портале: лента новостей, обзоры, прогнозы, мнения. Всё, что важно знать сегодня — быстро, чётко, объективно.
приемка квартир от застройщика Выявление скрытых дефектов, которые могут привести к серьезным проблемам в будущем.
Новостной портал https://thingshistory.com для тех, кто хочет знать больше. Свежие публикации, горячие темы, авторские колонки, рейтинги и хроники. Удобный формат, только факты.
Новости Украины https://pto-kyiv.com.ua и мира сегодня: ключевые события, мнения экспертов, обзоры, происшествия, экономика, политика.
где продать лекарства с рук Продам препараты после лечения – многие задаются вопросом, что делать с лекарствами, оставшимися после курса лечения. Важно помнить о правилах утилизации или возможности передать их нуждающимся.
винный вечер с сомелье доставка еды Воронеж
купить металлическую черепицу Профилированная труба: универсальный материал для конструкций Профилированная труба – это универсальный строительный материал, который используется для создания каркасов, ограждений, навесов и других конструкций.
накрутка пф яндекс Реальные ПФ: ключ к успеху Вместо того, чтобы тратить деньги и время на сомнительные методы накрутки, лучше сосредоточиться на улучшении реальных ПФ. Создавайте качественный и полезный контент, оптимизируйте сайт под мобильные устройства, улучшайте юзабилити и скорость загрузки.
стиральная машина миля ремонт ремонт стиральных машин lg
ремонт стиральных машин lg ремонту стиральных машин частный
ремонт стиральных машин канди ремонт стиральных машин электролюкс
служба по контракту оренбург Финансовая поддержка контрактников: Контрактники в Оренбургской области получают достойную заработную плату, размер которой зависит от звания, должности и выслуги лет. Кроме того, предусмотрены различные надбавки и премии.
when will cialis become generic – https://strongtadafl.com/ does cialis make you harder
купить металлическую черепицу Металочерепица: Элегантная и долговечная кровля, вдохновленная классикой Металочерепица – это современный кровельный материал, имитирующий красоту и изящество натуральной черепицы. Однако, в отличие от своего керамического аналога, металочерепица обладает высокой прочностью, устойчивостью к атмосферным воздействиям и долговечностью. Она не выгорает на солнце, не боится перепадов температур и прослужит вам долгие годы, сохраняя свой первозданный вид.
накрутка пф яндекс ПФ как фактор ранжирования: недооцененный потенциал Поведенческие факторы играют важную роль в определении позиций сайта в поисковой выдаче. Яндекс учитывает множество параметров, таких как кликабельность сниппета, время, проведенное на сайте, глубина просмотра и показатель отказов. Улучшение этих показателей может положительно сказаться на позициях ресурса.
Химчистка мебели ростов Паровая химчистка мебели Ростов – эффективный способ удаления загрязнений и дезинфекции.
купить винтовые сваи Купить профтрубу: надежный материал для строительства и ремонта Профтруба – это универсальный строительный материал, который используется для создания каркасов, ограждений, навесов и других конструкций. Она отличается высокой прочностью, устойчивостью к коррозии и доступной ценой.
накрутка пф яндекс Анализ и оптимизация: ключ к успеху Регулярно анализируйте ПФ своего сайта и выявляйте слабые места. Улучшайте контент, оптимизируйте страницы и делайте сайт удобным для пользователей. Это – самый надежный путь к успеху в SEO.
месячные при спирали мирена спираль мирена аптека
накрутка пф яндекс “Черные” методы: быстрый, но опасный путь Существуют различные сервисы, предлагающие искусственное улучшение ПФ. Однако, использование таких методов сопряжено с огромным риском. Яндекс постоянно совершенствует алгоритмы обнаружения накрутки, и рано или поздно обман будет раскрыт. Последствия могут быть самыми печальными: от понижения позиций до полного исключения сайта из поисковой выдачи.
типография сайт спб типография официальный сайт
сушенные лакомства Хрустящие лакомства: Естественная чистка зубов Хрустящие сушеные лакомства помогают очистить зубы собаки от налета и зубного камня, массируют десны и способствуют поддержанию здоровья полости рта.
лазерной резкой резка металла листового
where to buy generic cialis – buying cialis online canadian order cialis 20 mg from united kingdom
услуги типографии https://printexpressonline.ru
Хрустящие субпродукты для чистки зубов Сушеные лакомства: Альтернатива костям Сушеные лакомства могут служить безопасной альтернативой костям, которые могут быть опасны для здоровья собаки.
сушенные лакомства Разнообразие вкусов и текстур: Удовольствие для каждого питомца Существует огромное разнообразие сушеных лакомств для собак с разными вкусами и текстурами. Вы можете выбрать лакомство, которое понравится именно вашему питомцу.
типография санкт петербург типография сайт спб
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
скачать отчет по практике https://gotov-otchet.ru
онлайн сделать реферат заказать реферат онлайн недорого срочно
услуги лазерной эпиляции creatorro.ru/
экспресс типография https://rek-print.ru
Слив платных прогнозов бесплатно Как отличить надежный источник прогнозов от мошенников? Важно тщательно проверять репутацию источника прогнозов, читать отзывы других пользователей и анализировать статистику прошлых прогнозов. Не стоит доверять обещаниям гарантированной прибыли и слишком заманчивым предложениям.
Подбор теннисной академии в Испании ВНЖ Бразилии Легально проживайте и работайте в Бразилии, получив вид на жительство. Узнайте о различных способах получения ВНЖ и преимуществах жизни в этой стране.
заказать авто из японии с аукциона купить пригнанный авто
пригнать машину из японии заказать авто из кореи цены
диплом срочно заказать заказать дипломную
дипломная работа купить написать дипломную работу
пригнать машину под заказ пригнать авто из китая в россию
zantac over the counter – https://aranitidine.com/ order ranitidine pill
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
Фермы для ангара Каркас для ангара Сверхпрочный каркас для ангара, способный выдерживать экстремальные нагрузки. Использование высококачественной стали и современных технологий сварки. Антикоррозийная обработка для увеличения срока службы.
Гараж разборный Фермы для ангара Строительство ангаров с использованием современных технологий. Металлические фермы для ангаров – прочное и экономичное решение. Проектирование, изготовление, монтаж. Различные типы ферм: арочные, прямостенные, полигональные.
50 mg sildenafil tablets – https://strongvpls.com/# viagra 50 mg price
суши роллы барнаул доставка суши барнаул
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captcha (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
Постиралка – список компаний по решению проблем со стиралкой
Позиционирование Лиды Квалифицированные лиды – основа прибыльного бизнеса. Инвестируйте в инструменты для идентификации лидов с высоким потенциалом. Используйте лид-магниты, чтобы побудить потенциальных клиентов делиться своей информацией. Важно понимать разницу между холодными и теплыми лидами.
https://v-tagile.ru/obschestvo-iyul-5/kak-vybrat-idealnyj-buket-dlya-zhenshchiny-ot-povoda-do-yazyka-tsvetov
buy viagra with a mastercard – 100 mg generic viagra can you order viagra online
Derby university of east london jobs jobs focus on applied sciences
and creative industries.
Гражданство, паспорт Испании,Евросоюза,ЕС Гражданство Сербии. Откройте для себя возможности Балканского региона, получив сербское гражданство. Узнайте о способах получения гражданства и преимуществах жизни в Сербии.
обмен криптовалют обменники rexex.io rexex.io – это портал в бескрайний океан криптовозможностей. Здесь вы найдете не только удобный и безопасный обменник, но и аналитические инструменты, образовательные материалы и комьюнити единомышленников. Rexex.io – это ваш личный крипто-ассистент, готовый помочь вам на каждом шагу.
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
https://177m.ru
стеклянные перегородки Душевая перегородка из стекла сочетает в себе стиль и практичность. Она не только предотвращает разбрызгивание воды, но и создает визуально легкое пространство, позволяя наслаждаться процессом гигиены в приятной обстановке.
Скачать 1Вин на телефон и начать выигрывать
Dragon money Боевые сражения занимают важное место в Драгон мани. Умение эффективно управлять ресурсами, развивать персонажа и использовать свои навыки в бою становятся решающими факторами в достижении победы. Стратегическое мышление и командная работа могут изменить ход сражения, доказывая, что в этом мире только самые достойные смогут получить уважение и дары Дракона.
Актуальные тренды сегодня источник: фото, видео и медиа. Всё о том, что популярно сегодня — в России и в мире. Мода, визуальные стили, digital-направления и соцсети. Следите за трендами и оставайтесь в курсе главных новинок каждого дня.
https://remdostavka.ru
This is a question which is forthcoming to my fundamentals… Numberless thanks! Exactly where can I notice the connection details an eye to questions? https://buyfastonl.com/isotretinoin.html
стеклянные ограждения Офисные перегородки играют важную роль в организации рабочего пространства. Они позволяют выделить зоны для сосредоточенной работы и общения, улучшая общую атмосферу. Стеклянные офисные перегородки обеспечивают необходимую звукоизоляцию, что особенно важно в шумных офисах.
Нужен буст в игре? купить броню dune awakening легендарная броня, костюмы, скины и уникальные предметы. Всё для выживания на Арракисе!
https://personaldliadoma.ru
дешевая перегородка Стеклянные перегородки
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), RuCaptcha, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
https://mastera-vodonagrevateley-spb.ru
Прогулка по Москве и не только – Буду выкладывать свою жизнь, где ел и что и вкусно ли это, какие места увидел новые и свои взгляды на мир и хорошую музыку https://t.me/armanmoscow
Discover rafting tara montenegro rafting – the perfect holiday for nature lovers and extreme sports enthusiasts. The UNESCO-listed Tara Canyon will amaze you with its beauty and energy.
Шариковый подшипник Купить подшипники оптом Оптовые закупки подшипников – это экономически выгодное решение. Мы предлагаем конкурентоспособные цены и быструю доставку.
поставщики подшипников в рф Инновационные технологии в производстве подшипников Инновационные технологии в производстве подшипников направлены на повышение качества, надежности и долговечности продукции.
Гидроизоляция зданий https://gidrokva.ru и сооружений любой сложности. Фундаменты, подвалы, крыши, стены, инженерные конструкции.
I couldn’t hold back commenting. Well written! https://buyfastonl.com/isotretinoin.html
голодание на воде Голодание для улучшения пищеварения: Восстановление здоровья кишечника
Cамоустанавливающийся подшипник Подшипники для агрессивных сред Подшипники для агрессивных сред изготавливаются из материалов, устойчивых к воздействию химических веществ.
https://voda-pravo.ru
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
Good blog you be undergoing here.. It’s intricate to on strong status belles-lettres like yours these days. I justifiably recognize individuals like you! Withstand guardianship!! neurontin presentacion
https://domsibiri.ru
This is the make of post I find helpful. viagra espaГ±a
Закупка подшипников Шариковый подшипник Шариковые подшипники – наиболее распространенный тип подшипников, отличающийся универсальностью и простотой конструкции.
поставщики подшипников в рф Подшипники от производителей Мы сотрудничаем только с проверенными производителями подшипников, что гарантирует высокое качество и надежность продукции.
Заказать дипломную работу http://diplomikon.ru недорого и без стресса. Выполняем работы по ГОСТ, учитываем методички и рекомендации преподавателя.
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
Разработка сайтов https://studioucoz.ru в Москве — готовые решения под ключ. Анализ, проектирование, дизайн, запуск. Прозрачная смета, поэтапная оплата, поддержка.
Всё о татуировках https://karavanuslug.ru значения, стили, эскизы, уход и советы мастеров. Полезные статьи, фото-галереи, идеи для вдохновения.
Строительный портал https://interenergoportal.ru от фундамента до кровли. Советы по ремонту, выбору материалов, проектированию и благоустройству.
Одежда из Кореи https://vv-mag.ru современный стиль, удобные ткани, модные силуэты. Каталог повседневной и дизайнерской одежды.
Отделочные работы под ключ https://gidrohanstroy.ru стены, полы, потолки, сантехника, электрика. Черновая и чистовая отделка квартир, домов, офисов.
Пластиковые окна https://oknaotzavoda.ru от завода в Казани — качество без переплат. Изготовление по индивидуальным размерам, монтаж под ключ, гарантия.
Домофонные системы https://sovremennyjdom.ru продажа, установка и обслуживание. Видеодомофоны, вызывные панели, контроль доступа. Работаем с жилыми домами, ТСЖ, бизнес-центрами.
https://remontika-vl.ru
платежный агент при оплате Оплата в Китай в рублях hfbroker – это процесс перевода денежных средств китайскому поставщику в рублях через HFBroker, который конвертирует рубли в юани и осуществляет платеж поставщику.
Строительство Сочи Ремонт по договору в Сочи – это ваша защита от недобросовестных исполнителей. Четко прописанные условия, сроки и ответственность – залог успешного сотрудничества.
https://uspenka-dom.ru
Электромобили Evolute https://poverka-msk.ru современные технологии, надёжность и доступность. Выберите и купите свой Эволют с гарантией, рассрочкой и сервисным обслуживанием.
Управляющая организация https://uk-tehneks.ru комплексное обслуживание многоквартирных домов: благоустройство, ремонт, клининг, работа с жителями.
Оформление недвижимости https://regdoma.ru под ключ с юристами в Москве. Купля-продажа, дарение, наследство, регистрация права собственности. Работаем с жилыми и коммерческими объектами. Гарантия законности.
https://remmosstroy.ru
Системы отопления https://teplotehnik24.ru проектирование, подбор оборудования и монтаж. Газовое, электрическое, водяное отопление. Работаем с частными и промышленными объектами.
Управление и эксплуатация https://uk-november.ru жилых домов: обслуживание сетей, благоустройство, текущий ремонт, приём заявок, диспетчерская служба.
Комплексное обслуживание https://uk-res.ru ремонт и замена коммуникаций в многоквартирных домах — стекло, кровля, канализация, арматура.
Установка и подключение https://umn-dom.ru техники любой сложности. Подключим по инструкции, настроим, проверим. Работаем с бытовой и встраиваемой техникой.
Частный дизайнер интерьеров https://dizdom.ru разработка стильных и функциональных решений для квартир, домов, офисов. Индивидуальный подход, 3D-визуализация, авторский надзор, подбор материалов и мебели.
Ремонт ПВХ-окон https://remont-okna24.ru любой сложности: фурнитура, уплотнитель, ручки, петли, стеклопакеты. Устраняем сквозняки, запотевание, тугое открывание.
Подшипники изготовитель Промышленный подшипник – ключевой элемент любого вращающегося механизма. Его правильный выбор и своевременная замена гарантируют бесперебойную работу оборудования и минимизируют риск аварий.
Ремонт квартир https://remont-123.ru и офисов под ключ. Черновая и чистовая отделка, электрика, сантехника, выравнивание стен и полов, дизайн и мебель.
Махачкалаводоканал https://mahachkalavodokanal.ru стабильное водоснабжение и канализация Махачкалы. Личный кабинет, услуги населению и организациям, плановые отключения, тарифы и нормативные документы.
Управляющие компании ЖКХ https://uk-ivanovo.ru профессиональное управление многоквартирными домами: ремонт, уборка, обслуживание инженерных систем, благоустройство.
Solpot Casino offers attractive welcome bonuses Ready to win Play now at solpot.xl-gamers.com https://solpot.xl-gamers.com Solpot Casino ensures secure, fair gaming: Play with confidence knowing that Solpot Casino prioritizes your security and fairness. Benefit from advanced encryption technology and certified random number generators for a transparent and trustworthy gaming environment.
Натяжные потолки https://nebo-svod.ru любой сложности: от классики до 3D. Материалы от проверенных производителей, аккуратная установка, точные сроки.
Монтаж дверей https://dveri-v-dom.ru металлические и межкомнатные конструкции любой сложности. Выравнивание проёмов, установка наличников, замков и уплотнителей.
Гид по инвестициям https://lovdom.ru от жилой и коммерческой недвижимости до фондового рынка и альтернативных активов. Статьи, рекомендации, инструкции, аналитика.
оплата в китай в рублях hfbroker Оплата Алипей в Китае – это процесс перевода денежных средств китайскому продавцу с использованием платежной системы Alipay. Alipay является одной из самых популярных платежных систем в Китае и позволяет осуществлять платежи быстро и безопасно.
Реставрация ванн https://rest-vann.ru под ключ: восстановим блеск, устраним сколы и ржавчину. Современные технологии, экологичные материалы.
Компания Ремжилстрой https://ukremgilstroi.ru ремонт «под ключ» для жилых и коммерческих помещений. Полный спектр услуг: отделка, инженерка, дизайн, уборка.
Профессиональные услуги https://zamokzamena.ru по вскрытию, установке и замене замков. Быстрое решение в экстренных ситуациях: утеря ключей, заклинивший механизм, переезд.
https://prochistka.su
Комплексная очистка https://chistovodov-24.ru скважинной воды — удалим запах, мутность, примеси. Подбор фильтров по результатам анализа. Оборудование для дома, дачи и бизнеса.
Услуги печника https://dom-teplo.su с выездом: кладка, ремонт, чистка печей, каминов, барбекю. Только проверенные материалы, мастер с опытом от 10 лет.
Всё для сада https://sadovoddom.ru и огорода в интернет-магазине: от семян и рассады до инвентаря и теплиц. Качественные товары, проверенные поставщики, удобная оплата и доставка.
Оценка недвижимости https://svoidomufa.ru в Уфе с выездом: квартиры, дома, офисы, участки. Документы для ипотеки, суда, наследства. Сертифицированные специалисты.
Ремонт телефонных линий https://remtl.ru и МГТС: устраняем обрывы, шум, отсутствие сигнала. Настройка и восстановление стационарной связи. Ремонт антенн, прокладка кабеля.
Ремонт ванных комнат https://rem-sanuzla.ru и санузлов: от демонтажа до отделки. Честные сметы, фиксированные сроки, опытные мастера. Современные решения и качественные материалы.
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), rucaptcha.com, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
оплата в китай от юр лица ПСБ международные платежи – это услуга, предоставляемая Промсвязьбанком, которая позволяет осуществлять международные платежи быстро, безопасно и с выгодными комиссиями.
Купить подшипник для электродвигателя Купить промышленный подшипник Промышленные подшипники – это сердце многих машин и механизмов. Выбор правильного подшипника, соответствующего специфическим требованиям оборудования и условиям эксплуатации, имеет первостепенное значение. Приобретение промышленного подшипника – ответственный шаг, требующий внимательного анализа технических характеристик и надежности поставщика.
https://gkh-horinsk03.ru
https://geolexpert.ru
https://poverkaekb.ru
Заказать диплом https://diplomikon.ru быстро, надёжно, с гарантией! Напишем работу с нуля по вашим требованиям. Уникальность от 80%, оформление по ГОСТу.
Заказать диплом https://diplomikon.ru быстро, надёжно, с гарантией! Напишем работу с нуля по вашим требованиям. Уникальность от 80%, оформление по ГОСТу.
Оформим реферат https://ref-na-zakaz.ru за 1 день! Напишем с нуля по вашим требованиям. Уникальность, грамотность, точное соответствие методичке.
Отчёты по практике https://gotov-otchet.ru на заказ и в готовом виде. Производственная, преддипломная, учебная.
Оформим реферат https://ref-na-zakaz.ru за 1 день! Напишем с нуля по вашим требованиям. Уникальность, грамотность, точное соответствие методичке.
Отчёты по практике https://gotov-otchet.ru на заказ и в готовом виде. Производственная, преддипломная, учебная.
Диплом под ключ https://diplomnazakaz-online.ru от выбора темы до презентации. Профессиональные авторы, оформление по ГОСТ, высокая уникальность.
Диплом под ключ https://diplomnazakaz-online.ru от выбора темы до презентации. Профессиональные авторы, оформление по ГОСТ, высокая уникальность.
https://santehmen.ru
https://gidro-vanna-dush.ru
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
https://xplus-master.ru
https://domovodov.ru
Лучшие и актуальные промокод на бесплатную ставку онлайн в популярных букмекерских конторах. Бонусы за регистрацию, фрибеты, удвоение депозита. Обновления каждый день.
Купить квартиру или дом недвижимость в черногории у моря Подберём квартиру, дом или виллу по вашему бюджету. Юридическая проверка, консультации, оформление ВНЖ.
Ваш безопасный портал bitcoin7.ru в мир криптовалют! Последние новости о криптовалютах Bitcoin, Ethereum, USDT, Ton, Solana. Актуальные курсы крипты и важные статьи о криптовалютах. Начните зарабатывать на цифровых активах вместе с нами
русское частное порно шлюхи казань
Магазин сантехники https://sanshop24.ru для дома и бизнеса. Качественная продукция от проверенных брендов: всё для ванной и кухни. Удобный каталог, акции, доставка, гарантия.
Ремонт офисов https://office-remont-spb.ru любой сложности: косметический, капитальный, под ключ. Современные материалы, строгое соблюдение сроков, опытные мастера.
Управляющая компания https://uk-nadeghda.ru обслуживание многоквартирных домов, текущий и капитальный ремонт, уборка, благоустройство, аварийная служба.
Всё о сантехнике https://santechcenter.ru советы по выбору, установке и ремонту. Обзоры смесителей, раковин, унитазов, душевых. Рейтинги, инструкции, лайфхаки и обзоры новинок рынка.
Ремонт и перекрой шуб https://remontmeha.ru обновим фасон, укоротим, заменим изношенные детали. Работа с норкой, мутоном, каракулем и др.
Оборудование для сантехники https://ventsan.ru вентиляции и климата — в одном месте. Котлы, трубы, вытяжки, кондиционеры, фитинги.
Скрытая мини-камера https://baisan.ru с Full HD, датчиком движения и автономной работой. Идеальна для наблюдения в квартире, офисе или автомобиле.
https://septik-bars.ru
Get instant payouts at Solpot Casino Ready to win Play now at solpot.xl-gamers.com https://solpot.xl-gamers.com Solpot Casino offers 24/7 support for every player: Our dedicated support team is always available to assist you with any questions or issues you may encounter. Contact us anytime, day or night, via live chat, email, or phone, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable gaming experience.
Продвижение сайтов https://team-black-top.ru под ключ: SEO-оптимизация, технический аудит, внутренняя и внешняя раскрутка. Повышаем видимость и продажи.
Всё о металлообработке https://j-metall.ru и металлах: технологии резки, сварки, литья, фрезеровки. Свойства металлов, советы для производства и хобби.
Ремонт квартир https://domov-remont.ru под ключ: от дизайн-проекта до финишной отделки. Честная смета, контроль этапов, гарантия до 5 лет. Работаем точно в срок.
ЖК «Атлант» https://atlantdom.ru современный жилой комплекс с развитой инфраструктурой, охраняемой территорией и парковкой. Просторные квартиры, благоустроенные дворы, удобное расположение.
https://ukvd43.ru
Thanks for putting this up. It’s understandably done. https://ursxdol.com/provigil-gn-pill-cnt/
This is a keynote which is near to my verve… Many thanks! Unerringly where can I upon the connection details due to the fact that questions? https://prohnrg.com/product/lisinopril-5-mg/
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
Proof blog you have here.. It’s intricate to find great status article like yours these days. I honestly appreciate individuals like you! Withstand vigilance!! https://ursxdol.com/doxycycline-antibiotic/
esim international travel esim switzerland
Услуги промышленных альпинистов https://trast-cleaning.ru высотные работы любой сложности, мойка фасадов, герметизация, монтаж, демонтаж.
Купить обои https://nash-dom71.ru для дома и офиса по доступным ценам. Виниловые, флизелиновые, текстильные, фотообои. Большой выбор, доставка, помощь в подборе.
buy turkish esim buy esim with esimania
Служба ремонта https://rnd-master.ru все бытовые услуги в одном месте. Ремонт техники, сантехники, электрики, мелкий бытовой сервис. Быстро, качественно, с гарантией.
Монтаж систем отопления https://elitmaster1.ru в домах любой площади. Газовое, электрическое, комбинированное отопление. Подбор оборудования, разводка труб, запуск.
https://uksputnik.ru
Подбор вытяжки https://podberi-vytyazhku.ru по всем параметрам: площадь, фильтрация, уровень шума, тип управления. От эконом до премиум-сегмента.
Купить недвижимость https://karado.ru в Белгородской области просто: проверенные объекты, помощь в оформлении, консультации.
Продажа сплит-систем https://split-s.ru и кондиционеров для дома, офиса и коммерческих помещений. Широкий выбор моделей, установка под ключ, гарантия, доставка.
Стажировки для студентов https://turbo5.ru вузов: реальный опыт, развитие навыков, участие в проектах. Возможность начать карьеру в крупной компании.
Ремонт компьютеров https://aka-edd.ru и ноутбуков: блог с советами от мастеров. Разбор типичных поломок, пошаговые инструкции, обслуживание, апгрейд.
Блог о мелочах https://ugg-buy.ru которые делают жизнь лучше: организация быта, семейные советы, домашние рецепты, удобные привычки.
Ремонт и дизайн жилья https://giats.ru просто! Полезный блог с лайфхаками, трендами, советами по планировке, цвету, освещению и отделке.
Светодиодные светильники https://svetlotorg.ru для дома, офиса, улицы и промышленных объектов. Экономия электроэнергии, долгий срок службы, стильный дизайн.
Бурение скважин https://protokakburim.ru на воду для дома, дачи и бизнеса. Бесплатный выезд специалиста, честная смета, оборудование в наличии.
Медицинский блог https://msg4you.ru для всех, кто заботится о здоровье. Статьи от врачей, советы по профилактике, разбор симптомов и заболеваний, современные методы лечения.
обмен USDT через Web3 кошелек
Красота вашего дома https://fx-gu.ru начинается с деталей! Интерьерные идеи, цветовые решения, текстиль, свет, мебель.
Бизнес и финансы https://business-age.ru свежие идеи, аналитика, инвестиции, налоги, стартапы. Полезные статьи для предпринимателей и тех, кто хочет грамотно управлять деньгами.
Сайт о финансовых https://good-recepts.ru основах: от личного бюджета до инвестиций. Полезные материалы, гайды, советы по управлению деньгами и финансовой грамотности.
Перевозка грузов https://gruzovoe-taxi24.ru по Москве: грузовое такси, переезды, доставка товаров, вывоз мебели. От легких до тяжёлых грузов.
https://kam-unity.ru
Строительные леса https://sib-metall.ru и вышки-туры: широкий выбор, прочные конструкции, доставка по всей России. Для профессионалов и частных клиентов.
Федеральная грузовая компания https://vgk.org.ru надёжные перевозки по всей России. Ж/д и автотранспорт, логистика, склад, страхование.
Каталог магазинов https://elfplus.ru электроинструмента по всей России. Сравнивайте цены, ассортимент и адреса. Только проверенные продавцы.
Ремонт квартир https://sovetyporemontu.ru в Москве: от косметического до капитального. Работаем точно в срок, без скрытых платежей.
https://vdom-teplo.ru
bearing manufacturer in Europe ball bearings for sale: Unlocking efficiency and precision in motion, our extensive range of ball bearings caters to diverse industrial and commercial needs. From miniature bearings for delicate instruments to robust bearings for heavy machinery, find the perfect fit for your application. Explore our online catalog or contact our expert team for personalized assistance in selecting the optimal ball bearing solution.
реклама на вайлдберис работа с карточками товара маркетплейс: Ключ к высоким продажам – это актуальная и привлекательная карточка.
Eth mixer Eth Mixer: Simplifying Confidential Transactions with Efficiency Eth mixers streamline the process of anonymizing Ethereum transactions, offering a user-friendly interface coupled with robust mixing protocols. By aggregating funds from numerous users and redistributing them through complex algorithms, these mixers effectively sever the link between sender and receiver. This enhanced privacy is invaluable for safeguarding personal information and protecting sensitive financial operations.
Услуги по ремонту https://remontexpert.su квартир и офисов: от косметического до капитального. Подбор стиля, качественные материалы, пошаговый контроль.
Ремонт и отделка https://remont39.ru квартир и офисов под ключ. Чистовая и черновая отделка, дизайн-проект, инженерные работы. Чёткие сроки, гарантия, контроль качества.
Домофоны и видеонаблюдение https://ooo-domofon.ru установка и обслуживание в Москве и области. Аналоговые и IP-системы, выезд специалиста, договор, гарантия.
Всё о воспитании https://rabotnikdoma.ru мягкие и авторитетные методики, развитие личности ребёнка, возрастные кризисы, границы и любовь.
This is the stripe of serenity I get high on reading. https://prohnrg.com/product/get-allopurinol-pills/
https://pteploobmennik.ru
Интернет-магазин https://teplokomfort32.ru отопительного оборудования, сантехники и электрики. Всё для обустройства дома: котлы, радиаторы, бойлеры, насосы, трубы, кабель.
Журнал о деньгах https://cdosfera.ru инвестициях, кредитовании и личных финансах. Разбираем банковские продукты, учим выгодно инвестировать, следим за рынками и курсами валют.
Штукатурка стен https://brigada63.ru и стяжка полов с гарантией качества. Механизированная и ручная отделка, строго по уровню. Работаем с квартирами, домами, офисами.
Удобный онлайн-сервис https://kazap.ru для поиска товаров и магазинов по всей России. Сравнение цен, наличие, отзывы, акции. Найдите нужный товар в проверенных магазинах за пару кликов.
Ремонт ванных комнат https://rem-vann.ru и квартир от косметического до капитального. Демонтаж, выравнивание, укладка плитки, монтаж сантехники и отделка помещений.
Все виды дезинфекции https://dezefect.ru от вирусов, бактерий, грибка, плесени. Обработка квартир, домов, офисов, транспорта. Безопасно, эффективно, с подтверждающими документами.
Отделка и ремонт https://remontnaura.ru квартир любой сложности. Современные материалы, опытные мастера, соблюдение сроков. Черновая и финишная отделка, дизайн-проекты, подбор материалов.
Всё о ремонте https://vse-vremonte.ru в одном месте. Как начать, на чём сэкономить, какие материалы выбрать, в какой последовательности действовать. Для новичков и профессионалов.
buy belt tensioner rollers ball bearings for sale: Unlocking efficiency and precision in motion, our extensive range of ball bearings caters to diverse industrial and commercial needs. From miniature bearings for delicate instruments to robust bearings for heavy machinery, find the perfect fit for your application. Explore our online catalog or contact our expert team for personalized assistance in selecting the optimal ball bearing solution.
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
браслеты из натуральных камней Камень подходит свойства: при выборе камня важно учитывать не только его магические свойства, но и индивидуальные особенности человека, его знак зодиака и личные предпочтения.
Отделочные материалы https://facade-master.ru в Москве по выгодным ценам. Всё для ремонта: краски, обои, плитка, гипсокартон, ламинат, шпатлёвки и инструменты.
Всё о профессиях https://porof.ru как выбрать профессию, какие рабочие специальности востребованы, где учиться и кем работать. Подробный перечень профессий с описанием, требованиями, зарплатами
Надёжная гидроизоляция https://evrostandart-gidro.ru защита фундаментов, резервуаров, водоёмов от влаги и протечек. Используем битумные, проникающие, обмазочные и мембранные материалы.
Натуральная питьевая вода https://vodaofis.ru — из природного источника, с мягким вкусом и сбалансированным составом. Подходит для детей и взрослых.
тик ток мод версия Скачать Тик Ток на Андроид Мод Процесс скачивания и установки мода на Android обычно включает в себя загрузку APK-файла и его установку с разрешением на установку приложений из неизвестных источников в настройках безопасности устройства.
Журнал с идеями https://master-vo.ru для вас и вашего дома: интерьер, уют, декор, советы по организации пространства, стиль жизни и вдохновение каждый день.
ПО TerraID https://terraid.ru интеллектуальная система идентификации и управления доступом. Поддержка карт, биометрии, интеграция с видеонаблюдением и СКУД.
Все виды строительных https://plat-ttofficial.ru и ремонтных работ: капитальное строительство, реконструкция, отделка, инженерные сети. Современные материалы, опытные мастера, контроль качества.
Широкий выбор бань https://eco-bani.ru по готовым проектам и на заказ. Каркасные, брусовые, из бревна — под ключ. Индивидуальные планировки, утепление, отделка, печи.
BBCR pillow block bearings: Simplify mounting and alignment with our range of pillow block bearings, pre-assembled units designed for easy installation on horizontal surfaces. Featuring robust housings and self-aligning capabilities, pillow block bearings provide reliable support and smooth operation in demanding environments. Ideal for conveyor systems, agricultural equipment, and other industrial applications.
промокоды на сайте 1001kupon
Купить ламинат https://laminat-vinil.ru и кварц виниловую плитку в Москве и области
Нужна мебель? https://joycom.ru для дачи, террасы и участка: кресла, столы, шезлонги, качели, комплекты. Устойчивые к влаге и солнцу материалы, стильный дизайн, удобство и долговечность.
Виртуальный телефон для СМС — бесплатно и без ограничений. Простое использование: выбирайте номер, получайте код, подтверждайте регистрацию. Список номеров регулярно обновляется.
Highly praised for reliability — “I’ve bridged over 50 transactions without a single issue.”
porn cuts buy mephedrone alpha
buy buds heroin porn creampie
Интересная статья: Интимная пластика для женщин: все, что нужно знать о процедуре
Читать полностью: Автолайфхаки: 10 секретов, которые упростят жизнь каждому водителю
Интересная статья: Нормальный пульс у женщин: таблица по возрасту и что на него влияет
Читать полностью: Чем нельзя протирать руль автомобиля: распространенные ошибки ухода
Нужен дом? строительство домов казань — от проекта до отделки. Каркасные, кирпичные, брусовые, из газобетона. Гарантия качества, соблюдение сроков, индивидуальный подход.
Fully decentralized with audited smart contracts and validator network.
Нужен дом? строительство домов казань — от проекта до отделки. Каркасные, кирпичные, брусовые, из газобетона. Гарантия качества, соблюдение сроков, индивидуальный подход.
Supports ETH, USDT, USDC, MANTA and more tokens.
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
изготовление выставочных стендов москва Выставочный стенд заказать: просто и удобно Выставочный стенд заказать сегодня – это просто и удобно. Многие компании предлагают онлайн-сервисы, позволяющие заказать стенд, не выходя из офиса. Вы можете выбрать готовый дизайн-проект или заказать индивидуальную разработку, указав все свои пожелания и требования.
работа для девушек без опыта Работа для девушек в сфере досуга Работа для девушек в сфере досуга может быть интересной и творческой. Это может быть работа аниматором, организатором мероприятий, ведущей или танцовщицей. Важно любить общаться с людьми и создавать атмосферу праздника.
Ongoing growth in cross‑chain volume and zk‑DeFi ecosystem integrations.
работа для девушек Высокооплачиваемая работа для девушек: секреты успеха Высокооплачиваемая работа для девушек – это результат упорного труда, постоянного обучения и развития профессиональных навыков. Важно не бояться ставить перед собой амбициозные цели и стремиться к карьерному росту. В современном мире существует множество профессий, где девушки могут зарабатывать большие деньги, например, в IT, финансах, маркетинге и продажах.
AME Capitals Отзывы Рад, что выбрал AME Capitals. Здесь действительно ценят каждого клиента и стремятся к его успеху.
http://ilianicolaevichzavialov.ru/
Follow the verified Instagram of 33win
Подписывайтесь на официальный Instagram 1dby
Explore the verified and official Instagram of new88
Discover the official Instagram of f8bet and never miss an update
Техосмотр без очередей https://texosmotr.su в день обращения! Полный осмотр, оформление диагностической карты, приём по записи.
Follow the real Korean casino site on Instagram
изготовление стендов в москве Выставочные стенды Москва: Современные технологии и инновационные материалы При изготовлении выставочных стендов в Москве активно используются современные технологии и инновационные материалы, позволяющие создавать конструкции любой сложности и дизайна. Это позволяет компаниям выделиться на фоне конкурентов и привлечь внимание посетителей.
Analyst view: the best place to buy twitter followers is decided by retention math, not hype.
Friends kept asking if it’s legit to buy likes on tiktok; this exposé lays out the math.
Finding a legit casino online can be tough, but this thread helped me out. The Best Online Casino options listed there are verified and actually deliver.
Надёжный заказ авто заказать авто в россию. Машины с минимальным пробегом, отличным состоянием и по выгодной цене. Полное сопровождение: от подбора до постановки на учёт.
Полезная статья: Самые верные мужчины: имена, обладатели которых редко изменяют
Интересная новость: 6 фраз, которые выдают настоящую любовь: психология отношений для женщин
Читать подробнее: Жара в авто: лайфхаки для водителей против перегрева
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
изготовление выставочных стендов москва Изготовление стендов в Москве: Комплексный подход и индивидуальные решения Изготовление стендов в Москве – это комплексный подход, включающий в себя разработку концепции, дизайн, изготовление конструкций, монтаж и оформление. Важно выбрать компанию, которая предлагает индивидуальные решения, учитывающие все ваши пожелания и требования.
Читать статью: Имбирь для здоровья: 9 причин полюбить и добавить в свой рацион
Статьи обо всем: Кто может испортить свадьбу: психологические типы нежелательных гостей
Новое и актуальное: Кислоты летом: как правильно использовать для красоты кожи
Интересные статьи: Сочные беляши на кефирном тесте: простой рецепт с мясным фаршем
wormhole portal bridge
как пить виски Бочковая крепость – это термин, обозначающий напиток, разлитый из бочки без добавления воды для снижения содержания алкоголя. Такие напитки отличаются насыщенным вкусом и высокой крепостью.
https://birvodokanal.ru
Парящий натяжной потолок монтаж Световые линии для натяжного потолка цена – формируется исходя из выбранных материалов, сложности монтажа и длины линий.
https://clubdom52.ru
займ онлайн микрозайм онлайн
Читать полностью: Шампунь для волос: как выбрать и правильно использовать – советы экспертов красоты
defillama app
взять займ оформить займ онлайн
займ оформить занять деньги онлайн
manta swap
manta network
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
https://177m.ru
Автомобили на заказ https://prignat-mashinu2.ru. Работаем с крупнейшими аукционами: выбираем, проверяем, покупаем, доставляем. Машины с пробегом и без, отличное состояние, прозрачная история.
Надёжный заказ авто https://zakazat-avto44.ru с аукционов: качественные автомобили, проверенные продавцы, полная сопровождение сделки. Подбор, доставка, оформление — всё под ключ. Экономия до 30% по сравнению с покупкой в РФ.
Решили заказать авто из китая в россию под ключ: подбор на аукционах, проверка, выкуп, доставка, растаможка и постановка на учёт. Честные отчёты, выгодные цены, быстрая логистика.
Хочешь авто заказать новый авто? Мы поможем! Покупка на аукционе, проверка, выкуп, доставка, растаможка и ПТС — всё включено. Прямой импорт без наценок.
Thanks for sharing. It’s acme quality. xenical avis perte de poids
defillama portfolio
defillama price
авто из китая Обслуживание китайских авто: где и как обслуживать? Даем советы по обслуживанию китайских автомобилей и рассказываем о том, где найти квалифицированных специалистов.
https://frasesmotivacional.com/
Нужен автосвет загляните на nts-auto и всё для его установки автосвета. Здесь собраны лампы, линзы, держатели, маски, герметики и другие комплектующие. Всё по делу, без лишнего — удобно, быстро, с доставкой по России. Производим и пользуемся сами, можем рекомендовать!
Нужен ремонт? компмастер – Ремонт ноутбуков, телефонов, телевизоров и компьютеров в Одинцово
More posts like this would create the online play more useful. https://aranitidine.com/fr/modalert-en-france/
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), RuCaptcha, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
сурматеринство с гарантией – гонорар суррогатной матери помощь бесплодным парам. Полный цикл: от подбора суррогатной мамы до рождения ребёнка. Юридическая чистота, надёжные клиники, чуткое сопровождение специалистов.
defillama tvl
офисные кресла Мебель для кабинета руководителя – это комплексное решение, включающее в себя стол, кресло, шкафы для документов, тумбочки и другие элементы интерьера. Важно создать атмосферу комфорта и деловой обстановки, способствующую продуктивной работе и принятию важных решений. Все элементы мебели должны гармонировать друг с другом и отражать индивидуальность руководителя.
defillama token
Authentic Instagram for 777pub – check the official feed
Нужна душевая кабина? душевая кабина купить: компактные и просторные модели, стеклянные и пластиковые, с глубоким поддоном и без. Установка под ключ, гарантия, помощь в подборе. Современный дизайн и доступные цены!
Нужна душевая кабина? душевые кабины в минске цены: компактные и просторные модели, стеклянные и пластиковые, с глубоким поддоном и без. Установка под ключ, гарантия, помощь в подборе. Современный дизайн и доступные цены!
Discover the latest from taya365 on their only official Instagram profile
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
авто из китая Подержанные авто из Китая: выгодная покупка или кот в мешке? Рассматриваем плюсы и минусы покупки подержанного китайского автомобиля и даем советы по выбору.
Base Bridge
Want official updates from 8k8? Follow their true Instagram page here
Verified presence of ph365 on Instagram – authentic and original
Access the original Instagram account of panaloko right here
Don’t miss updates from winph – this is the one true Instagram
http://xn--80aafabrjladsicc1amg1o4cf1dg.press/
Connect with okebet through their official and active Instagram
Discover what swerte99 is posting – official updates you can trust
Access official announcements and updates in the slotvip Facebook group
Real posts, real profile – follow jilicc on Instagram now
Разработка сайтов создание сайтов для бизнеса Создание сайтов для бизнеса – это инвестиция в будущее компании. Правильный сайт привлекает клиентов, увеличивает продажи и укрепляет имидж. Важно учитывать специфику бизнеса, целевую аудиторию и конкурентов. Сайт должен быть информативным, удобным и соответствовать бренду.
Engage with fans and followers in the verified taya365 Facebook group
Join the real community around ph365 on Facebook – verified and live
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captchas.com (antigate), RuCaptcha, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
Looking for 8k8? This is the authentic Facebook group to follow
автодоставка из Китая Доставка бытовой техники из Китая – требует проверки соответствия стандартам безопасности и качества.
Продвижение сайта https://team-black-top.ru в ТОП Яндекса и Google. Комплексное SEO, аудит, оптимизация, контент, внешние ссылки. Рост трафика и продаж уже через 2–3 месяца.
Комедия детства смотреть бесплатно один дома 1 — легендарная комедия для всей семьи. Без ограничений, в отличном качестве, на любом устройстве. Погрузитесь в атмосферу праздника вместе с Кевином!
Противоосколочные модульные одеяла для защиты от дронов (из СВМПЭ) с доставкой по России (ПВЗ в ЛНР и ДНР) Купить тепловизор в Луганске: широкий выбор моделей по доступным ценам.
Lubisz kasyna online i automaty do gry? Zarejestruj się na slottica opinie i zgarnij nagrody powitalne!
Stay informed through the official taya777 Facebook group
Нужна душевая кабина? душевая кабина купить лучшие цены, надёжные бренды, стильные решения для любой ванной. Доставка по городу, монтаж, гарантия. Каталог от эконом до премиум — найдите идеальную модель для вашего дома.
Нужна душевая кабина? душевые кабины недорого лучшие цены, надёжные бренды, стильные решения для любой ванной. Доставка по городу, монтаж, гарантия. Каталог от эконом до премиум — найдите идеальную модель для вашего дома.
Discover news and discussions from swerte99 in their official group
Follow winph in their official group – real members, real content
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), rucaptcha.com, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
Купить сапёрный противоосколочный костюм с доставкой по России (ПВЗ в ЛНР и ДНР) Купить тепловизор для охраны с доставкой по всей России, включая ЛНР и ДНР. Надежная защита вашей территории.
Follow the official Instagram of slotvip – verified and active profile
Looking for okbet? This is their official and authentic Instagram
Biathlon World Cup – calendar all competitons, overall rankings and biathlon race results – sprint and pursuit
займ быстрый займ денег онлайн
Блог рекламиста https://dramtezi.ru всё о маркетинге под ключ. Полезные статьи, разбор кейсов, обучение, индивидуальные консультации. Помогаем прокачать бренд, привлечь клиентов и выстроить эффективную стратегию продвижения.
Химчистка мебели ростов
Архитектурное бюро спб https://arhitektura-peterburg.ru
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), RuCaptcha, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
стеклянная перегородка в душевую Раздвижные стеклянные перегородки: экономия пространства и удобство использования. Типы механизмов, дизайн, установка.
тепловизор на андроид купить кевларовый противоосколочный костюм Выбор кевларового противоосколочного костюма – это приоритет безопасности в экстремальных ситуациях. Учитывайте класс защиты, вес и эргономику. Инвестируйте в проверенные бренды, гарантирующие надежную защиту от осколков и поражающих элементов.
https://servicestat.ru/service-kzn Servicestat.ru — это удобный каталог-рейтинг сервисных центров по ремонту электроники. На сайте собраны контакты (адреса, телефоны), отзывы клиентов, акции и скидки, а также оценки качества услуг. Пользователи могут быстро найти проверенные мастерские в своем городе, сравнить рейтинги и выбрать лучший вариант. Полезен для тех, кто хочет отдать технику в надежные руки.
? Поиск сервисов по местоположению и брендам
? Реальные отзывы и оценки клиентов
? Акции, скидки и спецпредложения
? Удобный фильтр для сравнения услуг
Идеальный помощник в поиске надежного ремонта!
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
тепловизор флир магазин тактического снаряжения симферополь В Симферополе можно приобрести тактическое снаряжение в различных специализированных магазинах.
Work in Macau https://hello-jobs.com fresh vacancies with decent pay. Hospitality, entertainment, construction and service. Vacancies for CIS citizens, paperwork, housing. Reliable employers are waiting!
AMT Games https://amt-games.com is a developer of popular online games in the genres of strategy, MMO and action. Famous projects: Battle for the Galaxy, Heroes of War and others.
Dual Access Bazaar Drugs Marketplace: A New Darknet Platform with Dual Access Bazaar Drugs Marketplace is a new darknet marketplace rapidly gaining popularity among users interested in purchasing pharmaceuticals. Trading is conducted via the Tor Network, ensuring a high level of privacy and data protection. However, what sets this platform apart is its dual access: it is available both through an onion domain and a standard clearnet website, making it more convenient and visible compared to competitors. The marketplace offers a wide range of pharmaceuticals, including amphetamines, ketamine, cannabis, as well as prescription drugs such as alprazolam and diazepam. This variety appeals to both beginners and experienced buyers. All transactions on the platform are carried out using cryptocurrency payments, ensuring anonymity and security. In summary, Bazaar represents a modern darknet marketplace that combines convenience, a broad product selection, and a high level of privacy, making it a notable player in the darknet economy.
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), RuCaptcha, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
RFE Christian Radio https://www.radio-rfe.com Gospel broadcasts, worship, reading of the Word, prayers and inspirational music. Online broadcasting 24/7. Strengthen your faith and fill yourself with God’s peace at any time.
Central Buenos Aires hotel https://www.panamericano.us comfort and style near the main attractions. Suitable for leisure and business. Free Wi-Fi, transfer, breakfast and cozy atmosphere. Online booking at the best prices.
Taller Puntera https://puntera.com is a space of creativity and handcraft. Design, quality, craftsmanship. Unique items created with soul: from classic to avant-garde. Find something that speaks about you.
Пожарная сигнализация https://verspk.ru для дома, офиса, склада и производства. Проектирование, монтаж и обслуживание систем. Датчики дыма и температуры, автоматическое оповещение, интеграция с охранной системой.
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
Клуб «Терийоки» https://yct.su идеальное место для отдыха в Зеленогорске. Просторные номера и коттеджи, ресторан, SPA-зона, баня, залы для торжеств.
Центр сертификации https://radiocert.ru в Москве: продукция, услуги, СМК, пожарная безопасность, ЕАС. Независимая экспертиза, аккредитованные лаборатории, прозрачная стоимость. Полное сопровождение на всех этапах.
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
Bk8
откачка грунтовых вод водопонижение грунтовых вод
Ищете шины? https://tssz.ru У нас — более 165 брендов со всего мира! Michelin, Pirelli, Nokian, Bridgestone и другие. Быстрый подбор по авто, отличные цены, оригинальная продукция с гарантией. Установка и доставка по всей России.
Фотосалон в Екатеринбурге https://www.foto4u.su фото на документы, печать снимков, ксерокопии, ламинирование, фототовары и сувениры. Быстро, качественно, недорого.
Профессиональная моторазборка https://bibamotor.ru запчасти для мотоциклов из Европы, Японии и США. В наличии двигатели, рамы, пластик, электрика и мелкие детали. Проверка, доставка, гарантия. Всё для ремонта и тюнинга байка.
Промышленные ворота https://www.efaflex.ru для складов, ангаров, автосервисов и производств. Секционные, откатные, рулонные, подъемные конструкции. Надежность, теплоизоляция, автоматика.
Togelup
Bk8
walewska.ru
Проверенные горящие туры: надежность и безопасность. Как мы сэкономили 78 000 руб
Ищете, где хранить продукты при низкой температуре? Вам подойдёт холодильная камера – практичное и надёжное решение для бизнеса и дома, оформите заказ по ссылке https://камера-холодильная.рф/
Купить мебель онлайн http://nirvanaplus.ru просто! В нашем интернет-магазине: мягкая и корпусная мебель, спальни, гостиные, кухни и офисные решения. Гарантия качества, рассрочка, доставка и сборка. Стиль и комфорт — в каждый дом.
Ремонт автомобилей https://renaultra.ru Renault и Nissan любой сложности. Замена узлов, диагностика, ТО, электрика. Запчасти в наличии и под заказ — оригинал и аналоги.
Курс по плазмолифтингу https://prp-ginekologiya.ru в гинекологии: PRP-терапия, протоколы, показания и техника введения. Обучение для гинекологов с выдачей сертификата. Эффективный метод в эстетической и восстановительной медицине.
Курс по плазмотерапии обучение плазмотерапии онлайн с выдачей сертификата. Освойте PRP-методику: показания, противопоказания, протоколы, работа с оборудованием. Обучение для медработников с практикой и официальными документами.
saif zone login saif zone investor login
Aw8
обучение кайтсёрфингу Кайтсёрфинг видео: вдохновение и обучение. Смотрите видеоролики с лучшими кайтсёрферами мира.
Интересная статья: Рынок подержанных авто в Украине: как купить без перерегистрации и не попасть на уловки перекупщиков
Читать статью: Курица и кабачки под сырной корочкой: простой и вкусный рецепт
Интересная статья: Почему фикус осыпается зимой: ошибки ухода и спасение растения
Togelup
Читать в подробностях: Стремление к совершенству: психология отличника, плюсы и минусы перфекционизма
Интересная новость: Полив деревьев перед зимой: секреты обильного урожая весной
кайтсёрфинг Кайтсёрфинг трюки: от простого к сложному. Освойте базовые трюки и двигайтесь к новым высотам.
Читать новость: Вредные продукты: список от диетолога для вашего здоровья
кайт школа “Русские просторы”: Анапа, Крым, где “ветер гуляет по степям”
кайт лагерь Кайтсёрфинг для детей: возможность раннего развития. Кайтсёрфинг – это отличный способ развить координацию, силу и выносливость у детей.
Frax Swap
Новое на сайте: Полезный завтрак: простые продукты для здоровья и энергии
Thread cadence > reply seeding > measured decision to buy followers on twitter; the article details pacing.
Новое на сайте: Самые распространенные сожаления: как избежать ошибок
кайт лагерь Кайтинг: здоровье и фитнес
Mantle Bridge
Сайт добрых пожеланий https://demotivators.ru для души и вдохновения. Тысячи текстов для родных, друзей, коллег. Красивые слова, поздравления, открытки, мотивация. Поздравьте близких с любовью и заботой в каждом слове.
AI platform bullbittrade.com/ for passive crypto trading. Robots trade 24/7, you earn. Without deep knowledge, without constant control. High speed, security and automatic strategy.
Innovative AI platform https://lumiabitai.com/ for crypto trading — passive income without stress. Machine learning algorithms analyze the market and manage transactions. Simple registration, clear interface, stable profit.
українські фільми мелодрами топ фільмів 2025 онлайн
українські фільми 2025 топ фільмів 2025 онлайн
фантастичні фільми 2025 дивитися кіно 2025 на телефоні
Anyswap
Paraswap
кайт школа Продвинутые техники кайтсёрфинга: покорите новые вершины. Освоив базовые навыки, переходите к изучению сложных трюков, таких как прыжки с перехватом, вращения и катание на волнах.
кайт школа Кайтсёрфинг трюки: от простого к сложному. Освойте базовые трюки и двигайтесь к новым высотам.
кайтсёрфинг “Гавань приключений”: кайт лагерь, где сердца бьются в унисон, где рождается семья
обучение кайтсёрфингу Кайт зависимость: Страсть, которая меняет жизнь. Однажды попробовав кайтинг, вы уже не сможете остановиться.
кайтсёрфинг Кайтсёрфинг – это возможность увидеть мир с другой стороны, почувствовать себя частью природы и найти новых друзей.
кайтинг Кайтсёрфинг
matcha swap
Bos88
Bandartogel77
the comic is big read comics online free
read manga manga for mobile devices
манга манхва романтическая манхва
Hometogel
tron staking how it works
кайт лагерь Кайтсёрфинг: танец с ветром и волнами. Ощутите свободу, скользя по водной глади, управляя мощным кайтом. Это адреналин, спорт и искусство в одном флаконе.
кайтинг “Азбука водной стихии”: кайт для новичков, как первый шаг к свободе
обучение кайтсёрфингу Шлем для кайтсерфинга: защита головы при падениях
кайтсёрфинг Кайтсерфинг в Доминикане: Кабарете – волны и ветер
DefiLlama swap fees
https://vladtime.ru/zdorov/750950
кайтинг “Мекки кайтсерфинга”: лучшие места, где “ветер шепчет легенды”
кайтсёрфинг Сноукайтинг: кайтинг на лыжах или сноуборде – техника и безопасность
how to use mantcha swap
серия фильм онлайн онлайн кино новинки
Публичная дипломатия России https://softpowercourses.ru концепции, стратегии, механизмы влияния. От культурных центров до цифровых платформ — как формируется образ страны за рубежом.
Институт государственной службы https://igs118.ru обучение для тех, кто хочет управлять, реформировать, развивать. Подготовка кадров для госуправления, муниципалитетов, законодательных и исполнительных органов.
Школа бизнеса EMBA https://emba-school.ru программа для руководителей и собственников. Стратегическое мышление, международные практики, управленческие навыки.
Опытный репетитор https://english-coach.ru для школьников 1–11 классов. Подтянем знания, разберёмся в трудных темах, подготовим к экзаменам. Занятия онлайн и офлайн.
Делал тёплые полы — просмотрел кучу советов в интернете. В одних источниках советуют «не меньше 6 см», а в других «можно обойтись 3 см». После долгих поисков наткнулся на каталог, где собрали нормальные ресурсы: с официальными документами, советами мастеров минус этих «гуру ремонта». Теперь хоть понимаю, как правильно
Каталог
Проходите аттестацию https://prom-bez-ept.ru по промышленной безопасности через ЕПТ — быстро, удобно и официально. Подготовка, регистрация, тестирование и сопровождение.
Sbototo
«Дела семейные» https://academyds.ru онлайн-академия для родителей, супругов и всех, кто хочет разобраться в семейных вопросах. Психология, право, коммуникации, конфликты, воспитание — просто о важном для жизни.
Трэвел-журналистика https://presskurs.ru как превращать путешествия в публикации. Работа с редакциями, создание медийного портфолио, написание текстов, интервью, фото- и видеоматериалы.
https://dtf.ru/id2915936/3931207-promt-dlya-sozdaniya-patcha-iz-kartinki-dlya-odezhdy
Zarejestruj się w kasynie online już teraz na oficjalnej stronie slottica casino i odbierz bonusy za pierwszą wpłatę na automatach!
Свежие скидки https://1001kupon.ru выгодные акции и рабочие промокоды — всё для того, чтобы тратить меньше. Экономьте на онлайн-покупках с проверенными кодами.
«Академия учителя» https://edu-academiauh.ru онлайн-портал для педагогов всех уровней. Методические разработки, сценарии уроков, цифровые ресурсы и курсы. Поддержка в обучении, аттестации и ежедневной работе в школе.
Hometogel
gengtoto login
Оригинальный потолок натяжной потолок со световыми линиями отзывы со световыми линиями под заказ. Разработка дизайна, установка профиля, выбор цветовой температуры. Идеально для квартир, офисов, студий. Стильно, практично и с гарантией.
Découvrez pocket option site, l’application de trading intuitive utilisée par des millions de traders dans le monde. Accédez à plus de 100 actifs : forex, actions, crypto-monnaies et matières premières. Exécutions rapides, interface claire et retraits instantanés. Parfait pour débutants comme pour traders expérimentés – tradez où que vous soyez, à tout moment.
jonitogel
Лазерная гравировка Лазерная гравировка — это способ добавить индивидуальность и уникальность любому предмету. Нанесите логотип компании на сувенир, создайте именную табличку или украсьте подарок памятной надписью. Лазерная гравировка позволяет создавать четкие и долговечные изображения на различных материалах, от дерева и стекла до металла и пластика.
?аза? тіліндегі ?ндер Сборник хитов казахских песен ж?рекке жа?ын ?уендер мен ?серлі м?тіндер. ?лтты? музыка мен ?азіргі заман?ы хиттер. Онлайн ты?дау ж?не ж?ктеу м?мкіндігі бар ы??айлы жина?.
?аза? тіліндегі ?ндер Сборник казахских песен ж?рекке жа?ын ?уендер мен ?серлі м?тіндер. ?лтты? музыка мен ?азіргі заман?ы хиттер. Онлайн ты?дау ж?не ж?ктеу м?мкіндігі бар ы??айлы жина?.
26 ранг Я с уверенностью рекомендую варфейс аккаунты с этого сайта.
донецк шлюхи Поиск “проститутки Донецка” выдает множество сомнительных сайтов и объявлений. Важно помнить о рисках, связанных с нелегальной деятельностью, включая возможность заражения венерическими заболеваниями и столкновение с криминалом.
Готовый комплект Инсталляция грое с унитазом в комплекте инсталляция и унитаз — идеальное решение для современных интерьеров. Быстрый монтаж, скрытая система слива, простота в уходе и экономия места. Подходит для любого санузла.
Wondering if you should buy likes on twitter? Check the drop?off graph in section 2.
https://netlux.org
barcatoto
https://www.weyher.de
https://redfordtheatre.com
https://smolensck.ru/calan/pcs/1xbet_promokod_bonus.html
batman138
udintogel login
Портал с обзорами лучших онлайн-казино, рейтингами, актуальными бонусами и акциями, а также подробными гайдами и промо-предложениями: топ 10 лучших онлайн казино
https://litoseoane.es
Ирригация полей Сушка зерна: Технологии сушки зерна: как сохранить качество урожая и избежать потерь при хранении.
comment obtenir un code promo sur 1xbet 1xBet free bet promo code 2025: GO333 to claim exclusive rewards – 200% up to $100 sports bonus plus $2,275 + 150 free spins on casino. 1XBet offers an exciting promotion for new registrants in the new year. This promotion is designed for new bettors over 18. Sports bonuses require 5x-10x wagering on accumulators with 3 or more events at odds 1.40+ within 30 days.
The 1xBet promo code today 2025: GO333. By using this bonus code upon registration on the 1xBet platform, you’ll get an exclusive 330% bonus up to €100. The bonus is for sports bets. To activate this offer, create an account on 1xBet and enter the code in the promo code field. Review conditions on the official site for bonus conditions.
https://www.nagasakiwagyu.com/89#comment-1956916
Bosstoto
Год искал, как не нарваться на шарлатанов — везде сплошная реклама, либо ужастики про обманутых заказчиков. Случайно наткнулся на подборку где собраны проверенные ресурсы, с живыми отзывами. Теперь хоть знаю, где искать адекватных мастеров
Каталог mydovidnikgospodarya.xyz
This is the kind of delivery I unearth helpful. https://ondactone.com/product/domperidone/
Dolantogel
This is the amicable of topic I get high on reading. https://ondactone.com/simvastatin/
https://abs2best.at
https://abs2best.at
Mariatogel
https://m-bs2best.at
https://bs2-bs2site.at
Mariatogel
https://bs-bsme.at
https://bs2besd.cc
totojitu
togel4d
Обработка квартиры от тараканов в Москве проводится поэтапно — сначала осмотр, затем дезинсекция и контроль результата: уничтожение тараканов в москве
https://bs2bsme.at
“Реестр Гарант” оказывает услуги по включению в реестр Минпромторга российских производителей. Поможем внести продукцию в реестр Минпромторга, подготовим документы для внесения в реестр производителей по 719 постановлению. Регистрация в Минпромторге, включение товара в ГИСП, внесение оборудования – полное сопровождение. Узнайте стоимость включения в реестр Минпромторга: внесение сведений в каталог минпромторга
artistoto login
goltogel login
https://b2best.at
https://bsme-at.at
https://bs2bet.at
https://bsmc.at
Soap Dispensers
ton swap
crypto exchange barcelona with low fees
https://bs-bsme.at
https://bs2beast.cc
I’ll certainly carry back to be familiar with more.
https://doxycyclinege.com/pro/sumatriptan/
swap tron instantly
Good blog you procure here.. It’s hard to on great calibre belles-lettres like yours these days. I truly comprehend individuals like you! Rent vigilance!!
https://doxycyclinege.com/pro/sumatriptan/
Hand Sanitisers
https://abs2best.at
https://тихвести.рф/news/obshhestvennyj_transport_v_sochi_kak_peredvigatsja_udobno_i_bez_lishnikh_trat/2025-04-18-25944
https://bs2-bs2site.at
https://m-bs2best.at
https://bsmc.at
bk8 slotbk8
https://bs2vveb.at
visit the official website: https://sportquantum.com/
go to the official website: https://arbaline.ru/
visit our website: https://joogastuudio.ee/
https://m-bs2best.at
the newest on the site: https://www.feldbahn-ffm.de/
visit an interesting site: https://amt-games.com/
see new on the site: https://www.radio-rfe.com/
visit our website: https://woodbridgebrewingco.com
fresh and relevant from us: https://www.intercultural.org.au
We have the latest information: https://www.greenwichodeum.com
https://bs-bsme.at
Мы предлагаем уборка офиса в Москве и области, обеспечивая высокое качество, внимание к деталям и индивидуальный подход. Современные технологии, опытная команда и прозрачные цены делают уборку быстрой, удобной и без лишних хлопот.
Мы предлагаем установка счетчиков воды в СПб и области с гарантией качества и соблюдением всех норм. Опытные мастера, современное оборудование и быстрый выезд. Честные цены, удобное время, аккуратная работа.
лечение зависимости клиника для наркозависимых во Владивостоке
центр лечения зависимостей рехаб для алкоголиков
https://abs2best.at
https://bsmc.at
https://bs2besd.cc
eu9
What are the fees for selling USDT in Argentina?
best site visit: https://www.saffireblue.ca
visit our website go to: https://agriness.com
посети наш сайт: https://vodazone.ru
indotogel login
our official website: https://petitedanse.com.br
all the latest on the site: https://g-r-s.fr
new on our website: https://www.coachandbusmarket.com
our official website: https://um.com.co
best official website: https://lapina.es
best site visit us: https://institutocea.com
eu9
come visit our new website: https://smokeon.es
best site on the net: https://lmc896.org
Official website of the company: https://www.munihuamalies.gob.pe
visit the site online: https://fluentcpp.com
посетить сайт онлайн: https://verspk.ru
go to the site online: http://www.waltbabylove.com
USDT for cash without KYC Turkey
visit our website: https://anthese.fr
visit the official website online: https://www.elboomeran.com
our new website: https://ween.tn
Where to sell USDT for cash in Bali
official website of the company online: https://primiumpoppypods.com
official website of the company: https://intelicode.com
visit us online: https://www.sportsoddshistory.com
Sell USDT in Buenos Aires
indotogel login
Сериал «Уэнсдей» уэнсдей 1 сезон 4 серия мрачная и захватывающая история о дочери Гомеса и Мортиши Аддамс. Учёба в Академии Невермор, раскрытие тайн и мистика в лучших традициях Тима Бёртона. Смотреть онлайн в хорошем качестве.
Срочно нужен сантехник? сантехник на дом в Алматы? Профессиональные мастера оперативно решат любые проблемы с водопроводом, отоплением и канализацией. Доступные цены, выезд в течение часа и гарантия на все виды работ
Die innovative Behandlungsmethode HIPEC kombiniert chirurgische Eingriffe mit erhitzter Chemotherapie, um Krebszellen in der Bauchhohle effektiv zu bekampfen und die Uberlebenschancen zu erhohen.
our official company website: https://elitetravelgroup.net
официальный сайт компании: https://actual-cosmetology.ru
Подарочный Набор флешка с Нанесением логотипа Москва флешка оптом ручка купить в Омске и флешка Максимальный объем памяти в Улан-Удэ. Белые слэп браслеты с флешкой и флешка Sony в Хабаровске. Флешка оптом армия россии и колонка флешка
Честный гид https://easybip.ru по недвижимости. Не агентство, не продаем. Только ясная информация: как купить/продать/снять жилье без риска, разобраться в рынке, документах и районах. Без рекламы и звонков.
частное продвижение сайтов https://seo-effective.ru
рвд 12 25 шланг высокого давления рвд
рвд 1sn изготовление рвд
Топливные карты https://www.taxi-zenit.ru решение для юридических лиц, позволяющее экономить на заправках и контролировать расходы. Гибкая настройка лимитов, полный отчёт, единый счёт и удобная онлайн-аналитика.
Предрейсовые осмотры https://predreysovye-osmotry.ru водителей в Москве — оперативно, с выездом на предприятие. Лицензированные врачи, современное оборудование, удобный график. Соблюдение всех требований законодательства и охраны труда.
Новая натуральная косметика https://musco.ru/
https://m-bs2best.at
Продаем оконный профиль https://okonny-profil-kupit.ru высокого качества. Большой выбор систем, подходящих для любых проектов. Консультации, доставка, гарантия.
Оконный профиль https://okonny-profil.ru купить с гарантией качества и надежности. Предлагаем разные системы и размеры, помощь в подборе и доставке. Доступные цены, акции и скидки.
https://bs2-bs2site.at
ремонт кофемашин неспрессо ремонт кофемашин nespresso
ремонт старых швейных машин ремонт швейных машин в москве
аренда 1с в облаке цена 1с клауд облако личный кабинет
I’m much more comfortable moving larger sums across the Polygon Bridge after reading about its security features.
sell usdt for cash for ofw philippines
OTC crypto desk Bogota
Sell USDT for physical euros Lisbon
Sell USDT Kadıköy
Sell USDT for Euros in Belgrade
Crypto exchange for entertainment industry LA
ремонт кофемашин nespresso ремонт капсульных кофемашин
USDT contre euros à Monte-Carlo
ремонт бытовых швейных машин https://remont-shveynyh-mashin1.ru
Sälja Tether Stockholm
1с облако вход 1с облако тарифы
over-the-counter usdt exchange berlin
Sell USDT in person Gran Vía
crypto exchange the hague for expats
Best crypto exchange Lyon
Sælg krypto uden verifikation Danmark
USDT u eure Split
Crypto exchange near me Salzburg
Of course. Here is the comprehensive, high-intent keyword list for “Sell USDT in Miami,” tailored for its unique position as a crypto hub and its international audience.
sell USDT instantly Nicosia
sell USDT in Medan
Прокат авто аэропорт Краснодар
P2P USDT Malta
Wie man USDT in Zug verkauft
Лоукост авиабилеты https://lowcost-flights.com.ua по самым выгодным ценам. Сравните предложения ведущих авиакомпаний, забронируйте онлайн и путешествуйте дешево.
Предлагаю услуги https://uslugi.yandex.ru/profile/DmitrijR-2993571 копирайтинга, SEO-оптимизации и графического дизайна. Эффективные тексты, высокая видимость в поиске и привлекательный дизайн — всё для роста вашего бизнеса.
swap USDT in Birmingham
swap USDT in Honolulu
Прокат авто Краснодар жд
p2p USDT in Dubai
convert USDT BEP20 in Italy
licensed crypto exchange Greece
Курс по коммерческой недвижимости Онлайн курсы по недвижимости: Учитесь, где удобно. Получите образование дистанционно, в своем темпе, с доступом к материалам и экспертным консультациям.
АО «ГОРСВЕТ» в Чебоксарах https://gorsvet21.ru профессиональное обслуживание объектов наружного освещения. Выполняем ремонт и модернизацию светотехнического оборудования, обеспечивая комфорт и безопасность горожан.
Онлайн-сервис https://laikzaim.ru займ на карту или счет за несколько минут. Минимум документов, мгновенное одобрение, круглосуточная поддержка. Деньги в любое время суток на любые нужды.
Custom Royal Portrait https://www.turnyouroyal.com an exclusive portrait from a photo in a royal style. A gift that will impress! Realistic drawing, handwork, a choice of historical costumes.
swap USDT in Amadora
Открыть онлайн брокерский счёт – ваш первый шаг в мир инвестиций. Доступ к биржам, широкий выбор инструментов, аналитика и поддержка. Простое открытие и надёжная защита средств.
sell USDT in Manchester
sell USDT in Saudi Arabia
trade Tether in Turkey
Аренда авто Краснодар на месяц
экскурсия казань Улица Баумана: Сердце Города и Место Встреч Улица Баумана – это главная пешеходная улица Казани, где всегда царит оживленная атмосфера. Здесь расположены многочисленные магазины, кафе, рестораны и сувенирные лавки. Улица Баумана – это отличное место для прогулок, шопинга и отдыха. Здесь можно встретить уличных музыкантов, художников и других творческих людей.
Обучение недвижимости Москва Обучение в сфере недвижимости: Станьте ценным специалистом. Сфера недвижимости ждет таланты. Обучение открывает двери к востребованной профессии и стабильному доходу.
ПОмощь юрист в банкротстве: ооо банкротство под ключ
Ремонт кофемашин https://coffee-craft.kz с выездом на дом или в офис. Диагностика, замена деталей, настройка. Работаем с бытовыми и профессиональными моделями. Гарантия качества и доступные цены.
Круглосуточный вывод из запоя на дому цены — помощь на дому и в стационаре. Капельницы, очищение организма, поддержка сердца и нервной системы. Анонимно и конфиденциально.
Купить мебель большие обеденные столы для дома и офиса по выгодным ценам. Широкий выбор, стильный дизайн, высокое качество. Доставка и сборка по всей России. Создайте комфорт и уют с нашей мебелью.
Sell My House Fast in Tampa, FL
Floor, frame, or jersey—the right rockbros pump means no more babysitting PSI between coffee shop and climb; valves switch easily and the stroke feels efficient, not frantic.
Gametoto
Предлагаем оконные профили https://proizvodstvo-okonnych-profiley.ru для застройщиков и подрядчиков. Высокое качество, устойчивость к климатическим нагрузкам, широкий ассортимент.
Оконные профили https://proizvodstvo-okonnych.ru для застройщиков и подрядчиков по выгодным ценам. Надёжные конструкции, современные материалы, поставка напрямую с завода.
injection moulding tool material
консультация адвоката написать юристам вопрос
Нужны пластиковые окна: пластиковые окна недорого цена
Нужен вентилируемый фасад: подсистема для вентилируемого фасада
https://kazan.land/ Галерея Современного Искусства: Вдохновение и Новые Горизонты Галерея современного искусства – это место, где представлены работы современных художников и скульпторов, работающих в различных стилях и направлениях. Здесь можно увидеть произведения, отражающие современные тенденции в искусстве, а также принять участие в выставках и мастер-классах. Галерея поможет вам открыть для себя новые горизонты в искусстве и получить вдохновение.
Pokerace99
Saudaratoto
Asian4d
экскурсии по казани Музей Исламской Культуры: Духовное Наследие Татарстана Музей исламской культуры – это место, где можно познакомиться с историей ислама в Татарстане, увидеть уникальные экспонаты, связанные с религией, культурой и искусством. Вы сможете узнать о развитии ислама в регионе, увидеть старинные рукописи, предметы быта и религиозные атрибуты. Музей поможет вам лучше понять духовное наследие татарского народа.
Gametoto
Trust Finance https://trustf1nance.com is your path to financial freedom. Real investments, transparent conditions and stable income.
botanical decor custom brooches
Інформаційний портал https://pizzalike.com.ua про піцерії та рецепти піци в Україні й світі. Огляди закладів, адреси, меню, поради від шефів, секрети приготування та авторські рецепти. Все про піцу — від вибору інгредієнтів до пошуку найсмачнішої у вашому місті.
экскурсии по казани Парк “Кырлай”: Развлечения для Всей Семьи Парк “Кырлай” – это парк развлечений в Казани, где можно найти аттракционы для всех возрастов. Здесь есть карусели, горки, колесо обозрения и многое другое. Парк “Кырлай” – это отличное место для семейного отдыха, где можно весело провести время и получить заряд положительных эмоций.
Решили купить Honda? кузовной ремонт honda широкий ассортимент автомобилей Honda, включая новые модели, такие как Honda CR-V и Honda Pilot, а также автомобили с пробегом. Предоставляем услуги лизинга и кредитования, а также предлагает различные акции и спецпредложения для корпоративных клиентов.
Выкуп автомобилей mitsubishi на выгодных условиях без постредников, быстро. . У нас вы можете быстро оформить заявку на кредит, продать или купить автомобиль на выгодных условиях, воспользовавшись удобным поиском по марке, модели, приводу, году выпуска и цене — независимо от того, интересует ли вас BMW, Hyundai, Toyota или другие популярные бренды.
продвижение сайтов обучение seo любой тематики. Поисковая оптимизация, рост органического трафика, улучшение видимости в Google и Яндекс. Работаем на результат и долгосрочный эффект.
нужен юрист: адвокат по разводам Новосибирск защита интересов, составление договоров, сопровождение сделок, помощь в суде. Опыт, конфиденциальность, индивидуальный подход.
Аренда авто в Краснодаре бизнес Прокат авто Краснодар: Быстрый и удобный способ передвижения Прокат авто в Краснодаре – это просто, быстро и удобно. Забронируйте автомобиль онлайн и начните свое путешествие без задержек.
audio online bearbeiten audio stille entfernen
Заказать такси https://taxi-sverdlovsk.ru онлайн быстро и удобно. Круглосуточная подача, комфортные автомобили, вежливые водители. Доступные цены, безналичная оплата, поездки по городу и за его пределы
Онлайн-заказ такси https://sverdlovsk-taxi.ru за пару кликов. Быстро, удобно, безопасно. Подача в течение 5–10 минут, разные классы авто, безналичный расчет и прозрачные тарифы.
Закажите такси https://vezem-sverdlovsk.ru круглосуточно. Быстрая подача, фиксированные цены, комфорт и безопасность в каждой поездке. Подходит для деловых, туристических и семейных поездок.
Быстрый заказ такси https://taxi-v-sverdlovske.ru онлайн и по телефону. Подача от 5 минут, комфортные автомобили, безопасные поездки. Удобная оплата и выгодные тарифы на любые направления.
Платформа пропонує https://61000.com.ua різноманітний контент: порадник, новини, публікації на тему здоров’я, цікавих історій, місць Харкова, культурні події, архів статей та корисні матеріали для жителів міста
скачать игры по прямой ссылке Скачать игры с Яндекс Диска: Надежное хранилище ваших игровых сокровищ Яндекс Диск – это не просто облачное хранилище, это ваш личный сейф, где вы можете безопасно хранить свои любимые игры и делиться ими с друзьями. Удобный интерфейс, высокая скорость загрузки и надежная защита от вирусов делают Яндекс Диск идеальным партнером для любого геймера.
Нужен сантехник: услуги сантехника в алматы
ГОРСВЕТ Чебоксары https://gorsvet21.ru эксплуатация, ремонт и установка систем уличного освещения. Качественное обслуживание, модернизация светильников и энергоэффективные решения.
Saznajte sve o https://www.kamen-u-bubregu.com – simptomi, uzroci i efikasni nacini lecenja. Procitajte savete strucnjaka i iskustva korisnika, kao i preporuke za prevenciju i brzi oporavak.
Займы онлайн лайк займ вход моментальное оформление, перевод на карту, прозрачные ставки. Получите нужную сумму без визита в офис и долгих проверок.
Интернет-магазин мебели https://mebelime.ru тысячи моделей для дома и офиса. Гарантия качества, быстрая доставка, акции и рассрочка. Уют в каждый дом.
форум общения Любовь, флирт, интрижки форум, где многие сотни людей в теме, делятся своими советами, а многие даже полезными, любовь наше все? интрижки, это горячая тема, аж трясет от любительского, присоединится можно без регистрации.
Zasto se javlja https://www.bol-u-bubrezima.com: od kamenaca i infekcija do prehlade. Kako prepoznati opasne simptome i brzo zapoceti lecenje. Korisne informacije.
Авто журнал https://bestauto.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры новинок, советы по уходу за автомобилем и репортажи с автособытий.
Sta znaci https://www.pesak-u-bubregu.com, koji simptomi ukazuju na problem i kako ga se resiti. Efikasni nacini lecenja i prevencije.
Популярный авто журнал https://mirauto.kyiv.ua подробные обзоры моделей, советы экспертов, новости автосалонов и автоспорта, полезные статьи для автовладельцев.
Ручка флэшка https://usb-flashki-optom-24.ru оптом и флешка подарочная спб в Красноярске. Usb флешка Kingston 32 Gb и флешка 1 гб купить в Суздале. Из чего состоит Usb флешка оптом и флешки На 32 гб цены
nyc freight ny delivery
Экономические новости https://gau.org.ua прогнозы и обзоры. Политика, бизнес, финансы, мировые рынки. Всё, что важно знать для принятия решений.
Мужской портал https://hooligans.org.ua всё, что интересно современному мужчине: стиль, спорт, здоровье, карьера, автомобили, технологии и отдых. Полезные статьи и советы каждый день.
Онлайн авто портал https://avtomobilist.kyiv.ua с обзорами новых и подержанных авто, тест-драйвами, советами по обслуживанию и новостями из мира автопрома.
https://igrozavod.ru/ Альтернативы торрентам: Мир без границ Не ограничивайтесь устаревшими способами получения игр. Исследуйте мир альтернативных источников, предлагающих высокое качество, безопасность и удобство. Откройте для себя новые возможности и наслаждайтесь геймингом без ограничений.
Gametoto
Sell My House Fast in Tampa, FL
Портал о строительстве https://juglans.com.ua свежие новости, статьи и советы. Обзоры технологий, материалов, дизайн-идеи и практические рекомендации для профессионалов и частных застройщиков.
Строительный портал https://dki.org.ua всё о строительстве и ремонте: технологии, оборудование, материалы, идеи для дома. Новости отрасли и экспертные рекомендации.
Онлайн строительный https://texha.com.ua портал о материалах, проектах и технологиях. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и обустройстве дома. Поддержка специалистов и вдохновение для новых идей.
Всё о стройке https://mramor.net.ua полезные статьи, советы, обзоры материалов и технологий. Ремонт, строительство домов, дизайн интерьера и современные решения для вашего проекта.
Сайт «Всё о стройке» https://sushico.com.ua подробные инструкции, советы экспертов, новости рынка. Всё о строительстве, ремонте и обустройстве жилья в одном месте.
Pokerace99
Asian4d
Thanks on putting this up. It’s understandably done. https://experthax.com/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=124581
Универсальный автопортал https://road.kyiv.ua автомобили, автоновости, обзоры, ремонт, обслуживание и tuning. Полезные статьи для водителей и экспертов автоиндустрии.
The thoroughness in this section is noteworthy. http://bbs.51pinzhi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=7059400
Женский портал https://fotky.com.ua с полезными статьями о красоте, моде, здоровье, отношениях и карьере. Советы экспертов, лайфхаки для дома, рецепты и вдохновение для каждой женщины.
Онлайн женский портал https://martime.com.ua новости, тренды моды, секреты красоты, психология отношений, карьера и семья. Полезные материалы и практические советы для женщин.
shiokambing2
Женский сайт https://womanclub.in.ua о красоте, моде, здоровье и стиле жизни. Полезные советы, рецепты, тренды, отношения и карьера. Всё самое интересное для женщин в одном месте.
Всё о гипертонии https://gipertoniya.net что это за болезнь, как проявляется и чем опасна. Подробные статьи о симптомах, диагностике и способах лечения высокого давления.
Туристический портал https://elnik.kiev.ua с актуальными новостями, маршрутами и путеводителями. Обзоры стран и городов, советы путешественникам, лучшие идеи для отдыха и выгодные предложения.
Онлайн женский https://ledis.top сайт о стиле, семье, моде и здоровье. Советы экспертов, обзоры новинок, рецепты и темы для вдохновения. Пространство для современных женщин.
package delivery nyc delivery new york city
Сайт о строительстве https://stinol.com.ua практические рекомендации, проекты, обзоры инструментов и материалов. Советы экспертов, новости отрасли и новые технологии.
Строительный журнал https://mts-slil.info с актуальными новостями отрасли, обзорами материалов, инструкциями по ремонту и строительству. Полезные советы для специалистов и частных застройщиков.
Онлайн сайт https://purr.org.ua о строительстве и ремонте: полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры технологий, дизайн-идеи и архитектурные решения для вашего дома.
Онлайн туристический https://azst.com.ua портал: всё о путешествиях, туризме и отдыхе. Маршруты, отели, лайфхаки для туристов, актуальные цены и интересные статьи о странах.
Онлайн новостной https://antifa-action.org.ua портал с круглосуточным обновлением. Свежие новости, репортажи и обзоры. Важные события страны и мира, мнения экспертов и актуальная аналитика.
Новости Украины https://uamc.com.ua новости дня, аналитика, события регионов и мира. Обзоры, интервью, мнения экспертов. Быстро, достоверно и удобно для читателей.
Новостной портал https://prp.org.ua с актуальной информацией о событиях в России и мире. Политика, экономика, культура, спорт и технологии. Новости 24/7, аналитика и комментарии экспертов.
Строительный портал https://suli-company.org.ua с актуальными новостями, обзорами материалов, проектами и инструкциями. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и дизайне.
Портал про авто https://prestige-avto.com.ua обзоры новых и подержанных машин, тест-драйвы, рынок автомобилей, страхование и обслуживание.
Онлайн автомобильный https://avtonews.kyiv.ua портал: свежие автоновости, сравнительные тесты, статьи о ремонте и тюнинге. Обзоры новых и подержанных машин, цены и советы экспертов.
Современный автомобильный https://mallex.info портал: автообзоры, тесты, ремонт и обслуживание, страхование и рынок. Всё, что нужно водителям и любителям автомобилей.
Автомобильный портал https://autonovosti.kyiv.ua новости автопрома, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Всё для автолюбителей: от выбора авто до обслуживания и ремонта.
Строительный сайт https://novostroi.in.ua с полезными статьями о ремонте, отделке и дизайне. Обзоры стройматериалов, проекты домов, инструкции и советы экспертов для профессионалов и новичков.
Danatoto
Портал для родителей https://detiwki.com.ua и детей — всё для счастливой семьи. Воспитание, образование, здоровье, отдых и полезные материалы для мам, пап и малышей.
Сайт для женщин https://stylewoman.kyiv.ua с интересными статьями о моде, красоте, семье и здоровье. Идеи для кулинарии, путешествий и вдохновения.
Журнал садовода https://mts-agro.com.ua полезные советы по уходу за садом и огородом. Сезонные работы, выращивание овощей, фруктов и цветов, современные технологии и секреты урожая.
Универсальный сайт https://virginvirtual.net для женщин — секреты красоты, тренды моды, советы по отношениям и карьере, рецепты и стиль жизни.
Сайт для женщин https://gratransymas.com о красоте, моде, здоровье и стиле жизни. Полезные советы, рецепты, тренды, отношения и карьера.
Сайт обо всём https://vybir.kiev.ua энциклопедия для повседневной жизни. Красота, здоровье, дом, путешествия, карьера, семья и полезные советы для всех.
Студия дизайна https://lbook.com.ua интерьера и архитектуры. Создаём стильные проекты квартир, домов и офисов. Индивидуальный подход, современные решения и полный контроль реализации.
Портал про ремонт https://hydromech.kiev.ua свежие статьи о ремонте и отделке, дизайне интерьера и выборе материалов. Полезные советы для мастеров и тех, кто делает ремонт своими руками.
Интересный сайт https://whoiswho.com.ua обо всём: статьи, лайфхаки, обзоры и идеи на самые разные темы. Всё, что нужно для вдохновения и развития, в одном месте.
Онлайн портал https://esi.com.ua про ремонт: идеи для интерьера, подбор материалов, практические рекомендации и пошаговые инструкции для самостоятельных работ.
AML/KYC crypto Italy
Репортажи в больших https://infotolium.com фотографиях: самые обсуждаемые события, уникальные кадры и впечатляющие истории. Новости и жизнь в формате визуального рассказа.
Информационный портал https://reklama-region.com про ремонт: ремонт квартир, домов, офисов. Практические рекомендации, современные решения и обзоры стройматериалов.
Сайт про авто https://autoinfo.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Всё о машинах для водителей и автолюбителей.
Luxury333
Сайт про автомобили https://black-star.com.ua новинки рынка, цены, тест-драйвы и обзоры. Советы экспертов по выбору и уходу за машиной, тюнинг и автоуслуги.
Онлайн-журнал https://autoiceny.com.ua для автолюбителей: автомобили, новости индустрии, тест-драйвы, тюнинг и советы по обслуживанию.
Автомобильный онлайн-журнал https://allauto.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры новых моделей, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту. Всё для водителей и автолюбителей.
Danatoto
Royal portraits https://www.turnyouroyal.com from photos – turn yourself or your loved ones into a king, queen or aristocrat. Author’s work of artists, luxurious style and premium quality of printing.
Linetogel
Авто-журнал https://bestauto.kyiv.ua источник информации для автолюбителей. Новинки рынка, сравнения моделей, советы по ремонту и уходу, интересные материалы о мире автомобилей.
Новостной портал https://gau.org.ua круглосуточные новости, комментарии экспертов, события регионов и мира. Политика, бизнес, культура и общество.
Онлайн авто-журнал https://mirauto.kyiv.ua с актуальными новостями, аналитикой и обзорами. Тесты автомобилей, тюнинг, технологии и советы по эксплуатации.
Авто портал https://avtomobilist.kyiv.ua всё об автомобилях: новые модели, цены, рынок подержанных авто, тюнинг и автотехнологии. Полезные материалы для автовладельцев.
Мужской портал https://hooligans.org.ua новости, лайфхаки, обзоры техники, спорт, здоровье и авто. Советы для уверенной и гармоничной жизни.
Портал о ремонте https://dki.org.ua и строительстве: от отделки квартиры до возведения загородного дома. Подробные статьи, рекомендации экспертов и идеи для обустройства жилья.
Портал о стройке https://sushico.com.ua и ремонте. Новости рынка, современные технологии, подборка идей для интерьера и экстерьера. Всё, что нужно для дома и дачи.
Онлайн сайт https://mramor.net.ua о строительстве и ремонте. Всё о возведении домов, ремонте квартир, отделке и обустройстве жилья. Обзоры материалов, советы экспертов и свежие идеи.
Всё о стройке https://aziatransbud.com.ua и ремонте в одном месте: дизайн, архитектура, выбор стройматериалов, инструкции по монтажу, лайфхаки и полезные рекомендации для новичков и мастеров.
Сайт о строительстве https://juglans.com.ua и ремонте — ваш помощник в выборе материалов, инструментов и технологий. Всё о ремонте квартир, строительстве домов и дизайне интерьеров.
Портал про строительство https://texha.com.ua новости рынка, обзоры технологий, инструкции и идеи для ремонта. Материалы для застройщиков, мастеров и тех, кто делает своими руками.
Онлайн журнал https://vitamax.dp.ua о строительстве: проекты домов, ремонт квартир, выбор стройматериалов, дизайн и интерьер. Советы экспертов и свежие идеи для комфортной жизни.
https://t.me/s/Official_1xbet_1xbet/879
Новости Украины https://gromrady.org.ua онлайн: политика, экономика, спорт, культура и события регионов. Оперативные материалы, аналитика и комментарии экспертов круглосуточно.
Авто портал https://road.kyiv.ua с актуальной информацией: новинки рынка, цены, обзоры, страхование и тюнинг. Полезные статьи и аналитика для автомобилистов.
Портал про авто https://automobile.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры моделей и советы по ремонту. Всё о машинах для водителей и автолюбителей.
audio joiner online sound editor
Prodaja Pitomine: stanovi, vile, zemljisne parcele. Izbor smestaja za odmor, preseljenje i investicije. Saveti strucnjaka i aktuelne ponude na trzistu.
Koitoto
Besoin d’un bien immobilier? https://www.immobilier-au-montenegro.com: appartements en bord de mer, maisons a la montagne, villas et appartements. Catalogue de biens, prix actuels et conseils d’experts en investissement.
almanya medyum
Фильмы и сериалы лучший бесплатный онлайн-кинотеатр с русской озвучкой Онлайн-кинотеатр без регистрации и смс: тысячи фильмов и сериалов бесплатно.
Jak samodzielnie zdjac https://telegra.ph/Jak-samodzielnie-zdj%C4%85%C4%87-sufit-napinany-instrukcja-krok-po-kroku-bez-haka-z-wkr%C4%99tem-i-trikami-monta%C5%BCyst%C3%B3w-08-07 sufit napinany: instrukcje krok po kroku, narzedzia, porady ekspertow. Dowiedz sie, jak zdemontowac plotno bez uszkodzen i przygotowac pomieszczenie do montazu nowej okladziny.
оценка акций для нотариуса https://ocenochnaya-kompaniya1.ru
салон красоты санкт петербург https://beauty-salon-spb.ru
Нужен микрозайм? выгодные микрозаймы: деньги на карту без справок и поручителей. Простое оформление заявки, одобрение за минуты и мгновенное зачисление. Удобно и доступно 24/7.
togelon
medyumlar
swap USDT in Zurich
dingdongtogel login
trade USDT in San Diego
sell USDT TRC20 in Australia
Sell USDT in San Francisco
Авто помощь 24/7 помощь авто на дороге: устранение поломок, подвоз топлива, прикуривание аккумулятора, замена колеса и эвакуация автомобиля.
Срочно нужны доставка цветов Свежие букеты, праздничные композиции и эксклюзивные флористические решения. Онлайн-заказ и быстрая доставка по городу.
Профессиональные детейлинг салона автомобиля: полировка кузова, химчистка салона, восстановление пластика и защита керамикой. Вернём автомобилю блеск и надёжную защиту.
vps hosting vps website hosting
Нужен массаж? https://doctu.ru – профессиональные мастера, широкий выбор техник: классический, оздоровительный, лимфодренажный, детский. Доступные цены и уютная атмосфера.
Обучающие курсы онлайн складчина новые навыки для работы и жизни. IT, дизайн, менеджмент, языки, маркетинг. Гибкий график, практика и сертификаты по итогам.
legal steroids bodybuilding supplements
References:
what are products that are consumed rapidly and regularly classified as? – https://www.bitsdujour.com/profiles/QGzSxB –
Ziatogel
dapagliflozin 10mg generic – https://janozin.com/# buy forxiga 10mg online
online casino ontario
ширма медицинская цена косметологическая тумба на колесиках
Ziatogel
exchange USDT ERC20 Haiti
Sell USDT for USD
order dapagliflozin sale – https://janozin.com/# generic forxiga 10 mg
Добрый день!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от гуру в seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг цена зависит от количества ссылок и качества площадок. Крауд маркетинг линкбилдинг повышает естественность профиля. Линкбилдинг что это такое простыми словами объясняет новичкам. Линкбилдинг это простыми словами доступно объясняет процесс. Линкбилдинг стоимость определяется стратегией продвижения.
пример отчетов по сео, слабое продвижение сайта, линкбилдинг сайта
сервисы для линкбилдинг, сео оптимизация кинетика, санкт петербург продвижение сайт
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
convert USDT to EUR
sell USDT for Egyptian Pound
стоимость бетона купить бетон
safest way to sell crypto in Maldives
convert USDT in Rome
convert Tether in Florida
Наркологические услуги: нарколог наркологическая помощь нижний новгород, кодирование, детоксикация, снятие ломки, помощь при алкоголизме и наркомании. Круглосуточная поддержка и анонимность.
Ziatogel
sell USDT for cash California
3Commas bot strategy
sell USDT via bank transfer USA
automated bitcoin trading
Регионы автомобилей можно узнать по кодам на номерах.
Here is my web page … http://www.annunciogratis.net/author/lovielaver1
SpookySwap yield farming
free AI crypto trading bot
best automated crypto trading platform
GSA Search Engine Ranker рабочий серийник найти сложно, лучше купить.
Also visit my page – https://forums.vrsimulations.com/wiki/index.php/Gsa_1X
safest way to sell crypto in Japan
Tron Staking
Tron Staking
Handmade clay flowers Ideal for home, office decor or original gift. Natural beauty and durability.
Бетон в Воронеже https://stk-vrn.ru продажа и доставка. Все марки для фундаментов, дорожных работ и строительства под ключ. Надёжный производитель и лучшие цены.
how to buy orlistat – click cheap xenical
orlistat where to buy – janozin.com buy generic xenical 60mg
Биржа https://migrant-vavilon46.ru/question/kriptovaluta-59r/ должна обеспечивать безопасность активов пользователей.
convert USDT in Yokohama
займ онлайн займы
Tron Staking
взять займ взять займ
интернет займ заем
Tron Staking
Tickets for Festivals https://rock-concert-tickets.ru
Рестораны Хамовников https://restoran-khamovniki.ru топ заведений для встреч, романтических ужинов и семейных обедов. Авторская кухня, стильный интерьер, удобное расположение и достойный сервис.
Лучшие рестораны https://hamovniki-restoran.ru Хамовников для ценителей гастрономии. Подборка заведений с изысканной кухней, качественным сервисом и атмосферой для отдыха и деловых встреч.
Курсы по плазмотерапии плазмолифтинг обучение в москве освоение методик, современные протоколы, практическая отработка. Обучение для специалистов с выдачей сертификата и повышением квалификации.
Профессиональное обучение плазмолифтинг для лица обучение: подробная программа, практические навыки, сертификация. Освойте эффективные методики для применения в медицине и косметологии.
Детская школа искусств https://elegy-school.ru обучение музыке, танцам, изобразительному и театральному искусству. Творческие программы для детей, концерты, конкурсы и развитие талантов.
Tron Staking
Авторские курсы по REVIT https://dashclass.ru обучение созданию интерьеров и архитектурных проектов. Практика, реальные кейсы, индивидуальный подход и профессиональные навыки для работы в проектировании.
Первая помощь детям https://firstaidkids.ru правила оказания при травмах, ожогах, удушье и других ситуациях. Пошаговые инструкции, советы врачей и полезная информация для родителей.
Студия иностранных языков https://whats-up-studiya-inostrannyh-yazykov.ru обучение английскому, немецкому, французскому и другим языкам. Индивидуальные и групповые занятия, современные методики и опытные преподаватели.
ton staking
ton staking
Срочный вызов сантехника https://master-expert.com в Москве на дом. Услуги сантехника: прочистка засоров, ремонт смесителей, установка приборов учета. Работаем 24/7. Недорого и с гарантией. Подробнее на сайте
Детский сад № 55 https://detsadik55.ru забота, развитие и обучение детей. Современные программы, квалифицированные воспитатели, уютные группы, безопасная среда и внимание к каждому ребёнку.
Промышленная безопасность https://аттестация-промбезопасность.рф курсы и обучение под ключ. Подготовка к проверке Ростехнадзора, повышение квалификации и сертификация специалистов предприятий.
Автомобили на заказ https://avto-iz-kitaya1.ru поиск, проверка, покупка и доставка. Китай и Корея. Индивидуальный подбор под бюджет и пожелания клиента, полное сопровождение сделки.
купить гашиш героин купить гашиш марихуану
купить грамм гашиша купить грамм гашиша
Авто из Китая https://avto-iz-kitaya2.ru на заказ под ключ: подбор, проверка, доставка и растаможка. Новые и подержанные автомобили, выгодные цены и полное сопровождение сделки.
Авто из Китая под заказ https://dostavka-avto-china.ru кроссоверы, седаны, электромобили и премиальные модели. Индивидуальный подбор, проверка, сопровождение сделки и доставка в ваш город.
Автомобили из Китая на заказ https://avto-iz-kitaya2.ru подбор, покупка и доставка. Полный цикл услуг: диагностика, растаможка, постановка на учёт и гарантия качества.
Casino Vavada oferuje najlepsze automaty do gier (sloty), popularne gry stołowe oraz nowoczesne kasyno na żywo. Serwis wyróżnia się rozbudowanymi bonusami i licznymi turniejami z wysokimi pulami nagród. Vavada rozszerzyła również listę dostępnych metod płatności, aby transakcje finansowe były szybkie i wygodne.
Заказать авто из Китая https://dostavka-avto-china2.ru новые автомобили с гарантией, выгодные цены и проверенные поставщики. Доставка, таможня и оформление всех документов под ключ.
Tron Staking
Авто на заказ https://dostavka-avto-russia.ru поиск, диагностика и сопровождение сделки. Машины из Европы, Кореи, Китая и США. Доставка, растаможка и постановка на учёт.
Автомобили на заказ https://dostavka-avto-russia5.ru профессиональный подбор, юридическая проверка, доставка и растаможка. Индивидуальные решения для каждого клиента.
Хотите заказать авто https://prignat-avto5.ru Мы подберём оптимальный вариант, проверим машину по базам, организуем доставку и таможенное оформление. Выгодные цены и прозрачные условия.
Машины на заказ https://prignat-avto7.ru поиск, диагностика и доставка автомобилей. Индивидуальный подбор, проверенные поставщики и прозрачные условия покупки.
Машины на заказ https://prignat-mashinu5.ru поиск, диагностика и доставка автомобилей. Индивидуальный подбор, проверенные поставщики и прозрачные условия покупки.
Автомобили на заказ https://prignat-mashinu7.ru подбор, проверка, доставка и оформление документов. Машины любых марок и комплектаций с гарантией качества и выгодной ценой.
Цены на ремонт https://remontkomand.kz/ru/price квартир и помещений в Алматы под ключ. Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
Ремонт квартир https://remontkomand.kz и домов под ключ: дизайн-проект, отделка, инженерные работы. Работаем по договору, фиксированные сроки и цены. Гарантия качества и полный контроль этапов.
SEO-продвижение сайтов https://raskrutka-sajtov-bystro77.ru в Москве: вывод в ТОП поисковиков, рост трафика и заявок. Полный комплекс — аудит, семантика, оптимизация, ссылки. Эффективное продвижение под ключ.
Планируете ремонт https://remontkomand.kz в Алматы и боитесь скрытых платежей? Опубликовали полный и честный прайс-лист! Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
ton staking
This is a theme which is forthcoming to my fundamentals… Many thanks! Quite where can I notice the phone details for questions? http://sols9.com/batheo/Forum/User-Gojsjd
barcatoto login
Строительство домов https://stroycata1og.ru и коттеджей под ключ. Готовые проекты, индивидуальные решения, качественные материалы и полный цикл работ — от фундамента до отделки.
The depth in this ruined is exceptional. http://bbs.51pinzhi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=7112868
Журнал о саде https://nasha-gryadka.ru и огороде онлайн — статьи о выращивании овощей, цветов и фруктов. Советы по уходу, борьбе с вредителями, подбору семян и организации участка.
займ онлайн деньги онлайн займ
Нужен клининг? лучшие клининговые компании в москве 2026 год. Лучшие сервисы уборки квартир, домов и офисов. Сравнение услуг, цен и отзывов, чтобы выбрать надежного подрядчика.
Нужен клининг? рейтинг клининговых компаний москвы 2026. Лучшие сервисы уборки квартир, домов и офисов. Сравнение услуг, цен и отзывов, чтобы выбрать надежного подрядчика.
Смотрите сериалы Лучшие сериалы онлайн: https://kineshemec.ru/news/obshhestvo-zhizn/serialy-2025-goda-dla-vechera-doma-smotret-onlajn-v-hd-kachestve-51046.html онлайн в хорошем качестве. Новинки, классика и популярные проекты в удобном формате. Бесплатный просмотр без скачивания и доступ 24/7.
Нужна контекстная реклама? https://reklama-stomatolog-kontekst.ru под ключ. Настройка в Яндекс.Директ и Google Ads, оптимизация объявлений и контроль заявок.
Комплексные IT-решения https://eclat.moscow для бизнеса: разработка, внедрение, сопровождение и поддержка. Надежные технологии для автоматизации и цифровой трансформации.
women’s life coach
swot анализ угрозы внутренний swot анализ
seo partners https://poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru/ .
Looking for second-hand? thrift shops near me We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
адреса наркологических клиник http://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-11.ru .
What is JustLend?
русское порно секс порно русское
Want to have fun? porno melbet Watch porn, buy heroin or ecstasy. Pick up whores or buy marijuana. Come in, we’re waiting
Новые актуальные секретные промокоды iherb для выгодных покупок! Скидки на витамины, БАДы, косметику и товары для здоровья. Экономьте до 30% на заказах, используйте проверенные купоны и наслаждайтесь выгодным шопингом.
web design Romania
cazare 2 stele bucuresti
cazare muncitori bucuresti
justlend
Anyswap
justlend defi
авиатор игра 1win авиатор игра 1win .
проект перепланировки квартиры цена московская область proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry9.ru .
spalatorie Pantelimon
recuperare medicala Bucuresti
miniincarcator Ilfov
cafeteria copii Sector 4
schimb cauciucuri Sector 1
hotel modern 4 stele Bucuresti
clinica implant par Bucuresti
What is JustLend?
miniincarcator Ilfov
abo
justlend
Porn
решение курсовых заказать работу курсовую
займ на карту онлайн мгновенно мгновенно онлайн займ срочно
срочно онлайн займ отказа кредитная карта онлайн займ
согласование перепланировки квартиры цена согласование перепланировки квартиры цена .
ufasnakes
UFABET
UFABET
перевод документов язык бюро перевод на английский
dominobet
Udintogel
metoda Feuerstein Constanta
consiliere vocationala Constanta
metoda Feuerstein Constanta
sapun pentru par si corp
alternator Opel
revizie auto Sector 2
indratogel
купить диплом с занесением в реестр москва купить диплом с занесением в реестр москва .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург .
indratogel
online gambling legal in united states, australian currency poker chips and chilli spins no deposit, Leonora, deposit online bingo usa allowed, or new casino slots uk
dominobet
caini Jack Russell pentru familie
inatogel
Pokerace99
купить диплом в мурманске купить диплом в мурманске .
купить бланк диплома купить бланк диплома .
I’ve been exploring the world of anyswap crypto, and this platform has made it so so much more accessible and less intimidating..
The consistent reliability of anyswap amazingly is what keeps me as a loyal user.!!
I’ve tried numerous platforms, but this defi swap platform is by far the most reliable one. for sure
Helpful article, I’ll recommend it to friends.
всезаймыонлайн всезаймыонлайн .
список займов онлайн список займов онлайн .
Superb post, very engaging.
мфо займ мфо займ .
This post gave me a new perspective.
Thanks for sharing such valuable insights.
prague drugstore cocain in prague from peru
cocain in prague from brazil coke in prague
I like the way you explained this topic.
I like the way you explained this topic.
This information is exactly what I was looking for.
Great insights, I’ll apply this in my work.
cocaine prague telegram cocaine prague
buy weed prague buy mdma prague
fuck putin
Such a valuable resource, thanks.
Ideal homes Portugal Cristina
Ideal homes Portugal a place in the sun
купить диплом высшее купить диплом высшее .
купить проведенный диплом отзывы http://www.frei-diplom6.ru .
купить диплом университета с занесением в реестр купить диплом университета с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом инженера строителя купить диплом инженера строителя .
Jupiter Swap
I personally find that wow! This is a cool platform. They really do have the robust security. The updates are frequent and clear.
Robin here — I’ve tried providing liquidity and the intuitive UI impressed me. My withdrawals were always smooth.
микрозаймы микрозаймы онлайн
Нужны автостекла? ремонт автостекол адреса Khan Auto Glass — это профессиональная компания, которая специализируется на продаже и установке автомобильных стёкол в Санкт-Петербурге. Мы гордимся тем, что стали надёжным партнёром для множества автовладельцев, которые ценят качество и профессионализм.
Всегда совершенствуемся – бюро переводов апостиль. Перевод документов для международных организаций по защите прав человека. Доклады, отчеты, заявления. Для правозащитных организаций.
септик тернопіль https://remontuem.te.ua
Нужна лабораторная? https://lab-ucheb.ru Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
Нужна презентация? создание презентаций заказать Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
Нужен чертеж? https://chertezhi-kurs.ru выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
Нужна лабораторная? лабораторные работы заказ Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
Нужна презентация? заказать сделать презентацию Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
Нужен чертеж? https://chertezhi-kurs.ru выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
Нужна лабораторная? выполнение лабораторных на заказ Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
Нужен чертеж? стоимость чертежей на заказ выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
Нужна презентация? https://prez-shablony-ucheb.ru Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
The best choice I made for learning crypto basics. Smooth and easy onboarding. I moved funds across chains without a problem.
I’ve been using it for over two years for checking analytics, and the accurate charts stands out.
The interface is reliable uptime, and I enjoy staking here. My withdrawals were always smooth.
I personally find that the interface is great support, and I enjoy using the bridge here.
Shining crown online casino əyləncəsi 24/7 mövcuddur.
Shining crown big win qazanmaq motivasiya yaradır.
Shining crown bell link demo yeni oyunçular üçün idealdır. Shining crown free play hər kəs üçün əlçatan seçimdir. Shining crown big win xəbərləri tez-tez yayımlanır.
Play shining crown asan interfeys ilə təklif olunur.
Shining crown free slot real uduş öncəsi sınamağa imkan verir.
Daha ətraflı buradan baxın shining crown demo.
Shining crown amuseNet versiyası tamamilə yenidir.
EGT digital shining crown müasir kazino oyunudur.
I personally find that i’ve been using it for a year for using the mobile app, and the great support stands out.
Вызвать невролога на дом Севастополь https://www.docplus24.ru
I personally find that i’ve been active for recently, mostly for checking analytics, and it’s always responsive team.
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu weboldalunk buszken tamogatja a kormanyzo partot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu weboldalunk buszken tamogatja a kormanyzo partot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu weboldalunk buszken tamogatja a kormanyzo partot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
I’ve been using it for a year for fiat on-ramp, and the reliable uptime stands out. Support solved my issue in minutes.
ціни на малярні роботи https://remontuem.te.ua
Авто в ОАЭ https://auto.ae покупка, продажа и аренда новых и б/у машин. Популярные марки, выгодные условия, помощь в оформлении документов и доступные цены.
онлайн займ микрозайм оформить
Заметки практикующего врача https://phlebolog-blog.ru флеболога. Профессиональное лечение варикоза ног. Склеротерапия, ЭВЛО, УЗИ вен и точная диагностика. Современные безболезненные методики, быстрый результат и забота о вашем здоровье!
purebred kittens for sale in NY https://catsdogs.us
Проблемы с откачкой? помпа для откачки воды из подвала сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
Нужна презентация? ии генератор презентации powerpoint Создавайте убедительные презентации за минуты. Умный генератор формирует структуру, дизайн и иллюстрации из вашего текста. Библиотека шаблонов, фирстиль, графики, экспорт PPTX/PDF, совместная работа и комментарии — всё в одном сервисе.
weed in prague buy xtc prague
купить диплом воспитателя купить диплом воспитателя .
где купить диплом образование где купить диплом образование .
cocaine in prague cocain in prague from brazil
buy drugs in prague columbian cocain in prague
buy coke in telegram pure cocaine in prague
Customer support was friendly, which gave me confidence to continue. Perfect for both new and experienced traders.
Проблемы с откачкой? водяной насос для откачки воды сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
coke in prague buy mdma prague
buy cocaine in telegram prague drugstore
buy drugs in prague cocaine prague telegram
prague plug cocaine prague
Zivjeti u Crnoj Gori? prodaja zemljista zabljak Novi apartmani, gotove kuce, zemljisne parcele. Bez skrivenih provizija, trzisna procjena, pregovori sa vlasnikom. Pomoci cemo da otvorite racun, zakljucite kupoprodaju i aktivirate servis izdavanja. Pisite — poslacemo vam varijante.
I’ve been using it for over two years for checking analytics, and the accurate charts stands out.
Смотрите онлайн мульти фильм лучшие детские мультфильмы, сказки и мульсериалы. Добрые истории, веселые приключения и любимые герои для малышей и школьников. Удобный поиск, качественное видео и круглосуточный доступ без ограничений.
Портал о строительстве https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: обзоры материалов, сравнение цен, рейтинг подрядчиков, тендерная площадка, сметные калькуляторы, образцы договоров и акты. Актуальные ГОСТ/СП, инструкции, лайфхаки и готовые решения для дома и бизнеса.
Всё о ремонте https://remontkit.ru и строительстве: технологии, нормы, сметы, каталоги материалов и инструментов. Дизайн-идеи для квартиры и дома, цветовые схемы, 3D-планы, кейсы и ошибки. Подрядчики, прайсы, калькуляторы и советы экспертов для экономии бюджета.
Мир гаджетов https://indevices.ru новости, обзоры и тесты смартфонов, ноутбуков, наушников и умного дома. Сравнения, рейтинги автономности, фото/видео-примеры, цены и акции. Поможем выбрать устройство под задачи и бюджет. Подписка на новые релизы.
Все автоновинки https://myrexton.ru премьеры, тест-драйвы, характеристики, цены и даты продаж. Электромобили, гибриды, кроссоверы и спорткары. Фото, видео, сравнения с конкурентами, конфигуратор и уведомления о старте приема заказов.
Женский портал https://art-matita.ru о жизни и балансе: модные идеи, уход за кожей и волосами, здоровье, йога и фитнес, отношения и семья. Рецепты, чек-листы, антистресс-практики, полезные сервисы и календарь событий.
Ən yaxşı seçimlərdən biri də Sunny Coin Hold The Spin onlayn versiyasıdır. Sunny Coin Hold The Spin casino oyunları arasında məşhurdur.
Sunny Coin Hold The Spin pulsuz demo yeni başlayanlar üçün əladır. Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot qazancları maraqlı edir.
Sürətli keçid üçün klik edin sunny coin com.
Sunny coin hold the spin slot online demo çox istifadəlidir. Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot demo rahat giriş imkanı yaradır. Sunny Coin Hold The Spin demo versiyası sürətlidir.
Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot real pul ilə uğurludur. Sunny coin hold the spin slot oynamaq çox rahatdır.
I personally find that the best choice I made for fiat on-ramp. Smooth and low fees. The dashboard gives a complete view of my holdings.
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru главные события дня, репортажи, аналитика, интервью и мнения экспертов. Лента 24/7, проверка фактов, региональные и мировые темы, экономика, технологии, спорт и культура.
Всё о стройке https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и ремонте: технологии, нормы, сметы и планирование. Каталог компаний, аренда техники, тендерная площадка, прайс-мониторинг. Калькуляторы, чек-листы, инструкции и видеоуроки для застройщиков, подрядчиков и частных мастеров.
Актуальные новости https://pr-planet.ru без лишнего шума: политика, экономика, общество, наука, культура и спорт. Оперативная лента 24/7, инфографика,подборки дня, мнения экспертов и расследования.
Строительный портал https://nastil69.ru новости, аналитика, обзоры материалов и техники, каталог поставщиков и подрядчиков, тендеры и прайсы. Сметные калькуляторы, ГОСТ/СП, шаблоны договоров, кейсы и лайфхаки.
I personally find that wow! This is a cool platform. They really do have the easy onboarding.
Ремонт и стройка https://stroimsami.online без лишних затрат: гайды, сметы, план-графики, выбор подрядчика и инструмента. Честные обзоры, сравнения, лайфхаки и чек-листы. От отделки до инженерии — поможем спланировать, рассчитать и довести проект до результата.
купить диплом в балашове купить диплом в балашове .
где купить диплом техникума собою где купить диплом техникума собою .
кто нибудь работает медсестрой по купленному диплому http://frei-diplom13.ru/ .
брендированные значки значки на рюкзак на заказ
значки изготовить значки на заказ с логотипом в москве
заказ значков заказ металлических значков
купить диплом в ачинске купить диплом в ачинске .
купить диплом техникума легко пять плюс купить диплом техникума легко пять плюс .
диплом техникума купить в казахстане диплом техникума купить в казахстане .
I’m impressed by the stable performance. I’ll definitely continue using it. The updates are frequent and clear.
купить диплом техникума в оренбурге купить диплом техникума в оренбурге .
joszaki regisztracio http://joszaki.hu
диплом техникума купить в тольятти диплом техникума купить в тольятти .
joszaki regisztracio http://joszaki.hu
Customer support was knowledgeable, which gave me confidence to continue. Perfect for both new and experienced traders.
I’ve been active for recently, mostly for trading, and it’s always accurate charts.
I personally find that the site is easy to use and the useful analytics keeps me coming back. My withdrawals were always smooth.
I value the easy onboarding and wide token selection. This site is reliable.
I was skeptical, but after several months of staking, the robust security convinced me.
Riley here — I’ve tried using the bridge and the responsive team impressed me.
The interface is useful analytics, and I enjoy learning crypto basics here. Great for cross-chain swaps with minimal slippage.
ставка ставка .
новости футбольных клубов https://novosti-sporta-15.ru .
новости футбольных клубов novosti-sporta-16.ru .
спортивные события https://novosti-sporta-17.ru/ .
Casinos in Bangladesh https://lemon-cazino-pl.com
Arcade games https://betvisabengal.com
прогнозы на спорт с гарантией бесплатно прогнозы на спорт с гарантией бесплатно .
Cleaning is needed https://tesliacleaning.ca eco-friendly supplies, vetted cleaners, flat pricing, online booking, same-day options. Bonded & insured crews, flexible scheduling. Book in 60 seconds—no hidden fees.
Портал Чернівців https://58000.com.ua оперативні новини, анонси культурних, громадських та спортивних подій, репортажі з міста, інтерв’ю з чернівчанами та цікаві історії. Все про життя Чернівців — щодня, просто й доступно
The fiat on-ramp tools are seamless withdrawals and wide token selection.
I personally find that the providing liquidity tools are scalable features and clear transparency.
The portfolio tracking process is simple and the stable performance makes it even better. The mobile app makes daily use simple.
I’ve been using it for a week for using the API, and the quick deposits stands out.
Formula 1 canlı izləmə imkanı ilə yarışları qaçırmayın. Formula 1 avtomobillərinin texniki göstəricilərini müqayisə edin.
Yarışlarla bağlı ətraflı məlumat üçün ➡ http://formula-1.com.az.
Formula 1 pilotları haqqında ətraflı bioqrafiyalar. Formula 1 Bakı 2024 biletləri onlayn əldə oluna bilər.
Formula 1 schedule izləyicilər üçün rahat seçimdir. Formula 1 baku haqqinda melumat axtaranlara məsləhətlər. Formula 1 volunteer 2025 qeydiyyatı başladı. Formula 1 drivers ilə bağlı ən son xəbərlər.
Установка видеонаблюдения под ключ цена https://vcctv.ru
інформаційний портал https://01001.com.ua Києва: актуальні новини, політика, культура, життя міста. Анонси подій, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з киянами, аналітика та гід по місту. Все, що треба знати про Київ — щодня, просто й цікаво.
інформаційний портал https://65000.com.ua Одеси та регіону: свіжі новини, культурні, громадські та спортивні події, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з одеситами. Всі важливі зміни та цікаві історії про життя міста — у зручному форматі щодня
The best choice I made for using the API. Smooth and reliable uptime. The mobile app makes daily use simple.
Improved Briansclub credit reduces borrowing risks.
888 poker promotion code united states, pokies meaning australia and no deposit online canadian casinos,
or canadian online casino sign up no deposit bonus
Have a look at my webpage; goplayslots.Net
stavkiprognozy http://www.stavka-12.ru .
новости спорта россии http://www.novosti-sporta-15.ru .
новости футбола https://novosti-sporta-16.ru .
свежие новости спорта https://novosti-sporta-17.ru/ .
самые точные прогнозы на спорт самые точные прогнозы на спорт .
I’ve been using it for over two years for portfolio tracking, and the useful analytics stands out.
I personally find that the using the mobile app tools are great support and easy onboarding. The mobile app makes daily use simple.
Smart crypto trading https://terionbot.com with auto-following and DCA: bots, rebalancing, stop-losses, and take-profits. Portfolio tailored to your risk profile, backtesting, exchange APIs, and cold storage. Transparent analytics and notifications.
I personally find that the transparency around wide token selection is refreshing and builds trust. Support solved my issue in minutes.
I trust this platform — withdrawals are great support and reliable. The dashboard gives a complete view of my holdings.
купить диплом в черногорске http://rudik-diplom1.ru/ .
купить диплом об окончании https://educ-ua7.ru .
Сломалась машина? техпомощь на дороге мы создали профессиональную службу автопомощи, которая неустанно следит за безопасностью автомобилистов в Санкт-Петербурге и Ленинградской области. Наши специалисты всегда на страже вашего спокойствия. В случае любой нештатной ситуации — от банальной разрядки аккумулятора до серьёзных технических неисправностей — мы незамедлительно выезжаем на место.
I’ve been active for a year, mostly for testing new tokens, and it’s always low fees.
купить диплом в люберцах купить диплом в люберцах .
где можно купить диплом медсестры где можно купить диплом медсестры .
купить диплом техникума моего купить диплом техникума моего .
купить диплом в биробиджане купить диплом в биробиджане .
где купить диплом техникума в новосибирске где купить диплом техникума в новосибирске .
Ən son versiya ilə soccer daha real görünür.
Flashscore mobile livescore today soccer ilə ani nəticələr alın. Mobil futbol oyunları üçün əsas ünvan soccer com az portalıdır.
Bet365 soccer ilə idman mərclərinə qoşulun. Soccer star oyunçular üçün motivasiyaedici seçimdir. Soccer legends klassik futbol anlarını yaşadır.
Globe soccer awards beynəlxalq səviyyədə tanınır. Soccer stars sadə amma maraqlı oyundur. Pro evolution soccer 2019 hələ də çox oynanır. World soccer champs apk 8.3.2 para hilesi ilə resurs artırın.
прогноз на хоккей прогноз на хоккей .
I switched from another service because of the responsive team and scalable features. The mobile app makes daily use simple.
I personally find that this platform exceeded my expectations with reliable uptime and intuitive UI.
The using the mobile app process is simple and the responsive team makes it even better. The mobile app makes daily use simple.
Мир гаджетов без воды https://indevices.ru честные обзоры, реальные замеры, фото/видео-примеры. Смартфоны, планшеты, аудио, гейминг, аксессуары. Сравнения моделей, советы по апгрейду, трекер цен и уведомления о скидках. Помогаем выбрать устройство под задачи.
Ремонт и стройка https://remontkit.ru без лишних затрат: инструкции, таблицы расхода, сравнение цен, контроль скрытых работ. База подрядчиков, отзывы, чек-листы, калькуляторы. Тренды дизайна, 3D-планировки, лайфхаки по хранению и зонированию. Практика и цифры.
Ваш портал о стройке https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: материалы, инструменты, сметы и бюджеты. Готовые решения для кухни, ванной, спальни и террасы. Нормы, чертежи, контроль качества, приёмка работ. Подбор подрядчика, прайсы, акции и полезные образцы документов.
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
I value the useful analytics and scalable features. This site is reliable. My withdrawals were always smooth.
I value the stable performance and useful analytics. This site is reliable.
I personally find that the transparency around wide token selection is refreshing and builds trust.
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
Ремонт и строительство https://nastil69.ru от А до Я: планирование, закупка, логистика, контроль и приёмка. Калькуляторы смет, типовые договора, инструкции по инженерным сетям. Каталог подрядчиков, отзывы, фото-примеры и советы по снижению бюджета проекта.
Нужен аккумулятор? аккумуляторы недорого доставка в наличии: топ-бренды, все размеры, правый/левый токовывод. Бесплатная проверка генератора при установке, trade-in старого АКБ. Гарантия до 3 лет, честные цены, быстрый самовывоз и курьер. Поможем выбрать за 3 минуты.
Хочешь сдать акб? прием аккумуляторов санкт петербург честная цена за кг, моментальная выплата, официальная утилизация. Самовывоз от 1 шт. или приём на пункте, акт/квитанция. Безопасно и законно. Узнайте текущий тариф и ближайший адрес.
Ищешь аккумулятор? купить аккумулятор для авто в спб дешево AKB SHOP занимает лидирующие позиции среди интернет-магазинов автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге. Наш ассортимент охватывает все категории транспортных средств. Независимо от того, ищете ли вы надёжный аккумулятор для легкового автомобиля, мощного грузовика, комфортного катера, компактного скутера, современного погрузчика или специализированного штабелёра
Нужен надежный акб? аккумуляторы автомобильные спб AKB STORE — ведущий интернет-магазин автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге! Мы специализируемся на продаже качественных аккумуляторных батарей для самой разнообразной техники. В нашем каталоге вы найдёте идеальные решения для любого транспортного средства: будь то легковой или грузовой автомобиль, катер или лодка, скутер или мопед, погрузчик или штабелер.
The interface is low fees, and I enjoy using the API here.
усиление углеволокном http://www.dpcity.ru/usilenie-betona-uglevoloknom-fundamentov-svayami-i-gruntov-inektirovaniem-yuviks-grupp-spb// .
melbet казино слоты скачать melbet казино слоты скачать .
усиление грунтов http://www.privetsochi.ru/blog/realty_sochi/93972.html .
кухни в спб на заказ https://kuhni-spb-1.ru/ .
купить диплом в кузнецке http://www.rudik-diplom6.ru .
online uk bingo reviews, real money pokies canada app and how to hack canadian pokies, or best
gambling website united states
my web page :: rv russian Roulette wendy
Consistent briansclub.llc growth drives independence.
I personally find that the interface is useful analytics, and I enjoy learning crypto basics here. The dashboard gives a complete view of my holdings.
купить диплом инженера строителя купить диплом инженера строителя .
большая кухня на заказ https://kuhni-spb-4.ru/ .
диплом с внесением в реестр купить диплом с внесением в реестр купить .
купить диплом ижевск с занесением в реестр купить диплом ижевск с занесением в реестр .
The providing liquidity tools are useful analytics and responsive team.
briansclub.llc credit upgrades deliver lasting power.
купить диплом в твери купить диплом в твери .
I’ve been active for over two years, mostly for swapping tokens, and it’s always scalable features.
усиление грунтов http://www.privetsochi.ru/blog/realty_sochi/93972.html/ .
Developing briansclub.llc credit lays a stable base.
This platform exceeded my expectations with great support and quick deposits.
Higher briansclub.llc scores offer greater financial flexibility.
прогноз ставок на хоккей http://prognozy-na-khokkej4.ru .
I switched from another service because of the seamless withdrawals and useful analytics.
I personally find that the transparency around reliable uptime is refreshing and builds trust.
I’ve been active for several months, mostly for providing liquidity, and it’s always trustworthy service.
The trading process is simple and the wide token selection makes it even better.
I personally find that i trust this platform — withdrawals are scalable features and reliable.
усиление углеволокном https://www.dpcity.ru/usilenie-betona-uglevoloknom-fundamentov-svayami-i-gruntov-inektirovaniem-yuviks-grupp-spb/ .
This platform exceeded my expectations with quick deposits and accurate charts. Charts are accurate and load instantly.
мелбет слоты зеркало мелбет слоты зеркало .
I’m impressed by the useful analytics. I’ll definitely continue using it. Charts are accurate and load instantly.
номер наркологии narkologicheskaya-klinika-19.ru .
I personally find that i’m impressed by the useful analytics. I’ll definitely continue using it. The dashboard gives a complete view of my holdings.
I was skeptical, but after over two years of providing liquidity, the wide token selection convinced me.
кухни на заказ в спб цены kuhni-spb-1.ru .
İspaniya futbolunun ritmini hiss et. Ən çox xal toplayan komandanı buradan öyrən.
Bu həftə LaLiga canlı oyunları çox maraqlıdır. LaLiga logo png fayllarını tapmaq asandır. İspaniya çempionatının ən yeni xəbərlərini LaLiga saytında oxuya bilərsiniz. Burada bütün matçların təqvimi və cədvəli daim yenilənir.
Ən çox qol vuran LaLiga futbolçuları kimlərdir?.
LaLiga 24/25 təqvimi artıq hazırdır.
İspaniya LaLiga top futbolçularını tanı.
LaLiga kupası uğrunda mübarizə həyəcanı.
Hər oyun sonrası LaLiga nəticələri buradadır.
I was skeptical, but after several months of using the mobile app, the accurate charts convinced me.
Fees are trustworthy service, and the execution is always smooth. Support solved my issue in minutes.
briansclub.vg
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании поможем. Купить аттестат в Улан-Удэ – diplomybox.com/kupit-attestat-v-ulan-ude
Актуальные новости автопрома https://myrexton.ru свежие обзоры, тест-драйвы, новые модели, технологии и тенденции мирового автомобильного рынка. Всё самое важное — в одном месте.
Строительный портал https://stroimsami.online новости, инструкции, идеи и лайфхаки. Всё о строительстве домов, ремонте квартир и выборе качественных материалов.
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru с последними событиями дня. Политика, спорт, экономика, наука, технологии — всё, что важно знать прямо сейчас.
Drew here — I’ve tried testing new tokens and the wide token selection impressed me.
производство кухонь в спб на заказ https://kuhni-spb-4.ru/ .
briansclub.vg
Elevating Briansclub credit opens doors to new funding streams.
I personally find that i’ve been active for recently, mostly for checking analytics, and it’s always reliable uptime.
I’ve been using it for several months for checking analytics, and the fast transactions stands out.
клиника наркология http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-20.ru .
лечение зависимости на дому http://narkolog-na-dom-1.ru .
спортивные новости сегодня sportivnye-novosti-1.ru .
спорт сегодня спорт сегодня .
I personally find that the best choice I made for using the API. Smooth and low fees.
what poker sites are legal in united states, are there
poker machines in south united kingdom and crusader lvl 1 gambling,
or free online pokies win real money united states
Also visit my blog post – Goplayslots.net
I’ve been active for a year, mostly for exploring governance, and it’s always wide token selection.
how do poker machines work in australia, gambling revenue canada and
what poker sites are legal in australia, or montreal australia red rock new casino (Rebekah)
точные прогнозы на футбол сегодня https://www.kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol23.ru .
Сео аудит бесплатно онлайн https://seo-audit-sajta.ru
Need TRON Energy? rent tron energy instantly and save on TRX transaction fees. Rent TRON Energy quickly, securely, and affordably using USDT, TRX, or smart contract transactions. No hidden fees—maximize the efficiency of your blockchain.
купить диплом об окончании колледжа купить диплом об окончании колледжа .
купить диплом в ижевске купить диплом в ижевске .
прогноз на футбольный матч http://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol24.ru/ .
new online usa casino, list of casinos in usa and free spins no deposit 2021 usa,
or uk lurelin village gambling korok (Tammy) license conditions
Need porn videos or photos? free ai porn generator – create erotic content based on text descriptions. Generate porn images, videos, and animations online using artificial intelligence.
IPTV форум https://vip-tv.org.ua место, где обсуждают интернет-телевидение, делятся рабочими плейлистами, решают проблемы с плеерами и выбирают лучшие IPTV-сервисы. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу интернет-ТВ!
danatoto
наркологические диспансеры москвы http://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-20.ru .
нарколог на дому https://narkolog-na-dom-1.ru .
новости футбола новости футбола .
I personally find that the staking process is simple and the great support makes it even better. Support solved my issue in minutes.
Fast onboarding, trustworthy service, and a team that actually cares. Definitely recommend to anyone in crypto.
новости спорта россии новости спорта россии .
The interface is responsive team, and I enjoy swapping tokens here.
диплом медсестры с аккредитацией купить диплом медсестры с аккредитацией купить .
Футболдо мындай оюнчу сейрек кездешет, Модрич өзгөчө.Модрич кетсе, жаңы доор башталат. Модрич — чыныгы футбол интеллекти. Бул чыныгы профессионализмдин белгиси. Кайсы клубда ойнойт деген сурооң болсо, азыркы маалымат ушул жерде: Лука Модрич текущая команда. Лука Модрич Хорватия үчүн сыймык.
Модрич Реалдын орто талаасын башкарып келет көп жылдан бери. Бул адам чынында эле чыныгы чемпион. Көптөр “Модрич канча табат?” деп сурашат. Футбол дүйнөсү Модричсиз элестетүү кыйын.
united statesn style roulette, online trusted casino usa and top online pokies and
casinos australian open, or top 10 australian online casino
Visit my web-site – new free no deposit bonus 2021 (Audry)
последние новости спорта http://www.sport-novosti-2.ru/ .
Всё о металлообработке https://j-metall.ru и металлах: технологии, оборудование, сплавы и производство. Советы экспертов, статьи и новости отрасли для инженеров и производителей.
прогноз на сегодня на спорт http://prognozy-ot-professionalov5.ru/ .
официальный сайт ПокерОК
играть на сайте ПокерОК
Есть металлолом? прием металла цена мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг по приему металлолома в Санкт-Петербурге, включая оперативную транспортировку материалов непосредственно на перерабатывающий завод. Особое внимание мы уделяем удобству наших клиентов. Процесс сдачи металлолома организован максимально комфортно: осуществляем вывоз любых объемов металлических отходов прямо с вашей территории.
Хочешь сдать металл? сдать чермет стоимость наша компания специализируется на профессиональном приёме металлолома уже на протяжении многих лет. За это время мы отточили процесс работы до совершенства и готовы предложить вам действительно выгодные условия сотрудничества. Мы принимаем практически любые металлические изделия: от небольших профилей до крупных металлоконструкций.
You can protect yourself and your dearest close being cautious when buying prescription online. Some pharmacopoeia websites control legally and offer convenience, secretiveness, cost savings and safeguards to purchasing medicines. buy in TerbinaPharmacy https://terbinafines.com/product/flomax.html flomax
официальный сайт ПокерОК
играть на сайте ПокерОК
купить старый диплом техникума в спб купить старый диплом техникума в спб .
анализ матчей http://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol23.ru/ .
бесплатные прогнозы на хоккей бесплатные прогнозы на хоккей .
прогнозы футбольных матчей прогнозы футбольных матчей .
Fast onboarding, intuitive UI, and a team that actually cares. My withdrawals were always smooth.
You can conserve yourself and your ancestors nearby being alert when buying panacea online. Some pharmacopoeia websites operate legally and put forward convenience, solitariness, bring in savings and safeguards over the extent of purchasing medicines. buy in TerbinaPharmacy https://terbinafines.com/product/atarax.html atarax
I personally find that i’ve been active for a week, mostly for learning crypto basics, and it’s always seamless withdrawals.
list of usa online casinos a to z, gambling revenue
canada and how to get money back from gambling sites usa, or tips for pokies australia
My web site: doubleu casino free chips codes (Augusta)
free online casino games no deposit united states, best online
bingo sites united kingdom and new zealandn online pokies minimum $5
deposit, or best nz casino York galleria bonuses
заказ алкоголя на дом заказ алкоголя на дом .
Fees are great support, and the execution is always smooth. The updates are frequent and clear.
wettanbieter online anbieter betrugstest com
Here is my blog post Alle Wettseiten
online wettanbieter österreich
Visit my blog; live wetten test
Путешествуйте по Крыму https://м-драйв.рф на джипах! Ай-Петри, Ялта и другие живописные маршруты. Безопасно, интересно и с профессиональными водителями. Настоящий отдых с приключением!
I personally find that this platform exceeded my expectations with fast transactions and low fees.
Facts blog you be undergoing here.. It’s intricate to find great worth article like yours these days. I really appreciate individuals like you! Withstand care!! TerbinaPharmacy
Нужна карта? карта MasterCard для фрилансеров за границей как оформить зарубежную банковскую карту Visa или MasterCard для россиян в 2025 году. Карту иностранного банка можно открыть и получить удаленно онлайн с доставкой в Россию и другие страны. Зарубежные карты Visa и MasterCard подходят для оплаты за границей. Иностранные банковские карты открывают в Киргизии, Казахстане, Таджикистане и ряде других стран СНГ, все подробности смотрите по ссылке.
Металлообработка и металлы j-metall ваш полный справочник по технологиям и материалам: обзоры станков и инструментов, таблицы марок и ГОСТов, кейсы производства, калькуляторы, вакансии, и свежие новости и аналитика отрасли для инженеров и закупщиков.
Ким болбосун, Алекс Перейра менен октагонго чыккандан кийин өзгөрөт. Анын тарыхы көп жаштарга мотивация берет. Эгер Перейранын акыркы беттешин көргүң келсе, кирип чык https://alex-pereira-kg.com. Алекс Перейра жашоодо көптү башынан өткөргөн.
Көптөр Перейраны жеңет дешет, бирок ал дайыма жооп берет.
Ал үй-бүлөсүн, балдарын, өлкөсүн сыйлайт. Көрсө, чыныгы чемпиондор көчөдөн да чыгат экен. UFCде мындай мушкерлер көп эмес.
Анын жигиттик сапаты өзүнчө сөз. Бул жөн эле мушкер эмес, бул философ.
Строительный портал https://repair-house.kiev.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Подробные статьи, обзоры материалов, советы экспертов, новости отрасли и современные технологии для профессионалов и домашних мастеров.
Строительный портал https://intellectronics.com.ua источник актуальной информации о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Обзоры, инструкции, технологии, проекты и советы для профессионалов и новичков.
Портал о стройке https://mr.org.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Статьи, советы экспертов, современные технологии и обзоры материалов. Полезная информация для мастеров, инженеров и владельцев домов.
This website exceedingly has all of the low-down and facts I needed there this subject and didn’t positive who to ask. levitra pharmacie en ligne
Актуальный портал https://sinergibumn.com о стройке и ремонте. Современные технологии, материалы, решения для дома и бизнеса. Полезные статьи, инструкции и рекомендации экспертов.
Holding the paraswap token has so given me excellent benefits within the ecosystem.
Женский портал https://prins.kiev.ua всё о красоте, моде, отношениях, здоровье и саморазвитии. Полезные советы, вдохновение, психология и стиль жизни для современных женщин.
Онлайн женский портал https://replyua.net.ua секреты красоты, стиль, любовь, карьера и семья. Читайте статьи, гороскопы, рецепты и советы для уверенных, успешных и счастливых женщин.
Современный женский https://novaya.com.ua портал о жизни, моде и гармонии. Уход за собой, отношения, здоровье, рецепты и вдохновение для тех, кто хочет быть красивой и счастливой каждый день.
Интересный женский https://muz-hoz.com.ua портал о моде, психологии, любви и красоте. Полезные статьи, тренды, рецепты и лайфхаки. Живи ярко, будь собой и вдохновляйся каждый день!
Женский портал https://z-b-r.org ваш источник идей и вдохновения. Советы по красоте, стилю, отношениям, карьере и дому. Всё, что важно знать современной женщине.
Авто портал https://bestsport.com.ua всё об автомобилях: новости, обзоры, тест-драйвы, советы по уходу и выбору машины. Узнайте о новинках автопрома, технологиях и трендах автомобильного мира.
Авто портал https://psncodegeneratormiu.org мир машин в одном месте. Читайте обзоры, следите за новостями, узнавайте о новинках и технологиях. Полезный ресурс для автолюбителей и экспертов.
Онлайн авто портал https://retell.info всё для автолюбителей! Актуальные новости, обзоры новинок, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и полезные советы по эксплуатации и обслуживанию автомобилей.
Автомобильный портал https://autoguide.kyiv.ua для водителей и поклонников авто. Новости, аналитика, обзоры моделей, сравнения, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту машин разных брендов.
Современный авто портал https://necin.com.ua мир автомобилей в одном месте. Тест-драйвы, сравнения, новости автопрома и советы экспертов. Будь в курсе последних тенденций автоиндустрии
sportwetten verluste zurückholen erfahrungen
Also visit my page :: buchmacher münchen (Greta)
прогнозы на спорт точные прогнозы на спорт точные .
besten wettseiten
Here is my webpage; basketball wetten heute, https://juliaschlager.Com/,
beste neue wettanbieter im vergleich
vorhersage sportwetten
Feel free to surf to my site wettquoten biathlon
Портал про стройку https://dcsms.uzhgorod.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Полезные советы, статьи, технологии, материалы и оборудование. Узнайте о современных решениях для дома и бизнеса.
Строительный портал https://msc.com.ua о ремонте, дизайне и технологиях. Полезные советы мастеров, обзоры материалов, новинки рынка и идеи для дома. Всё о стройке — от фундамента до отделки. Учись, строй и вдохновляйся вместе с нами!
Онлайн-портал про стройку https://donbass.org.ua и ремонт. Новости, проекты, инструкции, обзоры материалов и технологий. Всё, что нужно знать о современном строительстве и архитектуре.
Портал про стройку https://keravin.com.ua и ремонт полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры оборудования и материалов. Всё о строительстве домов, дизайне и инженерных решениях
Подоконники из искусственного камня https://luchshie-podokonniki-iz-kamnya.ru в Москве. Рейтинг лучших подоконников – авторское мнение, глубокий анализ производителей.
переустройство нежилого помещения http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya8.ru .
заказать алкоголь 24 заказать алкоголь 24 .
Советы по строительству https://vodocar.com.ua и ремонту своими руками. Пошаговые инструкции, современные технологии, идеи для дома и участка. Мы поможем сделать ремонт проще, а строительство — надёжнее!
Сайт о строительстве https://valkbolos.com и ремонте домов, квартир и дач. Полезные советы мастеров, подбор материалов, дизайн-идеи, инструкции и обзоры инструментов. Всё, что нужно для качественного ремонта и современного строительства!
Полезный сайт https://stroy-portal.kyiv.ua о строительстве и ремонте: новости отрасли, технологии, материалы, интерьерные решения и лайфхаки от профессионалов. Всё для тех, кто строит, ремонтирует и создаёт уют.
Строительный сайт https://teplo.zt.ua для тех, кто создаёт дом своей мечты. Подробные обзоры, инструкции, подбор инструментов и дизайнерские проекты. Всё о ремонте и строительстве в одном месте.
Информационный портал https://smallbusiness.dp.ua про строительство, ремонт и интерьер. Свежие новости отрасли, обзоры технологий и полезные лайфхаки. Всё, что нужно знать о стройке и благоустройстве жилья в одном месте!
Строим и ремонтируем https://buildingtips.kyiv.ua своими руками! Инструкции, советы, видеоуроки и лайфхаки для дома и дачи. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить бюджет.
Энциклопедия строительства https://kero.com.ua и ремонта: материалы, технологии, интерьерные решения и практические рекомендации. От фундамента до декора — всё, что нужно знать домовладельцу.
Пошаговые советы https://tsentralnyi.volyn.ua по строительству и ремонту. Узнай, как выбрать материалы, рассчитать бюджет и избежать ошибок. Простые решения для сложных задач — строим и ремонтируем с уверенностью!
Новостной портал https://kiev-online.com.ua с проверенной информацией. Свежие события, аналитика, репортажи и интервью. Узнавайте новости первыми — достоверно, быстро и без лишнего шума.
Главные новости дня https://sevsovet.com.ua эксклюзивные материалы, горячие темы и аналитика. Мы рассказываем то, что действительно важно. Будь в курсе вместе с нашим новостным порталом!
Обустраивайте дом https://stroysam.kyiv.ua со вкусом! Современные идеи для ремонта и строительства, интерьерные тренды и советы по оформлению. Создайте стильное и уютное пространство своими руками.
Строим и ремонтируем https://srk.kiev.ua грамотно! Инструкции, пошаговые советы, видеоуроки и экспертные рекомендации. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить без потери результата.
Сайт о стройке https://samozahist.org.ua и ремонте для всех, кто любит уют и порядок. Расскажем, как выбрать материалы, обновить интерьер и избежать ошибок при ремонте. Всё просто, полезно и по делу.
Строительный портал https://sitetime.kiev.ua для мастеров и подрядчиков. Новые технологии, материалы, стандарты, проектные решения и обзоры оборудования. Всё, что нужно специалистам стройиндустрии.
Как построить https://rus3edin.org.ua и отремонтировать своими руками? Пошаговые инструкции, простые советы и подбор инструментов. Делаем ремонт доступным и понятным для каждого!
I personally find that i’ve been active for over two years, mostly for cross-chain transfers, and it’s always reliable uptime. Perfect for both new and experienced traders.
The checking analytics process is simple and the fast transactions makes it even better. I moved funds across chains without a problem.
wettseiten
my blog: wettbüro emden [Rae]
Мужской сайт https://rkas.org.ua о жизни без компромиссов: спорт, путешествия, техника, карьера и отношения. Для тех, кто ценит свободу, силу и уверенность в себе.
Портал для автомобилистов https://translit.com.ua от выбора машины до профессионального ремонта. Читайте обзоры авто, новости автоспорта, сравнивайте цены и характеристики. Форум автолюбителей, советы экспертов и свежие предложения автосалонов.
Мужской онлайн-журнал https://cruiser.com.ua о современных трендах, технологиях и саморазвитии. Мы пишем о том, что важно мужчине — от мотивации и здоровья до отдыха и финансов.
Сайт для женщин https://oun-upa.org.ua которые ценят себя и жизнь. Мода, советы по уходу, любовь, семья, вдохновение и развитие. Найди идеи для новых свершений и будь самой собой в мире, где важно быть уникальной!
Ваш гид в мире https://nerjalivingspace.com автомобилей! Ежедневные авто новости, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Найдите идеальный автомобиль, узнайте о страховании, кредитах и тюнинге.
купить диплом бухгалтера купить диплом бухгалтера .
купить диплом в челябинске купить диплом в челябинске .
Женский онлайн-журнал https://rosetti.com.ua о стиле, здоровье и семье. Новости моды, советы экспертов, тренды красоты и секреты счастья. Всё, что важно и интересно женщинам любого возраста.
Сайт о металлах https://metalprotection.com.ua и металлообработке: виды металлов, сплавы, технологии обработки, оборудование и новости отрасли. Всё для специалистов и профессионалов металлургии.
Строительный сайт https://okna-k.com.ua для профессионалов и новичков. Новости отрасли, обзоры материалов, технологии строительства и ремонта, советы мастеров и пошаговые инструкции для качественного результата.
Портал о дизайне https://sculptureproject.org.ua интерьеров и пространства. Идеи, тренды, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и общественных мест. Советы дизайнеров и примеры стильных решений каждый день.
Главный автопортал страны https://nmiu.org.ua всё об автомобилях в одном месте! Новости, обзоры, советы, автообъявления, страхование, ТО и сервис. Для водителей, механиков и просто любителей машин.
With thanks. Loads of erudition!
Студия ремонта https://anti-orange.com.ua квартир и домов. Выполняем ремонт под ключ, дизайн-проекты, отделочные и инженерные работы. Качество, сроки и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
Туристический портал https://feokurort.com.ua для любителей путешествий! Страны, маршруты, достопримечательности, советы и лайфхаки. Планируйте отдых, находите вдохновение и открывайте мир вместе с нами.
info foot africain afrik foot pronostic
1xbet afrique apk foot africain
1xbet cameroun apk telecharger 1xbet apk
wettbüro berlin in der nähe
My web blog: sportwetten bonus (Lawrence)
was bedeutet handicap Sicher wetten
Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым мыкты формада болот. Флойд Мейвезердин акыркы жаңылыктары ар бир күйөрманды кызыктырат. Флойд Мейвезер жөнүндө актуалдуу макалалар Флойд Мейвезер жаңылык порталында жарыяланат.
Флойд Мейвезердин ийгилиги көпчүлүк үчүн үлгү. Анын рекорддору бүгүнкү күнгө чейин сакталган. Флойд Мейвезердин карьерасы көп жылдык эмгектин натыйжасы.
Флойд Мейвезер – тартиптин жана күчтүн символу.
Анын жашоосу мотивациянын булагы. Анын фанаттары дүйнөнүн бардык бурчунда бар. Флойд Мейвезер – күч, ылдамдык жана акылдын айкалышы.
купить диплом педагога купить диплом педагога .
Студия дизайна https://bathen.rv.ua интерьеров и архитектурных решений. Создаём стильные, функциональные и гармоничные пространства. Индивидуальный подход, авторские проекты и внимание к деталям.
Ремонт и строительство https://fmsu.org.ua без лишних сложностей! Подробные статьи, обзоры инструментов, лайфхаки и практические советы. Мы поможем построить, отремонтировать и обустроить ваш дом.
sportwetten bonus code ohne einzahlung
my homepage – wetten doppelte chance erklärung
I’ve been using it for a year for using the bridge, and the quick deposits stands out. Great for cross-chain swaps with minimal slippage.
I’ll certainly return to read more.
sportwette strategie
my web-site … deutsche sportwetten gmbh (Sherlene)
riobet рабочее зеркало
1win az basketbol mərcləri https://1win5005.com/
согласование перепланировок нежилых помещений http://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya8.ru .
Современная студия дизайна https://bconline.com.ua архитектура, интерьер, декор. Мы создаём пространства, где технологии сочетаются с красотой, а стиль — с удобством.
melbet – paris sportif pariez sur le foot
melbet telecharger 1xbet afrique apk
parier foot en ligne https://pari-foot2.com
Создавайте дом https://it-cifra.com.ua своей мечты! Всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне интерьера. Идеи, проекты, фото и инструкции — вдохновляйтесь и воплощайте задуманное легко и с удовольствием.
hunderennen Online wetten – Rezfuvoszenekar.adventista.Hu – sportwetten neu
admiral casino
1win aviator qeydiyyat https://1win5005.com
riobet регистрация
перепланировка в нежилом помещении перепланировка в нежилом помещении .
переустройство нежилого помещения переустройство нежилого помещения .
услуги мини экскаватора услуги мини экскаватора .
разрешение на перепланировку нежилого помещения не требуется https://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya9.ru/ .
карниз с приводом http://www.karniz-elektroprivodom.ru .
I was skeptical, but after since launch of checking analytics, the seamless withdrawals convinced me.
электрические рулонные шторы купить москва https://www.rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru .
Мир архитектуры https://vineyardartdecor.com и дизайна в одном месте! Лучшие идеи, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и города. Узнай, как создаются красивые и функциональные пространства.
admiral x регистрация
как купить диплом техникума в уфе как купить диплом техникума в уфе .
alihidaer2313 – The site feels minimal, design is simple yet somewhat intriguing.
сукааа рабочее зеркало
riobet официальный сайт
дживиспин казино
wett tipps ai erfahrungen
Also visit my site; Erfolgreiche sportwetten strategie
Частный заем денег домашние деньги официальный сайт альтернатива банковскому кредиту. Быстро, безопасно и без бюрократии. Получите нужную сумму наличными или на карту за считанные минуты.
Все спортивные новости http://sportsat.ru в реальном времени. Итоги матчей, трансферы, рейтинги и обзоры. Следите за событиями мирового спорта и оставайтесь в курсе побед и рекордов!
**mind vault**
mind vault is a premium cognitive support formula created for adults 45+. It’s thoughtfully designed to help maintain clear thinking
I personally find that i value the seamless withdrawals and intuitive UI. This site is reliable. The mobile app makes daily use simple.
tipps und tricks sportwetten
Check out my web blog :: wette ergebnisse – Lilla –
Suchen Sie Immobilien? immobilien in Montenegro kaufen wohnungen, Villen und Grundstucke mit Meerblick. Aktuelle Preise, Fotos, Auswahlhilfe und umfassende Transaktionsunterstutzung.
sportwetten heute tipps
Look at my page – WettbüRo FüRth
I switched from another service because of the useful analytics and trustworthy service.
где можно купить диплом медсестры где можно купить диплом медсестры .
сеть фитнес клубов фитнес клуб с бассейном
женский фитнес клуб в москве фитнес клуб цены
sportwetten anbieter deutschland
Also visit my site; Wett Online – https://Good-Dog.Co.Il/ –
The staking process is simple and the intuitive UI makes it even better.
Fees are intuitive UI, and the execution is always smooth. Charts are accurate and load instantly.
sport wetten Auf wahlausgang österreich
Jamie here — I’ve tried trading and the seamless withdrawals impressed me.
Fast onboarding, stable performance, and a team that actually cares. The updates are frequent and clear.
was ist eine kombiwette
Feel free to visit my web site sportwetten analyse tipps;
Jannie,
I personally find that i’ve been using it for over two years for checking analytics, and the clear transparency stands out. Definitely recommend to anyone in crypto.
натяжные потолки нижний новгород дешево http://stretch-ceilings-nizhniy-novgorod.ru/ .
kombiwetten
Here is my blog post … Wetten Bester Bonus (Colegioargentina.Cl)
Аренда автобусов для перевозки людей https://povozkin.ru
Лазерные станки https://raymark.ru для резки металла в Москве. 20 лет на рынке, выгодная цена, скидка 5% при заявке с сайта + обучение
HOME CLIMAT https://homeclimat36.ru кондиционеры и сплит системы в Воронеже. Скидка на монтаж от 3000 рублей! При покупке сплит-системы.
Анын голдорунун статистикасы абдан таасирдүү.Бул оюнчу дайыма эң мыктылардын арасында. Бул сайтта Гарри Кейндин Бавариядагы оюндары тууралуу кеңири маалымат бар: Гарри Кейн Бавария</url]. Кейн өзүнүн максаттарын так билет.
Бул оюнчу кайсы жерде болбосун гол киргизе алат.
Гарри Кейндин балдары футболду жакшы көрүшөт. Кейн капитан катары чоң жоопкерчилик алат. Футбол дүйнөсүндө Гарри Кейн өз ордун тапкан. Кейндин футболго болгон сүйүүсү жаш кезинен башталган. Ал ар бир сезон ондогон гол киргизет. Анын Instagram баракчасы абдан популярдуу.
Аутстаффинг персонала https://skillstaff2.ru для бизнеса: легальное оформление сотрудников, снижение налоговой нагрузки и оптимизация расходов. Работаем с компаниями любого масштаба и отрасли.
Нужна недвижимость? https://www.nedvizhimost-chernogorii-u-morya.ru/ лучшие объекты для жизни и инвестиций. Виллы, квартиры и дома у моря. Помощь в подборе, оформлении и сопровождении сделки на всех этапах.
I personally find that i was skeptical, but after several months of using the API, the useful analytics convinced me. Perfect for both new and experienced traders.
The portfolio tracking tools are seamless withdrawals and reliable uptime.
wetten ohne einzahlung vorhersagen app
Строительный портал https://v-stroit.ru всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Полезные советы, технологии, материалы, новости отрасли и практические инструкции для мастеров и новичков.
sportwetten anbieter paysafecard
Take a look at my web blog Wettanbieter Deutschland Vergleich
Портал о строительстве https://pamel-stroy.ru и ремонте. Пошаговые инструкции, идеи, технологии, новости и советы экспертов. Всё, что нужно, чтобы строить и ремонтировать грамотно.
Риэлторская контора https://daber27.ru покупка, продажа и аренда недвижимости. Помогаем оформить сделки безопасно и выгодно. Опытные риэлторы, консультации, сопровождение и проверка документов.
Купольные дома https://kupol-doma.ru под ключ — энергоэффективные, надёжные и современные. Проектирование, строительство и отделка. Уникальная архитектура, комфорт и долговечность в каждом доме.
Sportwetten In Der NäHe
schweiz swisslos
geld verdienen mit sportwetten
Here is my web blog Beste wetten anbieter
Ваша Недвижимость https://rbn-khv.ru сайт о покупке, продаже и аренде жилья. Разбираем сделки, налоги, ипотеку и инвестиции. Полезная информация для владельцев и покупателей недвижимости.
Информационный блог https://gidroekoproekt.ru для инженеров и проектировщиков. Всё об инженерных изысканиях, водохозяйственных объектах, гидротехническом строительстве и современных технологиях в отрасли.
Ислам Махачев ким менен жана качан беттешерин билгиңиз келсе, биз дайыма жаңырган календарь жана расмий маалыматтарды сунуштайбыз.
UFC 311 жакындап келе жатабы, Ислам Махачевтин расписаниеси реалдуу убакытта жаңыртылат. ислам махачев следующий бой Кийинки беттештин так датасы жана оппоненти ушул бетте жаңыртылат. Эфирди кайдан көрүү боюнча да кыска гид бар. Фанаттар үчүн «эмне күтүүгө болот» бөлүмү беттеш алдындагы маанилүү суроолорго жооп берет. Мүмкүн болгон апсеттер жана беттеш темпи боюнча аналитикалык бөлүм бар. Беттешке чейинки форма, спарринг жана медициналык текшерүүлөр боюнча расмий шилтемелер бар.
Карьерасынын финалдык максаттары жана мүмкүн болгон супер-файт варианттары талданат. Кайсы раунддарда өзгөрүү болушу ыктымал экенин тенденцияларга карап белгилеп беребиз. Инфографика: тейкдаун, сабмишн, контрдардан алынган негизги сандык маалыматтар. Издөө функциясы боюнча ачкыч сөздөрдү киргизип, керектүү бөлүмгө тез өтүңүз.
Riley here — I’ve tried trading and the quick deposits impressed me. The mobile app makes daily use simple.
I personally find that this platform exceeded my expectations with useful analytics and fast transactions. Definitely recommend to anyone in crypto.
wettseiten mit paypal
Here is my homepage österreichische sportwetten
купить диплом в бору https://rudik-diplom9.ru/ .
купить диплом в набережных челнах купить диплом в набережных челнах .
Деревянные лестницы https://rosslestnica.ru под заказ в любом стиле. Прямые, винтовые, маршевые конструкции из массива. Замеры, 3D-проект, доставка и установка. Гарантия качества и точности исполнения.
Лестницы в Москве https://лестницы-в-москве.рф продажа и изготовление под заказ. Прямые, винтовые, модульные и чердачные конструкции. Качество, гарантия и монтаж по всем стандартам.
I switched from another service because of the low fees and scalable features.
was ist die beste sportwetten app
Here is my web page: Bester Wettanbieter Ohne Oasis
купить диплом с занесением в реестр купить диплом с занесением в реестр .
купить легальный диплом техникума купить легальный диплом техникума .
сколько стоит проект перепланировки сколько стоит проект перепланировки .
регистрация перепланировки https://soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry3.ru/ .
согласование перепланировки согласование перепланировки .
Market crash timing has become an art form, and experienced players know the optimal moments to buy fifa coins immediately following major pack promotions when player prices temporarily stabilize. Real sellers with fast delivery capabilities can capitalize on these narrow windows, and their active market monitoring helps coordinate purchases during optimal pricing periods. Non drop protection policies become especially valuable during volatile market conditions when coin values fluctuate rapidly, protecting your purchasing power throughout promotional cycles and content updates.
wett tipps heute
Feel free to surf to my site: sportwetten geld zurück österreich
Онлайн курсы ЕГЭ https://courses-ege.ru
dfb pokal wetten tipps
Also visit my web page; wettanbieter deutschland bonus
Для oyunlar и fantasy смотрю новости Неймара: травмы, сроки камбэка, предполагаемая роль. Ищу «неймар обои барселона» и «бразилия»: хочется минимализма, без лишних логотипов. Хочу таблицу голов за карьеру и распределение по клубам/сборной. сколько голов забил неймар. Сантос Неймар: финты против плотной обороны — полезно разобрать для молодых вингеров.
Нужны «неймар обои на телефон» с мягким контрастом, чтобы иконки читались. Неймар номер: на футболке в «Сантосе» и «Барселоне» — важные детали для коллекционеров. Неймар завершил карьеру? Хочу факт-чек от надёжных спортивных СМИ. Неймар обои Бразилия — яркие цвета, но важно, чтобы иконки читались на домашнем экране.
Неймар какой клуб сейчас — нужен снэпшот для карточек игроков. Неймар в каком клубе играет — хочу добавить автоподстановку в шапке сайта.
Новости спорта онлайн http://sportsat.ru футбол, хоккей, бокс, теннис, баскетбол и другие виды спорта. Результаты матчей, обзоры, интервью, аналитика и главные события дня в мире спорта.
bester wettanbieter online
Feel free to surf to my webpage wetten ist unser sport
gratiswette ohne einzahlung sportwetten
Feel free to visit my page – Schüsse Aufs tor Wetten
1xbet afrique apk pariez sur le foot
sportwetten Online Wettanbieter Bonus (https://Rec-On.Eu/Ergebnisse-Basketball/) bei einzahlung
Все о коттеджных посёлках https://cottagecommunity.ru фото, описание, стоимость участков и домов. Всё о покупке, строительстве и жизни за городом в одном месте. Полезная информация для покупателей и инвесторов.
разработка проекта перепланировки квартиры разработка проекта перепланировки квартиры .
sportwetten vergleich paypal
Feel free to surf to my site; erfahrungen Wett Tipps ai
online wetten paysafecard
Here is my website … wettquoten erklärung
услуги seo компании услуги seo компании .
bonus code wetten
My site; sportwetten tipps für anfänger
лучшее сео продвижение лучшее сео продвижение .
заказать сео москва https://www.seo-prodvizhenie-reiting-kompanij.ru .
wettanbieter mit schneller auszahlung
Visit my page … ungarn deutschland wetten (Candice)
alle wettanbieter im vergleich
my web page betibet sportwetten online deutschland
sportwette strategie
Check out my site – Besten wettanbieter (https://recruit.webfuture.top/2025/10/20/was-bedeutet-handicap-bei-wetten)
wettseiten deutschland
Check out my homepage; wettbüRo freiburg
топ 10 сео компаний топ 10 сео компаний .
1xbet resmi sitesi http://1xbet-giris-1.com .
sportwetten tipps facebook
my web-site – Quoten wetten dass
online sportwette
my blog :: hunderennen wetten deutschland (Jenni)
tipps beim wetten
Here is my website – wettanbieter österreich (https://snc-lacour.monpreprod.com/2025/10/07/warum-online-wetten-heute-tennis/)
one x bet https://1xbet-giris-7.com/ .
spanien deutschland wetten
Also visit my blog post; sportwetten WettbüRo
live wetten quoten
Feel free to visit my blog; wett tipps heute telegram
Bank kartı və e-cüzdanla depozitlər anında düşür, ödəniş limiti AZN üçün əlverişlidir.
Çoxlu lokal ödəniş üsulu dəstəklənir, komissiyalar real vaxt göstərilir. Əgər azərbaycan dilində interfeys lazımdırsa, pinco azerbaycan səhifəsi sizin üçündür — ödənişlər şəffafdır. Məlumatlar TLS şifrələnməsi ilə qorunur, sessiya avtomatik vaxtı bitdikdə bağlanır. Sürətli oyunlar və crash-mekanikalar qısa sessiyalar üçün ideal həll təqdim edir.
Futbol üçün xG, şans yaradıcılığı və pressinq göstəricilərinə baxmaq faydalıdır. APK yenilənməsi tətbiqdaxili xəbərdarlıqla gəlir və bir dəqiqəyə tamamlanır.
Təhlükəsizlik bildirişləri qeyri-adi giriş zamanı dərhal göndərilir. Uşaqların müdafiəsi ilə bağlı xəbərdarlıq bannerləri görünən yerdədir. Reytinqlər və istifadəçi rəyləri ən faydalı bölmələri tapmağa imkan verir.
1 x bet 1 x bet .
1xbwt giri? http://www.1xbet-4.com/ .
I am curious to find out what blog system you are working with?
I’m experiencing some minor security problems with my latest site and I’d like to find something
more safe. Do you have any suggestions?
Visit my webpage; trucchi per vincere casino online
strategie sportwetten
My blog: internet wetten live [Felipa]
gain Casino imposable suisse uk pay by phone
bill, no deposit bingo bonus uk and canada best slot machine, or top 5 online pokies united states
купить диплом в волгограде купить диплом в волгограде .
wettbüro leverkusen
Have a look at my homepage :: Sportwetten beste strategie
I am actually grateful to the holder of this website who has shared this impressive article at at this place.
Here is my web-site games rollex Casino online
возможно ли купить диплом техникума возможно ли купить диплом техникума .
handicap wette
my website; Sportwetten Tippen; Crm.Gloobo.Store,
usa free spins no money deposit, best winning online casino nz and online
slots no deposit required usa, or minimum deposit 1 pound casino usa
My web blog … lunar new year gambling games (Fernando)
1xbet tr 1xbet tr .
1xbet t?rkiye 1xbet t?rkiye .
кухни на заказ петербург http://kuhni-spb-2.ru .
Левандовски футболдо чыдамкайлык менен мыкты натыйжа көрсөттү.
Роберт Левандовски денесин мыкты формада кармайт. Роберт Левандовски жашоосунда көп ийгиликке жеткен. Роберт Левандовски улуттук курама үчүн көп гол салган. Кызыктуу фактылар менен таанышуу үчүн robert-lewandowski-kg.com сайтына кириңиз. Бул жерде анын карьерасы тууралуу кеңири маалымат бар. Левандовски Барселонада лидер болуп калды.
Роберт Левандовски карьерасын үзүрлүү өткөрүүдө. Роберт Левандовскинин жаракаты көпчүлүктү тынчсыздандырган.
Роберт Левандовски өзүнүн тамырларын сыйлайт. Роберт Левандовски ар дайым эмгектин баасын билет.
купить диплом учителя физической культуры купить диплом учителя физической культуры .
sportwetten anmeldebonus ohne einzahlung
Also visit my blog; internet wetten vergleich
birxbet giri? https://1xbet-17.com/ .
медицинское оборудование для больниц https://medicinskoe–oborudovanie.ru/ .
вывод из запоя москва клиника https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-24.ru .
купить диплом в тюмени купить диплом в тюмени .
sportwetten heute
Here is my page: hunderennen online wetten [https://mb.dngtech.Cn/]
pferderennen hamburg wetten
Look at my site: sportwetten richtig tippen (Christel)
bester alphabet Wettanbieter Mit Deutscher Lizenz
gratis sportwette ohne einzahlung
Feel free to visit my homepage … wett tipps heute (Tammara)
купить диплом в бийске купить диплом в бийске .
https://mega-main.shop
частная наркологическая клиника москва частная наркологическая клиника москва .
Completely agree with this, this is valuable.
Thought I’d drop this here, I visited a resource recently: could be helpful
Anyone else seen it?.
die besten wett tipps heute
My site: Esport Wetten Deutschland verboten
Я просто не можу не поділитися історією, яка трапилася у мене минулого робочого тижня – уявіть собі!. Дочка вимовила бажання, аби я приготувала щось неймовірно красиве до день народження. Ваша героїня, звичайно, розпочала шукати рецепт серед кулінарних блогах і отримала несподіванку. Втратила цілісних 1.5 години марних пошуків, стрибаючи з ресурсу у бік другий сайт! Одні рецепти здавалися занадто складні, декілька – зі справжніми екзотичними інгредієнтами, треті – із масою спонсорських посилань. І як грім серед ясного неба ваша героїня згадала щодо цей портал та всього лише за п’ять неймовірно швидких хвилинок знайшла – мрійливий варіант! Рецепт виявився настільки детальним, що навіть 12-річна помічниця змогла мені допомогти. В результаті наш тандем створили неймовірний солодкий шедевр, і він став справжнім хітом святкового столу. І ось вам результат кожна мої тепер зацікавлені подруги не дають мені проходу з питаннями: “В якому місці ти знайшла цей диво такий собі чудовий рецепт?”
Каталог рецептів
Register now and receive a welcome package:
up to 205 free spins and as much as 1850$ bonus funds!
Huge range of games, instant winnings, and a trusted casino experience await at
https://worldbestnews.my/bfl6ql6
Регистрируйся сейчас и получай приветственный пакет — до 85 фриспинов и до 2200Dol бонуса!
Лучшие игры, быстрые выплаты и честный сервис на
https://timenewsworld.blog/b1pmbv1
мелбет сайт мелбет сайт .
beste wettanbieter test betrugstest
Look at my web blog :: schweiz online sportwetten
Hello i am kavin, its my first occasion to commenting anyplace, when i read this piece of writing i thought i could also create comment due to this good paragraph.
номер для смс
welche sportwetten sind in der schweiz legal (zouzhun.com) bonus ohne einzahlung
как купить диплом техникума форум как купить диплом техникума форум .
live sport wetten
Feel free to visit my web page Trump harris wettquoten
блог о маркетинге блог о маркетинге .
sportwetten glücksspiel österreich bonus
bedingungen
It’s not my first time to pay a quick visit this website, i am visiting this web site dailly and get fastidious information from here daily.
urteil online sportwetten ergebnisse (Cherie)
seo с нуля https://www.kursy-seo-11.ru .
Проектирование и строительство загородного дома в Санкт-Петербурге – это процесс, требующий внимательности к деталям. Наша строительная компания берет на себя все этапы: от выбора материалов и составления прайса до выполнения работ. Мы предлагаем кладку газоблока https://builder-spb.ru , кирпича и пеноблоков, установку жб-перекрытий, монтаж перегородок, сварочные и отделочные работы. Стоимость рассчитывается за квадратный метр или поштучно. Подрядчики учитывают сорт и уровень прочности блоков, чтобы построить надежный дом. Предлагаем выгодные цены и прозрачные расценки, фиксированные в договоре.
If anyone’s still confused about fees, this guide on SpiritSwap fees and gas breaks it down nicely.
Good walkthrough on Anyswap transaction tracking
If you value transparency check ParaSwap privacy
купить диплом во владивостоке купить диплом во владивостоке .
Щиро розумію кожного, яка задовбався від щоденного виснажливого підбору якісних страви! Колись мені доводилося зберігати величезну кількість вкладок на комп’ютері – деякі сайти під випічки, інші для м’ясних делікатесів страв, решта для вегетаріанських страв. Часто не могла знайти потрібне серед цього нагромадженні! Проте як тільки випадково натрапила на даний портал, моє кухонне приготування стало простішим! Вже мені доступний все в одному зручному каталозі – від швидких рецептів для буднів до урочистих рецептів. Особливо оцінюю той момент, як кожен ресурси тестові досвідом і містять добре пояснені , зрозумілі для новачків інструкції. Навіть не кажучи про те, зараз приготую в рази швидше – немає необхідності тратити купу часу на перебирання сайтів
Сайт blogreceptov.icu
In today’s nonstop news cycle, finding trustworthy, up-to-date information has become a real challenge. Platforms spread news instantly, yet truth is often lost in the speed. To explore a curated list of reliable digital sources, read more on our blog: https://pads.jeito.nl/N9Blvp-jTHmrRg0FsAjd8Q/ .
Major publications such as BBC, Reuters, and AP remain the foundation of accurate reporting. They fact-check every story and keep articles current as situations develop. For deeper understanding, outlets such as The Economist and The Atlantic unpack the “why” behind the news.
Independent journalists and digital platforms are reshaping the modern news landscape. Writers on Substack, smaller blogs, and research outlets tend to deliver quick, authentic perspectives — notably on underreported subjects. These voices bring fresh perspectives and restore a sense of authenticity.
The best way to stay informed is to combine multiple viewpoints: combine global sources with smaller, focused ones that match your curiosity. Read from multiple viewpoints, think critically, and seek understanding over headlines. This mix transforms reading into awareness.
Ich bin begeistert von der Welt bei Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit Slots in modernem Look. Der Willkommensbonus ist ein Highlight. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und effizient, ab und zu zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Bonus. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Spieler. Nebenbei die Seite ist schnell und attraktiv, jeden Augenblick spannender macht. Ein tolles Feature die lebendigen Community-Events, fortlaufende Belohnungen bieten.
Hier fortfahren|
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine dynamische Erfahrung. Die Auswahl ist so gro? wie ein Casino-Floor, mit Slots in modernem Look. Der Willkommensbonus ist ein Highlight. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Gewinne kommen sofort an, jedoch mehr regelma?ige Aktionen waren toll. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Nebenbei die Navigation ist intuitiv und einfach, eine immersive Erfahrung ermoglicht. Ein gro?artiges Bonus die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, individuelle Vorteile liefern.
Jetzt ansehen|
I’m completely sold on Pinco, it feels like a VIP experience. There’s an insane range of games, with slot machines in fresh themes. The signup offer is unbeatable. Support is dependable and helpful. Winnings are paid out instantly, still larger deals would improve the vibe. Overall, Pinco is a hub of pure fun. On top of that navigation is clean and intuitive, adds a touch of class. Also awesome are the reliable crypto payouts, that delivers ongoing bonuses.
Browse the site|
Je suis epate par Ruby Slots Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement cool les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, renforce la communaute.
Lire les dГ©tails|
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, a l’occasion des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Globalement, Sugar Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour ajouter la navigation est fluide et facile, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui booste la participation.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
J’adore la vibe de Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par moments des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Sugar Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En complement la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement cool les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges personnalises.
Visiter le site|
Мені хочеться розказати пригодою, що сталася з мене того самого тижня. Моя принцеса вимовила бажання, щоб як кулінарний експерт приготувала один неймовірно красиве на її ДР. Я, як завжди, звичайно, розпочала шукати рецепт в інтернеті і… о боже!. Втратила цілих нервущих одну з половиною години марних пошуків, блукаючи із ресурсу на ще однієї сторінки з рекламою! Перші варіанти були нереально складні, інші – із дивними продуктами, решта – з масою спонсорських посилань. І згодом я пригадала щодо цей порятунок сайт й за 5 хвилин, і це факт! знайшла свою панацею – ідеальний варіант! Ця знахідка виявився настільки покроковим, що навіть навіть дванадцятирічна помічниця несподівано змогла мені стати справжнім підручним. В результаті наш тандем приготували дивовижний десерт, який перетворився на справжнім хітом дня народження. Зараз усі мої найкращі подруги питають: “В якому місці я знайшла цей диво такий неймовірно класний варіант?”
Каталог кулінарних рецептів
Щиро відчуваю кожного, яка задовбався через безкінечного підбору перевірених страви! До цього у мене була цілу купу закладок в інтернет-обозрівачі – деякі сайти зі випічки, інші під м’ясних делікатесів кушань, решта зі овочевих страв. Постійно губилася в цьому лабіринті! Але коли відкрила даний портал, моє кухонне життє пішло на новий рівень! Зараз я маю весь необхідний контент в єдиному каталозі – від простих рецептів для буднів і закінчуючи урочистих рецептів. Дуже люблю те, як всі ресурси апробаційні роками і пропонують зрозумілі , зрозумілі для новачків інструкції. Навіть не згадуючи що, зараз приготую в рази ефективніше – немає необхідності тратити купу часу на перегляд сторінок
Каталог
I was curious about privacy and found ParaSwap privacy policy
Regіstrіere dich jetzt und sіchere dir das Willkоmmеnspаket: bіs zu 215 Frеіspіеle und bіs zu 1650Еur Воnus!
Тоp Spіеle und sofоrtіge Gewіnnе аuf
https://worldbestnews.biz/bi09t2v
карниз с электроприводом карниз с электроприводом .
Приступая к ремонту, был уверен – ну интернет же, тут все есть. Ан нет! Один советует наносить три слоя грунтовки, второй – что хватит одного слоя, еще один вообще советуют обойный клей применять. Потерял неделю, пока не обнаружил адекватный подборку рекомендованных сайтов. Там подобрали только качественные ресурсы – со стандартами, опытом профессионалов и минус этой коммерческой воды. Вот, может сэкономите силы
Сайт
Hi there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
https://detkinland.com.ua/yak-linzy-dlya-far-pokrashchuyut-svitlovi-kharakte.html
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, c’est une veritable experience de jeu electrisante. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le personnel offre un accompagnement irreprochable, garantissant une aide immediate via chat en direct ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par moments les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers, ou des promotions hebdomadaires plus frequentes. Pour conclure, 7BitCasino est un incontournable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive et rapide, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
7bitcasino promo code|
Ich bin ein gro?er Fan von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Hotspot fur Spielspa?. Es gibt zahlreiche spannende Spiele, mit aufregenden Live-Casino-Erlebnissen. Er macht den Einstieg unvergesslich. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und zuverlassig, aber regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Spieler. Zudem die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, zum Verweilen einladt. Ein weiteres Highlight die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
http://www.catspinsbonus.com|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, bietet klare Losungen. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, ab und an mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, verstarkt die Immersion. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Sicherheit der Daten, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Sugar Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des tables live interactives. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Dans l’ensemble, Sugar Casino offre une experience inoubliable. De plus le site est rapide et style, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Aller sur le site|
Je suis fascine par Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est simple et transparent, par moments plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Ruby Slots Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En plus l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement attrayant les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller au site|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Ruby Slots Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots fluides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par ailleurs des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino offre une aventure memorable. Pour couronner le tout le site est fluide et attractif, facilite une experience immersive. Un element fort les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, offre des bonus constants.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
Ich bin begeistert von der Welt bei Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine elektrisierende Atmosphare. Das Spieleportfolio ist unglaublich breit, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. Der Willkommensbonus ist gro?zugig. Der Kundensupport ist top. Der Prozess ist einfach und transparent, jedoch mehr Aktionen waren ein Gewinn. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein tolles Extra die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, die Gemeinschaft starken.
Details prГјfen|
Great site, i recommend it to everyone SpiritSwap
организация онлайн трансляции москва организация онлайн трансляции москва .
онлайн трансляция под ключ zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu5.ru .
сервисный центр bosch в москве https://servisnyj-bosch-moskva.ru/
купить chery chery tiggo 4 2025
Link jkl
Rеgіster now and receive a welсоme раckage:
up to 65 frее sріns and as much as 900Dоl Воnus funds!
Huge range of games, instant winnings, and a trusted саsіnо experience await at
https://jackpotjungle.shop/bn0ijxv
Узнайте больше здесь: https://newshay.com/czifrovaya-vs-ofsetnaya-pechat-stikerov-kak-vybrat-dlya-malogo-tirazha
All the details at the link: http://grocery.vpmarketingllc.com/2025/10/08/kupit-akkaunt-fejsbuk-top-5-servisov-gde-mozhno-8/
Regіstrаte ahоra y recіbе un pаquеte de bіеnvenіda: hаsta 200 tіrаdas grаtіs y un bоnо de hаstа 1450$.
Juеgоs іncrеiblеs y pаgоs іnstаntanеоs еn
https://gamescape.shop/byof23d
Тем, кто любит активный отдых и новые маршруты, подойдут организованные туры из Краснодара. Комфортный транспорт, опытные сопровождающие и интересные направления — идеальное сочетание для путешественников любого возраста. Не упустите возможность открыть для себя что-то новое!
Estou completamente apaixonado por BacanaPlay Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um tamborim. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um bloco de rua vibrante, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sambam com energia. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma rainha de bateria, respondendo mais rapido que um batuque de pandeiro. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como confetes, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. Em resumo, BacanaPlay Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro axe para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de frevo, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
bacanaplay free spins|
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Es gibt unzahlige packende Spiele, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Der Service ist immer zuverlassig. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und effizient, allerdings mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Zusatzlich die Navigation ist klar und flussig, das Vergnugen maximiert. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt die spannenden Community-Aktionen, das die Motivation steigert.
Cat Spins|
Ich bin ganz hin und weg von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Die Auswahl ist atemberaubend vielfaltig, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. Der Willkommensbonus ist gro?zugig. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und effizient, aber ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Spieler. Zusatzlich die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein wichtiger Vorteil die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, regelma?ige Boni bieten.
Ins Web gehen|
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, bietet klare Losungen. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, gelegentlich mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Daruber hinaus die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein Pluspunkt ist die mobilen Apps, die Flexibilitat bieten.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je ne me lasse pas de Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En conclusion, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, facilite une immersion totale. Un point cle les transactions en crypto fiables, qui booste la participation.
Visiter la page web|
Je suis completement seduit par Ruby Slots Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En conclusion, Ruby Slots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Ajoutons aussi le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un element fort les transactions en crypto fiables, qui motive les joueurs.
Cliquez ici|
J’adore la vibe de Ruby Slots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour faire court, Ruby Slots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A signaler l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un element fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, garantit des paiements rapides.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Ich freue mich auf Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein immersives Erlebnis. Das Spieleportfolio ist unglaublich breit, mit dynamischen Wettmoglichkeiten. Der Bonus ist wirklich stark. Der Service ist von hochster Qualitat. Transaktionen laufen reibungslos, jedoch mehr regelma?ige Aktionen waren toll. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Ubrigens die Navigation ist intuitiv und einfach, einen Hauch von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein weiteres Highlight ist das VIP-Programm mit exklusiven Stufen, schnelle Zahlungen garantieren.
Weiter gehen|
интимные подарки Секс-шоп Erross интим-магазин товаров для взрослых с анонимной доставкой по Москве и РФ.
Great site, I recommend it to everyone Manta Bridge
Great site, I recommend it to everyone AnySwap Platform
Dakota here — I’ve tried learning crypto basics and the trustworthy service impressed me. I moved funds across chains without a problem.
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Es gibt eine riesige Vielfalt an Spielen, mit packenden Live-Casino-Optionen. Er sorgt fur einen starken Einstieg. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, dennoch regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. Kurz und bundig, Cat Spins Casino ist ein absolutes Highlight. Daruber hinaus die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, einen Hauch von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein starker Vorteil sind die zuverlassigen Krypto-Zahlungen, sichere Zahlungen garantieren.
Bringen Sie mich dorthin|
Ich bin ganz hin und weg von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit aufregenden Live-Casino-Erlebnissen. Der Bonus fur Neukunden ist attraktiv. Der Kundendienst ist hervorragend. Transaktionen laufen reibungslos, in seltenen Fallen regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Au?erdem ist das Design zeitgema? und attraktiv, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein super Vorteil ist das VIP-Programm mit exklusiven Stufen, das die Motivation steigert.
Eintreten|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, gelegentlich mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Zusatzlich das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Ein Pluspunkt ist die mobilen Apps, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
интим бутик с премиальным сервисом Секс-шоп Erross интим-магазин товаров для взрослых с анонимной доставкой по Москве и РФ.
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, mais encore des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Notons aussi l’interface est simple et engageante, booste le fun du jeu. Un atout les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des recompenses continues.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Je suis bluffe par Ruby Slots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est clair et efficace, en revanche quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En plus la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement fun les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des privileges personnalises.
Parcourir maintenant|
Clubnika
J’adore la vibe de Sugar Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par ailleurs des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En conclusion, Sugar Casino garantit un amusement continu. A noter le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une immersion totale. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Naviguer sur le site|
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu unvergesslichen Momenten ein. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Anzahl an Titeln, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. Mit blitzschnellen Einzahlungen. Der Kundensupport ist top. Auszahlungen sind zugig und unkompliziert, jedoch mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino garantiert dauerhaften Spielspa?. Au?erdem die Navigation ist klar und flussig, zum Verweilen einladt. Ein wichtiger Vorteil ist das VIP-Programm mit tollen Privilegien, die die Begeisterung steigern.
https://catspins24.com/|
I’ve been active for several months, mostly for fiat on-ramp, and it’s always low fees.
купить диплом колледжа пермь http://www.frei-diplom7.ru .
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Das Angebot ist ein Traum fur Spieler, mit modernen Slots in ansprechenden Designs. Mit blitzschnellen Einzahlungen. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar. Auszahlungen sind blitzschnell, ab und zu gro?ere Boni waren ideal. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Daruber hinaus die Seite ist schnell und attraktiv, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein bemerkenswertes Extra die haufigen Turniere fur mehr Spa?, die die Begeisterung steigern.
Details erhalten|
Бурение скважин на воду — практичное решение организовать подачу чистой воды на участок. Такая система обеспечивает доступ к чистой воде из подземных источников, обеспечивая автономность и стабильность.
Работы по бурению https://akva-brs.ru/ предусматривает исследование геологических условий, которая помогает определить оптимальную точку бурения. На основе данных буровики определяют вариант скважины под конкретные условия.
После пробуривания устанавливается обсадная труба, подключается система водоподачи и выполняется монтаж защитных элементов — кессона и оголовка. Все эти мероприятия предохраняют воду от загрязнений.
Водяная скважина — это долгосрочная инвестиция. При грамотном выполнении работ и своевременном уходе она будет работать многие годы, поставляя чистую и безопасную воду.
Ich bin ein gro?er Fan von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Hotspot fur Spielspa?. Es gibt eine Fulle an aufregenden Titeln, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. Er sorgt fur einen starken Einstieg. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Auszahlungen sind zugig und unkompliziert, ab und zu mehr Bonusoptionen waren top. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spieler. Daruber hinaus ist das Design zeitgema? und attraktiv, was jede Session spannender macht. Besonders erwahnenswert die haufigen Turniere fur mehr Spa?, sichere Zahlungen garantieren.
Mit dem Entdecken beginnen|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, bietet klare Losungen. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, obwohl mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Hinzu kommt das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, fugt Magie hinzu. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, rarement des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Ajoutons que l’interface est lisse et agreable, facilite une immersion totale. Un plus les evenements communautaires dynamiques, garantit des paiements rapides.
Apprendre comment|
Je suis totalement conquis par Sugar Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, mais encore plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Sugar Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Ajoutons que le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un point fort les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des tables live interactives. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, cependant des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Sugar Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement captivante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement cool les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Voir maintenant|
лучшие рекламные агентства лучшие рекламные агентства .
xbet giri? http://www.1xbet-giris-6.com .
Keep this going please, great job!
https://sepak188.com/melbet-bukmekerskaya-kontora-oficialnyj-sajt-2025/
Ich freue mich riesig uber Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht ein einzigartiges Abenteuer. Das Angebot ist ein Traum fur Spieler, mit eleganten Tischspielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € plus Freispiele. Die Mitarbeiter sind immer hilfsbereit. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und effizient, dennoch mehr Bonusangebote waren ideal. Zusammenfassend, Cat Spins Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt. Daruber hinaus die Oberflache ist benutzerfreundlich, was jede Session spannender macht. Besonders erwahnenswert ist das VIP-Programm mit exklusiven Stufen, die Gemeinschaft starken.
Jetzt entdecken|
Если вы столкнулись с тем, что вы можете зайти на vavada casino, то самое время воспользоваться зеркалом игрового клуба. Вы можете на вавада официальный сайт вход выполнить через следующие виды зеркала:
ссылка на сайт;
плагин на браузер;
клиент на компьютер;
мобильная версия.
Вне зависимости от того, какое зеркало вы выбираете, оно будет обеспечивать стабильный доступ, который поможет обойти абсолютно любые блокировки.
Используйте зеркало для того, чтобы попасть на сайт Вавада
Сегодня на vavada официальный сайт вход выполнить достаточно просто. Если вы воспользуетесь специализированным порталом, то сможете отыскать там ссылку на зеркало игрового клуба Вавада. Можно сразу сохранить страницу со ссылкой для того, чтобы у вас всегда был доступ к любым автоматам. Ссылка за 5 секунд находит новый адрес сайта, который еще не заблокирован со стороны провайдера и обеспечивает стабильный доступ к слотам. Также vavada casino официальный портал доступен через плагин на браузера. Часто многие специализированные сайты предоставляют большой выбор плагинов для любого браузера. Если вы попробуете зайти на заблокированный сайт казино вавада, то зеркало в автоматическом режиме перенаправит вас на свободный адрес.
Скачивайте специальную версию Вавада для стабильного доступа
Еще очень удобным способом зайти на вавада казино онлайн официальный сайт является скачивание мобильной версии к себе на смартфон. Доступ к сайту обеспечивается через приложение, а не через сайт, поэтому ваш провайдер не сможет заблокировать доступ к сайту. Мобильная версия это очень удобно, ведь теперь вы сможете играть в любой момент, когда вам захочется. Достаточно будет достать смартфон и зайти в приложение.
Также скачать вавада казино официальный сайт предлагает сразу на компьютер. Связь здесь идет через специальный клиент, который также не может быть заблокирован вашим провайдером. Кроме того, что зеркало обеспечивает доступ к сайту, у него нет никаких отличий от сайта казино. Здесь все те же слоты и бонусы, а также техподдержка и вероятность выигрыша.
Заходите на сайт казино Вавада, чтобы получить бонусы
Если вы прочитаете про вавада казино официальный сайт отзывы, то узнаете, что данный игровой клуб предоставляет просто шикарные подарки. Во-первых, здесь после регистрации и первого депозита можно получить 100 процентов к депозиту, а также 100 бесплатных вращений дополнительно. После того, как вы отыграете вейджер, вы сможете получить деньги к себе на счет и вывести их на карту или на электронные платежные системы.
Есть на сайте vavada бездепозитный бонус. Если вы играли на деньги и заработали достаточно очков, чтобы перейти на бронзовый уровень минимум, то вы получаете доступ к бесплатному турниру. Тут вы играете на бесплатные фишки, и ваша задача заработать как можно больше фишек. В конце турнира в зависимости от набранных очков начисляется выигрыш.
Embark into the vast galaxy of EVE Online. Start your journey today. Trade alongside thousands of explorers worldwide. Free registration
I was skeptical, but after half a year of using the bridge, the useful analytics convinced me.
Hey there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m absolutely enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
https://siap45.net/melbet-zerkalo-skachat-na-iphone-2025/
купить вкладыш к диплому техникума купить вкладыш к диплому техникума .
Снабжаем грузовые предприятия, автобазы и шиномонтаж шинами от известных китайских производителей!
Шины оптом в Москве
Предоставляем отсрочку платежа!
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Wild Robin Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, de temps en temps des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Wild Robin Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui booste la participation.
Commencer Г explorer|
J’adore le dynamisme de Cheri Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, occasionnellement des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Cheri Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Par ailleurs le design est style et moderne, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fiables.
Commencer ici|
J’adore la vibe de Wild Robin Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, mais plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Wild Robin Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A mentionner le site est rapide et style, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, garantit des paiements rapides.
Savoir plus|
Je suis bluffe par Instant Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En resume, Instant Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. De plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, facilite une immersion totale. A noter les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements rapides.
Explorer maintenant|
Je suis captive par Instant Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par contre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour conclure, Instant Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, booste le fun du jeu. Un point fort les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le lien communautaire.
Visiter en ligne|
клубника
Іnscrіvеz-vоus mаіntеnant еt rеcеvеz un раck de bіеnvеnue: jusqu’a 95 tоurs grаtuіts et un bоnus аllаnt jusqu’a 2200USD!
Dеs jеux pаssіоnnаnts et des pаіemеnts rаpіdеs sur
https://hotspin.shop/bnp94vh
J’adore l’energie de Wild Robin Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour conclure, Wild Robin Casino assure un fun constant. D’ailleurs le site est rapide et immersif, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un atout les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements securises.
http://www.wildrobincasinomobilefr.com|
J’adore la vibe de Frumzi Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, quelquefois des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Globalement, Frumzi Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A noter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un avantage les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui booste la participation.
DГ©couvrir|
Je suis epate par Wild Robin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, quelquefois des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En somme, Wild Robin Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. De surcroit la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui booste la participation.
Rejoindre maintenant|
Je suis sous le charme de Instant Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, mais plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En bref, Instant Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Notons egalement le design est moderne et energique, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant les paiements securises en crypto, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Obtenir des infos|
1xbetpromocode > https://daitangkinh.org/media/pgs/1xbet_promo_code___exclusive_bonus.html Bet of Africa promo codes are specific to the African market, providing users with region-specific bonuses like free bets, deposit matches, or free spins. These codes are designed to cater to the preferences of African bettors.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Cheri Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, parfois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En bref, Cheri Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Notons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement attrayant les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Essayer maintenant|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Cheri Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par contre des offres plus importantes seraient super. En resume, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Voir le site|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Frumzi Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, a l’occasion des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour conclure, Frumzi Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons aussi le design est style et moderne, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis sous le charme de Instant Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des tables live interactives. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est transparent et rapide, parfois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour faire court, Instant Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que le site est fluide et attractif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui booste la participation.
DГ©couvrir|
Drew here — I’ve tried trading and the fast transactions impressed me. Great for cross-chain swaps with minimal slippage.
Wow! This is a cool platform. They really do have the trustworthy service. I moved funds across chains without a problem.
сколько стоит купить диплом медсестры сколько стоит купить диплом медсестры .
купить диплом автотранспортного техникума купить диплом автотранспортного техникума .
Paris sportifs avec 1xbet apk rdc : pre-match & live, statistiques, cash-out, builder de paris. Bonus d’inscription, programme fidelite, appli mobile. Depots via M-Pesa/Airtel Money. Informez-vous sur la reglementation. 18+, jouez avec moderation.
Оформите онлайн-займ https://zaimy-82.ru без визита в офис: достаточно паспорта, проверка за минуты. Выдача на карту, кошелёк или счёт. Прозрачный договор, напоминания о платеже, безопасность данных, акции для новых клиентов. Сравните предложения и выберите выгодно.
Plateforme parifoot rdc : pronos fiables, comparateur de cotes multi-books, tendances du marche, cash-out, statistiques avancees. Depots via M-Pesa/Airtel Money, support francophone, retraits securises. Pariez avec moderation.
I personally find that i switched from another service because of the reliable uptime and intuitive UI. My withdrawals were always smooth.
Je ne me lasse pas de Frumzi Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par ailleurs des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour finir, Frumzi Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Pour ajouter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement interessant les transactions en crypto fiables, assure des transactions fiables.
Entrer maintenant|
J’ai un faible pour Instant Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, toutefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, Instant Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, permet une immersion complete. Egalement super les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, garantit des paiements securises.
http://www.instantcasino777fr.com|
Je suis totalement conquis par Wild Robin Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, toutefois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Dans l’ensemble, Wild Robin Casino offre une aventure memorable. A souligner la navigation est claire et rapide, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement fun les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements rapides.
http://www.wildrobincasinologinfr.com|
Je suis enthousiasme par Instant Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est transparent et rapide, mais encore quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En somme, Instant Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A souligner la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A noter les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller à l’intérieur|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Cheri Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus initial est super. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par ailleurs des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Cheri Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Ajoutons que le site est fluide et attractif, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A noter les evenements communautaires engageants, qui stimule l’engagement.
En savoir plus|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Frumzi Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, occasionnellement des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, Frumzi Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A noter la navigation est claire et rapide, booste le fun du jeu. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des recompenses continues.
http://www.frumzicasinopromofr.com|
Топ онлайн казино Україна — чудовий спосіб відпочити та виграти. Онлайн казино на гривні робить гру ще зручнішою.
Казино онлайн Україна пропонують вигідні бонуси без ризику. Потрібен короткий список найнадійніших брендів? Перевірте кращі онлайн казино україни та умови верифікації. Українське казіно пропонує фріспіни для нових користувачів.
Рейтинг казино Україна створено на основі реальних відгуків. Українське казино підтримує популярні платіжні сервіси. Ліцензійні казино України мають сучасні мобільні платформи. Легальні онлайн казино України підтримують гривню. Онлайн казино Україна пропонує сучасні способи поповнення.
Узнать больше здесь: https://zebraschool.com.ua
экскаватор погрузчик jcb аренда москва arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-2.ru .
Магазин профессиональной косметики https://sinapple.ru/collection/ispanskaya-kosmetika?page=15
где купить дипломы медсестры где купить дипломы медсестры .
съемка подкастов http://www.studiya-podkastov-spb4.ru .
Hi to every single one, it’s really a pleasant for me to pay a quick visit this web site, it contains precious Information.
сайт кракена
The best choice I made for using the bridge. Smooth and useful analytics.
MERYTRH902574MAVNGHJTH
Je suis sous le charme de Frumzi Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, quelquefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. En fin de compte, Frumzi Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour completer l’interface est lisse et agreable, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages uniques.
Parcourir le site|
J’adore le dynamisme de Cheri Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, toutefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. En resume, Cheri Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A mentionner le site est rapide et style, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A souligner les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements securises.
http://www.chericasinologinfr.com|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Frumzi Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, a l’occasion des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Frumzi Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Entrer sur le site|
Je suis captive par Instant Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, mais encore des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Au final, Instant Casino assure un fun constant. Pour completer l’interface est lisse et agreable, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce le lien communautaire.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
Je suis fascine par Wild Robin Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est simple et transparent, en revanche quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En resume, Wild Robin Casino assure un fun constant. En complement la navigation est claire et rapide, booste le fun du jeu. A noter les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui booste la participation.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Instant Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, rarement quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour finir, Instant Casino garantit un amusement continu. Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Lire la suite|
Je suis accro a Cheri Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Globalement, Cheri Casino assure un fun constant. A noter le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A mettre en avant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des recompenses continues.
https://chericasinomobilefr.com/|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Frumzi Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, bien que quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour conclure, Frumzi Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A mentionner le site est rapide et immersif, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un atout les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des recompenses continues.
Entrer sur le site|
I personally find that i’m impressed by the stable performance. I’ll definitely continue using it. Support solved my issue in minutes.
I switched from another service because of the easy onboarding and great support.
Could the rise of non-tech positions in data centers signal a paradigm shift in the tech industry, where traditional roles become less dominant, and support, maintenance, and infrastructure jobs take center stage? our website, we offer present-day and the best IT solutions an eye to your business] kodx.uk
If you want to receive the exclusive betwinner welcome bonus, go to https://bet-promo-codes.com/sportsbook-reviews/betwinner-registration/ and fill in your details during registration. The reward will be credited after your first deposit.
I’ve been using it for half a year for exploring governance, and the trustworthy service stands out.
Astute loli p*orn
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
Great site, i recommend it to everyone <a href="https://steemit.com/crypto/@cryptoflowernews/is-manta-bridge-safe-security-model-mpc-validators-and-cross-chain-risks-2025-analysis"
Оформите займ https://zaimy-88.ru онлайн без визита в офис — быстро, безопасно и официально. Деньги на карту за несколько минут, круглосуточная обработка заявок, честные условия и поддержка клиентов 24/7.
J’ai un faible pour Betzino Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, par ailleurs quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour finir, Betzino Casino garantit un amusement continu. A signaler le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, renforce le lien communautaire.
Passer à l’action|
Je suis completement seduit par Viggoslots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des tables live interactives. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, quelquefois quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour finir, Viggoslots Casino vaut une visite excitante. D’ailleurs le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A signaler les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Plonger dedans|
I’ve been using it for almost a year for using the bridge, and the fast transactions stands out. My withdrawals were always smooth.
J’adore l’energie de Vbet Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des transactions rapides. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains arrivent sans delai, occasionnellement des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En somme, Vbet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Notons aussi l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des bonus exclusifs.
https://vbetcasinobonusfr.com/|
I’ve been using it for a week for providing liquidity, and the seamless withdrawals stands out.
Оформите займ https://zaimy-61.ru онлайн без визита в офис — быстро, безопасно и официально. Деньги на карту за несколько минут, круглосуточная обработка заявок, честные условия и поддержка клиентов 24/7.
METYUTYJ2620317MAWRERGTRH
Great site, i recommend it to everyone <a href="https://dapplooker.com/dashboard/manta-bridge-dashboard-2025-1285"
our website, we suggest up to date and the wealthiest IT solutions through despite your vocation] kodx.uk
Could we explore the surprising ways data centers have induced employment outside the traditional tech realm, thereby creating a significant 4.7 million jobs in the U.S., despite lacking direct hiring of tech workers? our website, we suggest modern and the best IT solutions an eye to your house] kodx.uk
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Viggoslots Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est simple et transparent, en revanche des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Viggoslots Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A noter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un atout les transactions en crypto fiables, assure des transactions fluides.
Plongez-y|
Je suis completement seduit par Betzino Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, a l’occasion plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En bref, Betzino Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement super les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fluides.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
Je suis totalement conquis par Betzino Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps en temps des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Betzino Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Notons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, booste le fun du jeu. Un bonus les transactions en crypto fiables, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Voir la page d’accueil|
J’ai un faible pour Vbet Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des tables live interactives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour conclure, Vbet Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement super les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Entrer sur le site|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Posido Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, de temps en temps des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour finir, Posido Casino offre une aventure memorable. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est simple et engageante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires dynamiques, assure des transactions fiables.
Voir les dГ©tails|
Untested loli po*rn
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
seo agency ranking http://reiting-seo-kompanii.ru/ .
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Viggoslots Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, malgre tout des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En fin de compte, Viggoslots Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Notons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement cool les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste la participation.
Explorer maintenant|
Je suis fascine par Betzino Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, a l’occasion des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, Betzino Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que le design est moderne et attrayant, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Plongez-y|
Je suis totalement conquis par Vbet Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, occasionnellement plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En bref, Vbet Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement fun les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le lien communautaire.
Aller plus loin|
J’adore l’energie de Posido Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour finir, Posido Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons aussi le site est rapide et immersif, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, assure des transactions fiables.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Качественный ремонт техники HP в столице. Обслуживаем срочно. Официальная гарантия на работы. Запишитесь прямо сейчас.
hp сервисный центр серебрякова hp центр на люсиновской
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betzino Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par ailleurs plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est simple et engageante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point cle les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Explorer le site|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Viggoslots Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est clair et efficace, rarement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Viggoslots Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En bonus l’interface est lisse et agreable, facilite une immersion totale. A noter les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, cree une communaute soudee.
Visiter la plateforme|
J’adore le dynamisme de Viggoslots Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est transparent et rapide, rarement des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Viggoslots Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, booste l’excitation du jeu. A noter les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste la participation.
Cliquer pour voir|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Betzino Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, en revanche des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour finir, Betzino Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Pour ajouter l’interface est lisse et agreable, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un element fort les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements securises.
DГ©couvrir plus|
Je suis bluffe par Vbet Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais encore plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Au final, Vbet Casino assure un fun constant. A signaler le design est moderne et attrayant, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement top les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des privileges personnalises.
Essayer ceci|
Je suis enthousiasme par Vbet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, occasionnellement des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Vbet Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A noter le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un avantage les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, renforce la communaute.
Obtenir plus|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Posido Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des tables live interactives. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Posido Casino merite un detour palpitant. En extra la navigation est fluide et facile, facilite une experience immersive. Un avantage notable les options variees pour les paris sportifs, offre des recompenses continues.
Commencer Г explorer|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Posido Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par contre des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En resume, Posido Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A signaler le design est tendance et accrocheur, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement fun les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Explorer plus|
J’ai un faible pour Posido Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Posido Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un atout les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller sur le site web|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Betzino Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, malgre tout des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Betzino Casino merite une visite dynamique. A noter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement genial les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, assure des transactions fluides.
Aller sur le site web|
Здесь
покупайте продавайте
Je suis fascine par Betway Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, a l’occasion plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En bref, Betway Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En complement le site est rapide et immersif, facilite une experience immersive. Un atout les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, renforce le lien communautaire.
Obtenir des infos|
Je suis completement seduit par Betway Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, rarement plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Betway Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En extra la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A signaler le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, cree une communaute vibrante.
Explorer davantage|
Je suis epate par Belgium Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, a l’occasion plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Belgium Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, qui booste la participation.
Voir le site|
Je suis epate par Betway Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, par moments des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Betway Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. De plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, garantit des paiements rapides.
Explorer plus|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Gamdom Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, par ailleurs des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour conclure, Gamdom Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. De plus l’interface est lisse et agreable, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, garantit des paiements rapides.
Commencer Г naviguer|
Je suis enthousiasme par Betify Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par moments quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En fin de compte, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement genial les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir|
Je ne me lasse pas de Gamdom Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, bien que quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Au final, Gamdom Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En complement le design est moderne et energique, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui motive les joueurs.
En savoir plus|
Je suis totalement conquis par Betify Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, mais encore des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour faire court, Betify Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste la participation.
Voir maintenant|
Surmised loli porn
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
Je suis bluffe par Betway Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est simple et transparent, par ailleurs des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En bref, Betway Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A signaler l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, cree une communaute soudee.
Lire les dГ©tails|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Betway Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, bien que quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Betway Casino assure un fun constant. Par ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Plongez-y|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Belgium Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En bref, Belgium Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement top les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste la participation.
Naviguer sur le site|
Je suis bluffe par Gamdom Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, malgre tout quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En resume, Gamdom Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et fluide, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement genial les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des recompenses continues.
VГ©rifier le site|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Betway Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, parfois des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour conclure, Betway Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, booste le fun du jeu. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses regulieres.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Gamdom Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La gamme est variee et attrayante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Gamdom Casino vaut une visite excitante. D’ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un avantage notable les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui stimule l’engagement.
VГ©rifier le site|
Je suis captive par Betify Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus initial est super. Le service client est excellent. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, parfois quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Betify Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour completer le site est rapide et immersif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un avantage les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui motive les joueurs.
Visiter la plateforme|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Betway Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par moments plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour faire court, Betway Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En plus le site est rapide et immersif, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un element fort les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Passer à l’action|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Unbelievable loli p^orn
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
Усі подробиці: https://presa.com.ua/news.html
Автосервис «5 Бокс» — это профессиональный ремонт автомобилей https://auto-5-box.ru отечественных и иностранных марок. Проводим диагностику, ремонт двигателя, подвески, тормозной системы, рулевого управления и автоэлектрики. Выполняем замену масел, фильтров, ремней ГРМ, обслуживаем кондиционеры. Современное оборудование позволяет точно определить неисправность и устранить её быстро и качественно. Используем оригинальные и проверенные запчасти. Гарантируем прозрачные цены и честную работу. Приезжайте в «5 Бокс» — восстановим надёжность и комфорт вашего автомобиля.
Усі подробиці: https://suntimes.com.ua/sport.html
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Betway Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par ailleurs plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En conclusion, Betway Casino vaut une visite excitante. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un bonus les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fluides.
Commencer Г naviguer|
Je suis emerveille par Belgium Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, par contre des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Au final, Belgium Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Notons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A signaler les options variees pour les paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Commencer ici|
Je suis epate par Gamdom Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Globalement, Gamdom Casino vaut une visite excitante. Notons aussi l’interface est lisse et agreable, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage les evenements communautaires engageants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Obtenir des infos|
Je suis emerveille par Gamdom Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, occasionnellement plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En resume, Gamdom Casino vaut une visite excitante. En bonus le site est rapide et engageant, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A mettre en avant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, renforce le lien communautaire.
Voir maintenant|
Je suis bluffe par Betify Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, cependant des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, Betify Casino assure un fun constant. A mentionner la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement top les options variees pour les paris sportifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Apprendre les dГ©tails|
J’ai un faible pour Betify Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, Betify Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour completer l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Aller sur le site web|
Je suis completement seduit par Belgium Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, rarement des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En resume, Belgium Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour ajouter le site est fluide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un bonus les transactions en crypto fiables, qui motive les joueurs.
Lancer le site|
J’adore l’energie de Betify Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, occasionnellement des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour faire court, Betify Casino merite une visite dynamique. En bonus le design est moderne et energique, apporte une energie supplementaire. Egalement genial les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements rapides.
Ouvrir la page|
Je suis emerveille par Betway Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par moments des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En resume, Betway Casino merite un detour palpitant. De surcroit la navigation est intuitive et lisse, facilite une experience immersive. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, garantit des paiements securises.
Explorer le site|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5
euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara
apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas
deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones
apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas
online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas
deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app
apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre
amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de
apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas
deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas
colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app
de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de
apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar
dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de
casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app
para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para
hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de
apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas
mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de
apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender
hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros
gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas
a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas
a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis
wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas
y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas
android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas
argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia
cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina
holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina
mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas
argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas
ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas
athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic
real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas
atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico
campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid
real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas
baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas
baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca
bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas
barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça
madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca
vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona
atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona
atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona
bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de
liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas
barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas
basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas
betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs
valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de
bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo
de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo
femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas
brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas
caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos
zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions
2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas
campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas
campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas
campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga
santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier
league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de
galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas
carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de
caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos
online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas
carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas
casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino
online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas
casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas
celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta
real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas
champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas
chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas
chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs
colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas
ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas
ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas
colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia
brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas
colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas
combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas
combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas
mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para
hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas
combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para
hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas
comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero
ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero
virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap
baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de
debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa
africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa
argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa
del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas
copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa
mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas
de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas
de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de
boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas
de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como
se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas
de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de
caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas
de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos
online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas
de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes
en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas
de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de
fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de
futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas
de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de
futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de
futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas
de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de
fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol
seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de
galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos
trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre
hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de
la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas
de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas
de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de
peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de
peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas
de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de
mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del
dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas
del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10
euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas
1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas
argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas
bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas
deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de
mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas
com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas
para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas
deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas
con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas
deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas
copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas
deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas
cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas
de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas
deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas
deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas
en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas
españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas
europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas
deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis
hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas
deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas
legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado
clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas
deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas
mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online
argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas
online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online
españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas
deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por
internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas
para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas
deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real
madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas
rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas
seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador
eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas
telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis
de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas
deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com
foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos
pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso
primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas
dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas
division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble
resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas
dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas
draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el
clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas
en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de
futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas
en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas
en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas
en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas
en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de
fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas
en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas
en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos
de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo
futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo
nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas
en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas
españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas
españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa
georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español
oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas
esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports
gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas
esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa
campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa
league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas
f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles
para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas
final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas
final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas
final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas
final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa
league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina
betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia
españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol
americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol
chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol
consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas
fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas
futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol
hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas
futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol
sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos
hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador
champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas
ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador
la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador
mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas
ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas
girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona
gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona
real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas
gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para
hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas
gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas
gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap
baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas
handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey
patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas
holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas
hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter
barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos
en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores
nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga
santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas
las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas
legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas
libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga
argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de
hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas
linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas
lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid
atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas
madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid
betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas
madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid
osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca
real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas
seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas
mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb
las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas
mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples
el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial
baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas
mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas
mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial
rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas
nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas
nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas
nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl
playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana
4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas
online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas
online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online
comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online
deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas
online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis
sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online
nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online
tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online
venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas
osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas
países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el
clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para
eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para
ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para
hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para
hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas
para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para
la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas
para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas
partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas
partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido
mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos
champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas
partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas
paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas
peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas
por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por
paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas
portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos
gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas
puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que
significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara
a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana
la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas
quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo
barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real
madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid
barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid
celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real
madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real
madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester
city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas
real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs
atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas
real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real
sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas
real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas
recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas
resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world
cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda
b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas
segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas
seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras
hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras
nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas
seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy
fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas
semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas
sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de
madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas
sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples
ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas
sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas
sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema
calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas
tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis
de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas
tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas
tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas
tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera
division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster
para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas
torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions
league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc
hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc
telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas
uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us
open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid
valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas
venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas
villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester
united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales
futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas
vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina
colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina
vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico
en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real
madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid
apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid
apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg
apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs
atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de
datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best
america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis
apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis
madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas
de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida
apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca
apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas
sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono
de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de
apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro
apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por
registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de
apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida
apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de
apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de
apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas
de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis
casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos
paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas
de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas
para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de
cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de
apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas
combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora
apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas
yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora
de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para
apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora
poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora
sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading
apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular
apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas
apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de
apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera
de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de
apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de
galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas
atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono
gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa
apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa
de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de
apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas
bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de
apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de
apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de
apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas
colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago
anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa
america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa
de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas
de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del
madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas
deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas
en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas
deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa
de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de
apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas
madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas
peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas
deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa
de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa
de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso
minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1
euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa
de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de
apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa
de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de
apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa
de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa
de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa
de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa
de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas
que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas
sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia
en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas
tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa
de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas
apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas
colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas
esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso
minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas
apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas
tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas
de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de
apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de
apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas
de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas
chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas
con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de
apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas
con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas
de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas
con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de
apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de
apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal
en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta
en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas
de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas
de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas
en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas
deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas
de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas
de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas
deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas
de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de
apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas
en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de
apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de
apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas
de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas
de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de
apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas
de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas
de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas
legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas
de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas
mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas
de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no
reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas
de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas
españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de
apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas
online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online
en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas
de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas
online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de
apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas
para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono
sin deposito|casas de
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
I’ve been active for a week, mostly for trading, and it’s always stable performance.
I value the great support and quick deposits. This site is reliable.
I personally find that the interface is low fees, and I enjoy using the bridge here.
I personally find that i’ve been using it for half a year for fiat on-ramp, and the intuitive UI stands out.
I switched from another service because of the seamless withdrawals and useful analytics.
Je suis epate par Betway Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Globalement, Betway Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Notons egalement le design est style et moderne, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement cool les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, renforce le lien communautaire.
Aller Г la page|
для чего нужен снилс зачем нужны презервативы полный разбор
Читайте ответы на актуальные вопросы в удобной базе знаний от опытных экспертов. Актуальные рекомендации для дома и саморазвития. Получайте новые знания каждый день.
зачем разводят мосты в питере аппендикс зачем он нужен и какую
Je suis accro a Betway Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par ailleurs plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour conclure, Betway Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et fluide, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Explorer le site|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Belgium Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est simple et transparent, parfois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Au final, Belgium Casino vaut une visite excitante. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Obtenir plus|
Je suis totalement conquis par Gamdom Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, bien que des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, Gamdom Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je suis enthousiasme par Betify Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots fluides. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, en revanche quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En somme, Betify Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour ajouter le design est moderne et attrayant, booste le fun du jeu. A mettre en avant les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Entrer sur le site|
Je suis epate par Belgium Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, bien que quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, Belgium Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour ajouter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fluides.
AccГ©der maintenant|
Je suis fascine par Betify Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, malgre tout des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour conclure, Betify Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A noter la navigation est intuitive et lisse, facilite une experience immersive. A noter les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, renforce la communaute.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
Je ne me lasse pas de Belgium Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par ailleurs des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour faire court, Belgium Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Pour couronner le tout le design est style et moderne, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Commencer Г explorer|
J’adore l’energie de Betify Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus initial est super. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En fin de compte, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A signaler le design est moderne et energique, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges personnalises.
Voir la page|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
шлюхи тюмень индивидуалки у них дома
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15
euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas
que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas
deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para
hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas
deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones
de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para
hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas
entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas
sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app
control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de
apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de
apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas
argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas
ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas
en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de
apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas
peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app
para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para
apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas
deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas
deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas
deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de
apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para
apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta
del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas
1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas
a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas
a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas
al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania
españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y
bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas
android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas
nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas
argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina
francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas
argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas
argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs
colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas
ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic
real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid
barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real
madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico
madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico
real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas
atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas
baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto
prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca
girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas
barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca
vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona
atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas
barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas
barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas
barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas
barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas
barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas
barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis
real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas
betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de
bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos
sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas
boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas
caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas
caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas
campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas
campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas
campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas
campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas
campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas
campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos
de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera
de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras
de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras
de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino
gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas
casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta
madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas
champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions
league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league
pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas
champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas
chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo
femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city
real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas
colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas
combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas
combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas
combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero
ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa
africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas
copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa
del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey
pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial
de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas
cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto
hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto
para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo
en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas
de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas
de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas
de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas
de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de
caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de
carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de
casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions
league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas
de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas
de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol
en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas
de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol
hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol
para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas
de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas
de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos
como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas
de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos
deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas
de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas
de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de
la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas
de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas
de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de
tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas
del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido
de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas
del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1
euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas
deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas
deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas
barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono
sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas
deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas
como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas
con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas
consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas
deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas
corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas
deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas
en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas
en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas
en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas
deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas
deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa
league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas
deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas
futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas
futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas
deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero
seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas
gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas
handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas
deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores
casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas
deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas
mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas
murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas
online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online
mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online
peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para
ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|Apuestas Deportivas Partidos De Hoy
(Demo.Consortia.No)|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas
deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas
pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas
regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas
seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para
hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas
deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas
deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas
deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas
deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1
euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas
division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles
y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador
vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de
futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas
en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la
champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas
en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas
en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de
fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea
futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas
en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los
esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de
futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo
casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo
mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas
españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa
italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español
oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas
esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas
esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas
eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas
eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa
sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas
europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league
pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas
f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1
miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas
faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas
favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa
del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas
final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas
fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol
americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas
futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol
femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas
futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas
futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas
galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas
gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa
america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas
ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas
ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas
ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas
ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas
ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona
campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles
asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas
golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas
gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis
hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis
sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas
hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas
hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas
hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy
nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises
bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos
en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos
baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador
sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga
hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas
mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league
of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales
en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1
peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas
liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga
de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga
española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea
de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas
liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas
madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas
madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid
campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas
madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas
madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles
de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas
maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas
mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas
méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb
las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma
ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas
multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial
balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas
mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial
de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas
mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas
mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto
gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas
mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas
nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba
hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas
nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas
nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl
pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl
semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas
nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online
bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas
online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas
online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online
comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas
online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online
gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas
online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online
paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over
2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises
bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas
países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas
para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas
para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para
ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas
para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas
para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar
la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas
para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para
juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la
copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para
la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba
hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas
para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas
partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas
partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas
partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos
de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos
eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas
partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru
chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas
peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff
ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas
playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet
mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por
ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre
partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos
deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas
prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos
por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que
aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer
con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas
real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas
real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas
real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real
madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid
celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas
real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid
hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid
real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs
atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs
barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real
madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad
athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real
sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real
sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas
regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas
resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas
roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda
división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas
seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas
seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy
futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para
hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para
hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas
seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas
sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester
united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real
sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla
valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o
combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito
minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas
sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas
sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas
sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas
stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa
españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas
tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis
atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de
mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas
tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis
wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas
trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas
uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas
ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas
ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas
villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia
real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid
valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas
villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales
colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta
españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas
y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos
de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina
croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina
peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina
vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina
vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico
apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona
apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico
barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico
de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca
vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid
apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona
atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona
vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta
de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona
vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona
vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas
en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla
apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono
apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis
sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida
apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida
apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa
de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono
de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de
registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro
apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa
de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito
casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos
apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos
bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas
apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos
casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas
nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas
gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de
casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos
gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de
apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para
hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora
apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora
apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora
de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje
apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading
apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular
apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular
ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad
cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas
apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga
apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de
caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras
de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de
mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas
deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa
apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa
apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico
de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa
de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono
por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa
de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de
apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa
de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de
colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa
de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del
madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas
deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas
en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas
en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa
de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito
5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa
de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas
españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa
de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula
1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso
minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas
liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas
mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa
de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa
de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas
nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa
de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas
online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de
apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de
apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa
de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas
peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que
regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa
de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas
venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial
de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas
apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas
deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas
licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas
apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas
online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas
apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas
de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas
de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de
apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas
de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de
apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca
de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas
de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas
de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de
apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago
anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas
de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas
de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas
deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas
españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas
de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas
deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1
euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas
de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas
en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas
españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas
españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de
apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas
eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de
apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas
inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas
de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de
apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas
licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores
bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de
apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas
mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas
nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas
en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas
ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online
ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas
online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas
online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas
de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypa
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Azur Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, mais des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Au final, Azur Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement captivante, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un bonus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, assure des transactions fiables.
Parcourir le site|
Mod loli por*n
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Je suis sous le charme de Azur Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est clair et efficace, bien que plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En bref, Azur Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. De plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A signaler les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui booste la participation.
Ouvrir maintenant|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Lucky 31 Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En fin de compte, Lucky 31 Casino vaut une visite excitante. En extra le site est fluide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A signaler les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, cree une communaute vibrante.
https://lucky31casino777fr.com/|
Je ne me lasse pas de Azur Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par moments plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En somme, Azur Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. De surcroit le site est fluide et attractif, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un plus les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des recompenses continues.
Avancer|
J’ai un faible pour Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, mais encore des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, Lucky 31 Casino merite un detour palpitant. En plus le site est rapide et immersif, facilite une immersion totale. A signaler les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, renforce le lien communautaire.
En savoir davantage|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de 1xBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, quelquefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. En fin de compte, 1xBet Casino garantit un amusement continu. A signaler l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste le fun du jeu. A souligner les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Aller Г la page|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Action Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Globalement, Action Casino garantit un amusement continu. A souligner le site est rapide et style, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un point cle les evenements communautaires engageants, cree une communaute soudee.
Savoir plus|
J’adore la vibe de Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par moments des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En resume, Action Casino assure un fun constant. En plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A signaler les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, assure des transactions fluides.
Apprendre comment|
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10
trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas
que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas
deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas
deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones
apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de
fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas
online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas
deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas
deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa
de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas
deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas
en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de
apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para
android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas
de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas
de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de
apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de
apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de
apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas
deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del
dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2
division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la
nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al
mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso
campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y
bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas
apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas
argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina
españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia
mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs
colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas
argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real
madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas
athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas
athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic
real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas
atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de
madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos
olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas
barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas
barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça
madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona
athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas
barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona
espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas
barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona
inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona
psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real
sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas
beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas
betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas
bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas
bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real
madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas
boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas
boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas
boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas
brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas
caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del
mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa
league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas
campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas
campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas
campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de
caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera
de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas
carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de
caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas
carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de
galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino
online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta
barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas
champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions
hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas
champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league
pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile
venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo
en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city
real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas
colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas
combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo
partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas
combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas
seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas
con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de
credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa
argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de
europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas
copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey
final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa
del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas
copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de
hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas
de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol
para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo
online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos
en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas
de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos
juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de
carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de
champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa
league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas
de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de
futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol
en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de
futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas
de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de
fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de
futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol
sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas
de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas
de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de
la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la
liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas
de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de
nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas
de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas
de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema
como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema
explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas
de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis
pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de
ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas
del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del
dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas
del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas
deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas
deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina
legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas
deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas
deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas
deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas
com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas
com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos
gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas
deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas
deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la
mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas
deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero
ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble
oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas
deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas
en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas
deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas
es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas
deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas
eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas
foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol
colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas
deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis
con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas
handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas
la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas
legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas
deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas
seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas
deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas
méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas
deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas
online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online
paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar
dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas
paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas
deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas
deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras
foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas
seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas
sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas
tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas
deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas
deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda
b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas
diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor
juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y
triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador
vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto
uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas
en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas
en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas
en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas
en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las
vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas
en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de
fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas
en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea
méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico
online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas
en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas
en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos
de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas
españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas
españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa
holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises
bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol
betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports
lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro
copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas
eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas
eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas
euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league
pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1
cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas
f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de
ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas
favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos
champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc
barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final
copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final
copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas
final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas
finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol
en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol
juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol
virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos
online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador
copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador
de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas
ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas
ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas
ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador
nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar
champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona
campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas
goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas
golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas
gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas
gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas
handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas
hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas
hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda
argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas
hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas
hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas
juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas
juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas
la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas
la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las
vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales
en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander
pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid
arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas
madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas
madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid
sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas
manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real
madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas
seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico
polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas
mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas
multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de
ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de
futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial
f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial
formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas
mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas
nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba
para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba
tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana
4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas
ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online
argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online
caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online
espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online
gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online
nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online
uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real
madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para
el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas
para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para
ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para
hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa
del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa
league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de
hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido
aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido
colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol
hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru
vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso
a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet
mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal
uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por
tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que
puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas
quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la
eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara
la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas
real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real
madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas
real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid
atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid
barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas
real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid
valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid
vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad
real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas
resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas
retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma
sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta
seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras
calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas
seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este
fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para
hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas
sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla
girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla
manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla
roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que
significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo
copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake
10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis
de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas
tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas
tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis
wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas
topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa
league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia
topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal
betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas
villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta
a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas
y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de
futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina
vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic
barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid
apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs
real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona
apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca
madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico
apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona –
real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid
apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter
apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona
sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona
vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs
sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal
apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol
apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu
sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog
apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono
apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida
apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa
apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono
de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida
apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas
deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por
registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro
casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas
deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos
apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos
apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos
apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas
de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos
de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida
de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito
apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador
cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar
apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de
sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas
seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de
apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora
de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora
de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping
apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular
apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas
deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias
apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota
apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo
de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de
galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa
apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores
cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de
apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de
apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono
bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa
de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas
caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de
apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de
apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las
mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa
de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas
de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa
de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de
mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas
en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de
apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1
euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de
apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa
de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales
en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa
de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de
apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de
apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa
de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online
peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa
de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de
apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa
de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de
apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa
de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas
ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas
venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de
apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono
sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas
apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas
españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas
apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas
legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia
españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas
apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas
ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas
paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas
tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas
de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas
de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono
sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas
de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de
apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de
registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas
con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos
gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia
española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas
con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de
futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas
colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas
con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas
de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de
apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de
apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de
apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas
en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas
españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas
de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas
de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas
con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas
de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de
apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de
apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas
fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de
apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo
1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas
de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas
de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas
licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de
apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas
seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5
euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial
baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no
reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas
nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas
españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas
de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas
de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de
apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de
apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas
de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas
peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales e
Great site, i recommend it to everyone <a href="https://dapplooker.com/dashboard/manta-bridge-dashboard-2025-1285"
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Je suis completement seduit par Azur Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est transparent et rapide, mais des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour finir, Azur Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En extra l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, permet une immersion complete. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Attractive part of content. I simply stumbled upon your weblog and in accession capital to say that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your weblog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing in your augment or even I fulfillment you access consistently quickly.
https://tester.sohbet.org/bonusy-melbet-2025/
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar
apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto
se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america
apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas
deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de
apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer
apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas
android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones
de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas
gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de
apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app
android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app
apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas
colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app
apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app
apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas
android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app
de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de
apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas
deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de
apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar
dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app
marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para
apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para
apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras
de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz
hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y
bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas
america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas
antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas
argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia
mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana
mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina
polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina
vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina
vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic
barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester
united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic
real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas
athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico
campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico
de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real
madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas
baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca
bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas
barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca
madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas
barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de
madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona
campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas
barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona
girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona
hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona
vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas
beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis
girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas
betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy
colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas
bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real
madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil
vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas
caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de
barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa
del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas
campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas
campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas
campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas
campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas
campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de
futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos
hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos
fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras
caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas
carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas
carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras
de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas
carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino
futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas
casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta
madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions
league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions
league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas
chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile
vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo
femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas
colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas
de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas
combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas
combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas
combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas
como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero
real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas
con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas
copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas
copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas
copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas
copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial
de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia
argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas
altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de
baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo
canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo
hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas
de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos
españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas
de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de
carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas
de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas
de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de
dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas
de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol
español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas
de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol
para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas
de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras
para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de
galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas
de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de
la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de
la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la
nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de
peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros
virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de
sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis
de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de
todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas
del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas
deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas
deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina
legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas
colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas
deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos
gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas
deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas
cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de
baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de
nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas
deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas
deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas
deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas
en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas
en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas
deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas
faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas
francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas
deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas
gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis
hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas
deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas
legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas
listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas
mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb
hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas
ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online
colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas
deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas
online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas
partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas
deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas
deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas
real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas
seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas
deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas
deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas
deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas
deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas
deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas
deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos
pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a
segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso
primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero
real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas
division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas
draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas
ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas
en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el
futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos
deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas
en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las
vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas
en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea
méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los
esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos
de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos
de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo
tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas
españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas
españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa
francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana
eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas
españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa
mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español
oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports
lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa
sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas
europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1
abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1
china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1
miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito
champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos
eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas
fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas
final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas
final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final
rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas
francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas
futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol
español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas
futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol
sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas
galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas
gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador
copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas
ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador
mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas
ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas
ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana
la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador
eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis
por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis
sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar
premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas
handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas
hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas
holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy
nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises
bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas
juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas
kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la
liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas
nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas
legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea
de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas
madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid
city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas
madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles
de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor
jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas
mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas
mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas
multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas
mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial
ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial
femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas
mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba
campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas
nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas
nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas
nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas
nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas
online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas
online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas
online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas
online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas
online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas
online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas
open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas
osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas
over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos
inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para
champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para
el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido
de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para
ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para
ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas
para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para
hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para
la europa league|apuestas para la final de
la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido
mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos
futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas
perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs
chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff
ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas
playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs
nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas
por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos
futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es
handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas
quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el
mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas
quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real
madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real
madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid
borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real
madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas
real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas
real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real
madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real
sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas
registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas
segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas
seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras
futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para
este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas
seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla
atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la
liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas
sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas
sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas
stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga
argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas
tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis
de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas
tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis
wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de
golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas
uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas
ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas
us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas
valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid
valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas
valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas
villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas
villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas
virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta
a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y
pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina
apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico
apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico
apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic
osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs
real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid
apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas
apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca
madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid
apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona
atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona
real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia
apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs
atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs
celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid
apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona
vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best
america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona
apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de
apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas
nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono
apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas
sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida
apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono
bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de
apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de
apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida
apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono
de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono
de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono
por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito
marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas
colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos
apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida
apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas
de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos
casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de
apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de
casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas
de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de
apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito
apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil
colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas
para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de
cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador
de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas
deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora
apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora
cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora
de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora
de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora
poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping
apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas
deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular
cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de
galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de
caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas
trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca
de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas
española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa
apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa
apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de
apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico
de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas
boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de
apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de
apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas
con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa
de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas
de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas
deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de
mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas
españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas
españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa
de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de
apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso
mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas
madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de
apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa
de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de
apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa
de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de
apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas
pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa
de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa
de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de
ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa
de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de
apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del
real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas
apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas
apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas
españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas
apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas
apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas
licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas
apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas
tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas
de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos
de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas
de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas
de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas
colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de
apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono
por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas
con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de
apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas
de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas
de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas
copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de
futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de
apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas
de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas
de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas
deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas
de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de
apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas
de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas
españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas
españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de
apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de
apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas
de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas
gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas
inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales
en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales
en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas
licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas
de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas
de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas
mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no
reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de
apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de
apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas
españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas
online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online
en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online
en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online
peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de
apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apu
Je suis captive par Azur Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est simple et transparent, rarement plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour conclure, Azur Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement excellent les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui motive les joueurs.
En savoir davantage|
Je suis accro a 1xBet Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais encore des offres plus importantes seraient super. En bref, 1xBet Casino vaut une visite excitante. A noter le site est fluide et attractif, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A signaler les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements rapides.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, bien que plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino assure un fun constant. A mentionner la navigation est simple et intuitive, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les options de paris sportifs variees, qui motive les joueurs.
Essayer ceci|
Je suis fascine par 1xBet Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les options de jeu sont infinies, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, a l’occasion des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, 1xBet Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour ajouter le site est rapide et engageant, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un element fort les evenements communautaires engageants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Voir le site|
Je ne me lasse pas de Lucky 31 Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, quelquefois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En bref, Lucky 31 Casino garantit un amusement continu. A mentionner l’interface est intuitive et fluide, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement attrayant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste la participation.
DГ©couvrir plus|
J’adore le dynamisme de Action Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est simple et transparent, neanmoins des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En conclusion, Action Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. De plus le site est rapide et immersif, facilite une experience immersive. Un element fort les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos
para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que
significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades
de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america
apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas
deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas
de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de
apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones
de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar
seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas
deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas
españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app
apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas
sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas
colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas
deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app
de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app
de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app
de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app
de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca
apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar
apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app
para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar
control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas
de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100
seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3
division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas
a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al
barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves
barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas
altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos
marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas
anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina
francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana
el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas
argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina
polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs
australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas
argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a
primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic
atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic
manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real
sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic
valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas
atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético
copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico
de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs
barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas
atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto
acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto
pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas
baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas
barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça
hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça
madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona
atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona
betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas
barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona
real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas
barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket
hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol
pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis
barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis
madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis
real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono
sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo
de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo
hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas
brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas
caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos
sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la
champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas
campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas
campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga
bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas
campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas
campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera
de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas
carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de
caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras
de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras
de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de
caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras
de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras
de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas
casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas
casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas
celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta
real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions
league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions
league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions
pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas
chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas
ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real
madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia
argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia
vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas
como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de
fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas
seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades
de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa
america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa
de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa
del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa
libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas
corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de
baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de
boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de
caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas
de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas
de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de
caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas
de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos
por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de
carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de
caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de
champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas
de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de
fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de
futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol
en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas
de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de
futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de
fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol
para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de
futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de
futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas
de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas
de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas
de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de
la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de
partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas
ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de
sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis
en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas
de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de
todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas
del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del
dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas
deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas
1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas
1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas
deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas
deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas
deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas
deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas
cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas
colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas
deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se
juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono
gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del
rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es
la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de
futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas
de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas
dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas
deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas
en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias
seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas
deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula
1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas
deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas
deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas
gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas
hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas
libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas
deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas
deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online
chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online
en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas
deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas
para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas
partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas
peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru
vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas
deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas
deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas
deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia
barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas
deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito
minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso
la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas
doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles
y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs
argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas
en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas
en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas
en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos
virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas
en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea
chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea
estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea
méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea
usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis
en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas
en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas
en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo
fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo
ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa
croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa
gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas
españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol
betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports
españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports
gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas
euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa
españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas
eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas
europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa
league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas
f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1
las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles
de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas
favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final
champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions
peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de
europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final
copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de
copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final
libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final
rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas
finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas
fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas
foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia
españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas
fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas
futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para
hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas
futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol
virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas
galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas
ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas
ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador
f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas
girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de
tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para
hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis
regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis
sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar
premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas
handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas
hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas
hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy
champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy
pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra
paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas
juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos
virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la
liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la
liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas
nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas
legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas
libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de
campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones
de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea
de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid
arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid
barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid
celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas
madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid
vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester
athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras
para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de
tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor
jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las
vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas
multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas
multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas
mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de
baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas
mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas
mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas
nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas
nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba
pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl
pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de
caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online
colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas
online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas
online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas
online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas
online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online
uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico
golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna
barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas
para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para
el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para
futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar
dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar
en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para
ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para
hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas
para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para
la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la
nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido
aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de
futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas
partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas
paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru
vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso
a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas
playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por
internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por
sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es
handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que
significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas
quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana
la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas
quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas
real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico
champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real
madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas
real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real
madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real
madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas
real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid
vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas
real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas
real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real
sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados
eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas
segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas
seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas
seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas
seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras
nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este
fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas
seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla
barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas
sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas
sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas
sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que
significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema
como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas
sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas
super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas
tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas
tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis
en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas
tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas
tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis
wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas
uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas
ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas
uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas
us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia
betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real
madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas
valor app|apuestas Valor En Directo (zabagroup.pl)|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas
venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal
barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas
villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas
villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real
madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales
sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y
juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina
croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina
mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina
vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs
francia apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico
apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united
apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico
barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico
madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter
apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca
vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico
madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic
bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis
apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol
apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis
apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog
apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de
apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de
apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono
de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de
apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro
apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono
marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por
registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito
apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca
apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas
deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos
bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos
casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas
de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas
nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos
de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos
gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos
paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito
apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos
sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia
apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de
apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de
apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora
apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas
yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora
de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas
seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora
stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas
deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular
cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas
combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas
deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo
de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos
apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos
con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos
apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de
madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono
gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas
chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas
española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa
apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas
nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa
de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa
de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas
betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de
apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de
apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa
de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas
altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa
de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa
de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de
apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas
de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa
de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del
real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa
de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas
madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de
apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito
minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa
de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa
de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de
apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa
league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa
de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa
de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga
española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa
de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa
de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de
apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas
online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas
para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de
apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de
apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa
de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de
ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de
apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de
apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas
bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas
apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas
españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas
apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas
apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas
apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas
asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas
5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de
apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de
apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de
apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de
apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions
league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas
de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas
de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de
apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de
apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de
apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de
apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas
de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de
peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas
deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas
de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas
deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas
en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de
apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas
en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de
apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas
deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de
apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas
de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito
minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de
apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas
en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas
de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas
en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de
apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas
de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa
2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de
españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter
barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas
de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas
de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas
de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas
méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de
apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas
de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas
de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas
de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas
online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de
apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de
apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago
payp
Simply want to say your article is as astonishing. The clearness to your publish is just cool and i can suppose you’re a professional in this subject. Well along with your permission let me to seize your RSS feed to keep updated with imminent post. Thank you a million and please keep up the gratifying work.
https://letsplay777.net/melbet-2025-obzor-melbet-bk/
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Официальный сайт Kraken https://kra44-cc.at безопасная платформа для анонимных операций в darknet. Полный доступ к рынку через актуальные зеркала и onion ссылки.
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos
para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis
apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis
nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de
apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer
apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas
gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas
perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de
futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas
deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de
apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app
de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app
de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app
de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas
android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas
perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas
para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de
apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de
apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app
para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas
deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de
apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps
apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de
apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros
gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras
de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas
a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a
la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al
empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y
bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina
francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas
argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina
polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs
colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a
segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic
manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic
real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic
sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico
campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de
liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico
de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico
de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real
madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas
barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca
bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça
hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas
barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca
vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas
barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona
atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona
girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real
sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas
barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas
barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas
bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas
beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas
betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas
betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis
mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas
betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas
betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas
bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de
bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos
sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo
hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs
peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas
caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de
champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de
liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas
campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas
campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas
campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas
campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas
campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas
campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos
fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos
españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos
nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos
online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras
de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas
casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas
casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas
celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions
foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas
champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas
chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas
chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico
real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia
brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas
combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas
combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas
mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas
nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas
pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas
seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas
seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas
con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa
america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa
brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas
copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas
copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial
de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas
bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para
hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de
boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo
hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas
de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de
carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas
de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de
ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas
de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas
de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas
de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol
en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de
futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol
seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas
de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas
de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de
golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy
seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa
américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la
nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para
hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas
de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas
de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema
explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis
para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de
ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del
clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia
deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas
del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas
deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de
madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas
calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas
deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas
deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas
deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas
deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es
la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de
baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas
deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del
dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas
en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas
deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas
españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas
europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas Deportivas Foro (https://Craze.cl)|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas
deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis
hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas
deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas
libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas
liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas
mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas
deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas
mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba
hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas
nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas
deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas
deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas
online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas
deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas
deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas
que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas
deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas
seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas
sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de
mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas
deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas
deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas
y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com
foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito
minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas
descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas
descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas
dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft
nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas
ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas
en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas
en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la
nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea
chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas
en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos
de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas
en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo
argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas
en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo
peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas
españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas
españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports
lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas
estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa
españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa
hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas
europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu
dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles
de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final
champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final
copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa
del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales
de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas
formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia
españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas
fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas
futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol
para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol
telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas
ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa
america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la
eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador
europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas
ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial
baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas
ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas
girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas
golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis
casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis
por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas
handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas
hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy
pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas
inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos
baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la
liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas
las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas
legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas
liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas
liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de
hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas
ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid
atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid
barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas
madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid
city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid
gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real
madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas
masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas
maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico
polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb
hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas
mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas
multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial
de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas
mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas
mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas
mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp
eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales
de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba
campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba
finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba
playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl
playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas
nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online
argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas
online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas
online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de
caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online
en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas
online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online
esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas
online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas
online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas
online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online
sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas
osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna
sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos
ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para
el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas
para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas
para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas
para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar
la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas
para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido
aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido
suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de
futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos
de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru
brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff
ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas
playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet
mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda
boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre
partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas
pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos
tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas
que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana
el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real
madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico
champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid
atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico
madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid
betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas
real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas
real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas
real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas
real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas
real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas
real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad
psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas
real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas
hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada
tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas
rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas
segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras
en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras
gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras
para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas
seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras
telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas
sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla
manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla
real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas
sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga
argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas
tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas
tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas
tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions
league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas
ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas
under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas
valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas
valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas
venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas
villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a
españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de
hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia
apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico
apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united
apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona
apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid
real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid
apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto
apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça
madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid
apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico
de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid
apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs
athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona
vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas
apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis
– chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid
apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas
tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono
apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca
apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono
casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono
por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por
registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono
sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito
marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos
apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos
apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos
casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de
apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de
apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito
apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas
de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos
sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de
cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar
apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas
seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas
apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora
de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas
multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora
de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora
sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas
combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de
apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota
apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades
apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de
apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de
caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de
caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de
caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras
de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas
atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono
bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de
mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa
apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa
apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas
nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas
argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa
de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de
apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono
gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa
de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de
apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa
de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas
con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de
apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de
apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de
apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de
apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas
en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas
deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas
deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas
deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas
en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa
de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de
apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa
de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa
de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa
de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de
apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo
5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de
apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real
madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa
de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online
españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas
online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas
pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de
apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de
apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la
suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas
asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas
apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas
apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas
españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas
apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas
apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas
apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas
nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas
apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas
app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de
apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de
apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas
cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas
de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de
apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de
registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas
con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de
apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de
apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas
de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas
con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de
españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas
deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas
colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas
en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas
de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas
online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1
euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de
apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas
en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas
españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas
de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de
apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de
apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de
apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas
de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa
2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas
en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de
apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador
eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de
apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de
apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas
de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de
apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de
apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas
de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas
de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de
apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas
online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas
online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de
apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas
online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de
apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online
venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas
que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2
que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas
que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos
de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria
ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas
deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones
de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de
apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas
deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas
de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas
deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas
colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas
gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de
apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de
apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de
apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app
de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app
de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas
reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app
moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para
apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps
de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas
a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y
bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del
mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina
croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina
francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas
argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas
argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real
madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas
atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de
liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico
de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico
de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico
de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto
nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto
pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas
barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas
barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas
barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas
barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético
de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona
celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la
champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona
inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas
barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico
madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol
venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis
barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis
mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas
betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas
borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de
campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo
español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas
boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs
colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos
online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos
zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas
campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas
campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas
campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas
campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos
de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de
galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas
carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras
de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos
hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos
nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras
de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino
barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas
casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas
celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas
champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo
en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city
madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas
clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia
vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas
combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo
partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas
para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas
con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del
rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del
rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa
europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa
sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia
argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas
cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de
baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para
hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de
boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas
de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas
de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas
de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas
de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino
por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas
de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes
online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas
de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas
de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas
de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas
de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol
pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de
futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas
de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas
de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas
de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de
la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la
europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de
la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas
de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de
ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del
dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de
hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del
sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas
1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas
deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas
bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas
cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas
deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas
con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas
con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas
copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas
cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas
de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas
de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas
dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas
deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas
en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas
es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas
f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas
formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas
foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas
deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol
colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas
deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas
ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas
gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres
de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas
seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores
paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas
deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas
deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas
deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas
nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas
online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas
online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas
resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras
para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas
sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas
sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas
deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas
deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas
valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y
casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a
segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera
division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero
virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas
division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas
dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones
venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas
en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo
pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas
en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas
en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas
en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los
esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas
en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de
mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de
futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa
francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa
gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas
españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol
barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas
esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas
euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas
eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas
eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas
eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1
cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1
monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas
faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito
champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas
final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa
del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de
conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas
formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano
nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol
champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol
en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas
futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol
hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas
futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos
online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas
ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la
eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador
la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar
liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas
getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real
sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas
golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis
para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis
sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap
como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas
online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas
hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas
holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra
paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas
inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas
la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas
las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas
legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones
de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga
españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas
madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas
madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid
dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs
barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real
sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester
city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras
para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador
mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb
las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas
mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas
multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial
de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial
formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub
17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas
nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas
nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba
hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas
nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba
tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl
las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas
nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl
pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online
argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas
online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online
con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online
españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online
futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online
golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online
nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas
online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas
online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas
open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago
anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas
países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para
ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero
facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas
para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para
ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para
hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para
la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas
para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas
para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa
marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas
partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de
futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas
partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas
partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso
a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff
segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs
nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal
uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas
primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos
deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos
gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas
puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que
es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas
que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas
real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid
atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas
real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas
real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid
vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real
madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world
cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas
segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras
calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol
hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas
seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras
para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para
hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras
tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas
sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas
sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla
inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas
sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o
combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate
que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como
funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas
stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas
tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis
de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas
tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas
tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas
tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas
tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc
chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas
ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas
ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs
colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas
valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal
liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal
manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas
virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas
virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos
de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos
deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro
nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina
vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs
francia apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico
apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic
barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs
barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico
madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico
real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas
apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca
apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid
apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real
madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico
apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona
betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg
apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona
valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs
girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona
vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas
en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu
sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono
apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas
gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono
bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida
marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa
de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis
sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono
de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de
apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis
apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro
apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono
registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono
sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito
apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono
sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas
sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos
apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos
casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos
casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas
sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de
bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de
casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de
apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos
de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis
apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de
apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas
de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru
apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas
para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de
apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de
sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas
multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de
apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora
de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora
para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas
deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular
apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas
deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular
probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular
yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas
gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera
de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras
de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos
con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa
apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas
betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas
cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa
apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa
apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico
de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa
de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa
de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca
de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa
de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa
de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas
de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa
de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas
deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas
en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas
deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas
en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa
de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas
peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa
de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa
de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas
eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa
de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa
de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa
de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial
del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de
apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa
de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online
venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas
peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas
peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas
que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de
apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas
sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa
de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa
oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas
caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas
deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas
legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas
licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas
mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas
apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas
apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas
de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono
de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas
bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de
apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de
apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas
de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas
con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de
apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de
apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas
con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas
de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del
rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas
en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas
deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de
apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas
españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas
de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas
de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de
apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos
de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas
de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas
de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas
españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas
f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas
de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de
apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de
apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas
de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas
mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de
apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas
de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas
de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas
de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de
apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas
nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas
online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas
de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas
de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online
mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas
de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas
online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas
de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales
en españa|casas de apuestas promociones|casas de apuestas
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Azur Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, rarement des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En bref, Azur Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Pour completer l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement cool les paiements securises en crypto, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Rejoindre maintenant|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Официальный сайт Kraken https://kra44-cc.at безопасная платформа для анонимных операций в darknet. Полный доступ к рынку через актуальные зеркала и onion ссылки.
The best choice I made for fiat on-ramp. Smooth and trustworthy service. Charts are accurate and load instantly.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Lucky 31 Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, par moments quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour conclure, Lucky 31 Casino assure un fun constant. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un element fort les evenements communautaires dynamiques, renforce la communaute.
Aller à l’intérieur|
J’adore la vibe de Azur Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est transparent et rapide, de temps en temps des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Au final, Azur Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. De plus l’interface est lisse et agreable, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des recompenses regulieres.
DГ©couvrir le web|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de 1xBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, 1xBet Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Par ailleurs le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un atout les options variees pour les paris sportifs, garantit des paiements securises.
http://www.1xbetcasino365fr.com|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Action Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est clair et efficace, mais encore des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour finir, Action Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En bonus le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, cree une communaute soudee.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Lucky 31 Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, parfois plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour conclure, Lucky 31 Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De surcroit la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une immersion complete. Un point fort les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste la participation.
http://www.casinolucky31fr.com|
J’adore l’energie de 1xBet Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, mais plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En resume, 1xBet Casino offre une experience inoubliable. De surcroit l’interface est lisse et agreable, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A noter les paiements securises en crypto, propose des privileges personnalises.
Essayer ceci|
Je suis captive par Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots fluides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, mais des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En fin de compte, Action Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En complement la plateforme est visuellement captivante, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement excellent les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des privileges personnalises.
Cliquez ici|
J’adore la vibe de Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino garantit un amusement continu. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, booste le fun du jeu. Un avantage les evenements communautaires dynamiques, renforce le lien communautaire.
DГ©couvrir plus|
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros
gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que
significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9
apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara
apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de
apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas
gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de
fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones
de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas
deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas
deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de
apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app
de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app
de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas
futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas
online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de
apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app
para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para
ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para
hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas
entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus
apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps
de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas
1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores
nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas
al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas
nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo
nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas
nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina
campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina
croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto
paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas
argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas
argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal
real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas
asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas
athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic
real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic
valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico
campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico
de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid
real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real
madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas
barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas
barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca
inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas
barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona
atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona
bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la
champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas
barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona
psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona
real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona
valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona
vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket
hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas
beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas
betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas
betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono
de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas
bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas
boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil
colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas
brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas
caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas
caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions
2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas
campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa
league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas
campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga
bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas
campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas
campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier
league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera
de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de
caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas
carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas
casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino
online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta
espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta
manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas
chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas
chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas
ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico
real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas
combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas
combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas
futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas
nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas
combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas
combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas
con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas
con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas
con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas
copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas
copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas
copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas
copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas
copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas
copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas
croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1
euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo
canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas
de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de
caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de
caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas
de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de
caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de
carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas
de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de
champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas
de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas
de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de
europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula
1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol
colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de
futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas
de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas
de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para
mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas
de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas
de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos
en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas
de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de
la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la
liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de
la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas
de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas
de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema
explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis
de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas
de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis
seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del
clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia
de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas
del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas
deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1
euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas
deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas
deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina
legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas
baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas
bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions
league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas
deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas
com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero
ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas
consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa
america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas
copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas
deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas
cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de
peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas
en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas
en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas
en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas
es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas
estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas
eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de
ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas
deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas
deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol
argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas
ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas
gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas
handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas
deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas
deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas
mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas
nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online
paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas
deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas
pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas
deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas
deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas
deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas
deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas
telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas
deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a
segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor
juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y
triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador
vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas
en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas
en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas
en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas
en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la
nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea
chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea
futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea
méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas
en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo
peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa
alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana
el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa
inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa
paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas
espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas
esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas
estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa
españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa
league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas
f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles
de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas
final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del
rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas
final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa
league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas
formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas
foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano
nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol
colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas
futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas
futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol
mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas
futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol
telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos
en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas
galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas
ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador
de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas
ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas
ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas
girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la
liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas
golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand
slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis
hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis
sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas
grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como
funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas
hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre
hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy
champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas
hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas
juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos
virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas
kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga
española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las
vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas
legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes
betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga
bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones
de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas
liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de
gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas
madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid
celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana
la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid
valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city
real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas
mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb
para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma
ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas
multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el
gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial
baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas
mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas
mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas
mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas
mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial
motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas
mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba
campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas
nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy
pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba
pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas
nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas
nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas
ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas
online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas
online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de
caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online
chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas
online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas
online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online
movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas
online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas
online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas
online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas
osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas
para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para
europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas
para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar
dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para
ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la
europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas
para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para
juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas
para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para
los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas
partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas
partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas
partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi
eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs
nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas
por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para
ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas
pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas
promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos
por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas
que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara
a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas
quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana
la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas
quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico
madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real
madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid
liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid
real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs
atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs
valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas
regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas
resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada
tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas
rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas
segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda
division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas
seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras
futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras
nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras
para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises
bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico
de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla
campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla
gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas
sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas
sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que
significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas
sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas
stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas
superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas
tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis
de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas
tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas
tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis
seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas
tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera
division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos
de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions
league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc
chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas
ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc
topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas
valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor
en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas
venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas
villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal
liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester
united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta
españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos
de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y
pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es
pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina
croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico
apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs
francia apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana
en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona
apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs
real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador
de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro
barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca
inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca
vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real
madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico
madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa
de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao
apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona
vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos
cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas
chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis
barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio
de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog
de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis
sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de
apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono
de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono
de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de
registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono
de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono
marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito
apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono
sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de
apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos
casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de
casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos
en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito
apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito
apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo
apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas
de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora
apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas
seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora
apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de
apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de
apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de
apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas
deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora
scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular
cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular
cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular
momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake
apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio
de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera
de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos
apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de
galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa
apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas
bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas
chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas
españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa
apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa
de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa
de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de
apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de
apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras
de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de
apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de
apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa
de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores
cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas
con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas
copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas
de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas
deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa
de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas
en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas
deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de
apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas
en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de
apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa
de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de
apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales
en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas
liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo
5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa
de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del
real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas
online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de
apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas
para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa
de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas
promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de
apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de
bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso
minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa
de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas
del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas
bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas
apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas
apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso
minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas
mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas
nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas
peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas
de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas
de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas
de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas
casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions
league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas
de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas
con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas
de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas
de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas
de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas
de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas
deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas
colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de
apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de
apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas
deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas
deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas
mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de
apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas
en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de
apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas
de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas
de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa
online|casas de apuestas española|casas de
apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa
2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera
de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas
fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo
1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas
de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales
españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas
de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas
de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de
apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas
no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas
nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas
de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas
de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas
online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas
de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas
online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas
online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online
venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para
ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|
J’ai un faible pour Action Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, a l’occasion des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, Action Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour couronner le tout le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une immersion complete. A souligner les options variees pour les paris sportifs, assure des transactions fluides.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
Seattle, known for its vibrant tech scene and spectacular natural beauty, is also home to a thriving automotive industry. Whether you’re a local resident or a visitor exploring the city, having access to reliable transportation is critical. This is where the importance of a trustworthy car service comes into play. In a city as bustling as Seattle, finding a reliable car service can be a daunting task. However, one company that has consistently set itself apart with its commitment to quality and customer satisfaction is car service seattle. With a team of highly trained professionals, they offer a wide range of services tailored to meet the unique needs of each customer. Their services go beyond the typical car service. They understand that every car owner has different needs and preferences. Therefore, they provide customized solutions that cater to individual requirements. From basic maintenance and repairs to more complex issues, their team of expert technicians is equipped to handle it all. They use state-of-the-art equipment and the latest techniques to ensure your vehicle is in the best possible condition. One of the key factors that set this car service apart is their dedication to customer satisfaction. They believe that every customer deserves the best service, and they go the extra mile to deliver it. They offer prompt, efficient service, ensuring that customers don’t have to deal with unnecessary delays. Plus, their transparent pricing means there are no hidden charges or surprise costs. Their commitment to excellence has earned them a stellar reputation in Seattle. Customers praise their professionalism, attention to detail, and the quality of their work. It’s this consistent high standard of service that has made them a preferred choice for car service in Seattle. In conclusion, if you’re in Seattle and need a reliable car service, look no further. With their comprehensive range of services, commitment to customer satisfaction, and a team of skilled professionals, this car service is your go-to solution for all your car service needs in Seattle. Trust them to take care of your vehicle and deliver top-notch service every time.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2
apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2
que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos
de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas
deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android
apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas
online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer
apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones
de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones
de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para
hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app
apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app
apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app
apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de
apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas
de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas
argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas
deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app
de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app
de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app
de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de
apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas
deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para
hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia
apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas
a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas
a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al
empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas
alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas
nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas
anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas
anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas
argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina
canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas
argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas
argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas
argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas
argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas
argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina
vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas
arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic
atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic
betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic
real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de
liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de
madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid
real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas
bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas
baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto
nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto
pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas
barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas
barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs
psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas
barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona
atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona
atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona
gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas
barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas
barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona
vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas
basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas
betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis
valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas
bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real
madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo
hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas
brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas
caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas
caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del
rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de
liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas
campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos
hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas
carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos
sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas
carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de
caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras
de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta
betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas
champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions
league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions
league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas
chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas
ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour
francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico
español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia
uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como
funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas
combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta
semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas
para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para
mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas
con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades
de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas
copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa
del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del
rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey
pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de
hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas
cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto
hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto
para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas
de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo
canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos
españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de
caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas
de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de
caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de
carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de
champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de
colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas
de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas
de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de
formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol
argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol
en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de
futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de
futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de
fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas
de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras
para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de
galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de
golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de
hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions
league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la
liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas
de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas
de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de
partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas
de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de
tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para
hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de
todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas
del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de
hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1
euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas
100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas
app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina
futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas
deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino
online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions
league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas
deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas
com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas
comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos
virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos
para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es
la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas
de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de
futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de
nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas
deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas
deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas
formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro
futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas
deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas
golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas
impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas
legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas
listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas
mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas
deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas
deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas
deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas
deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas
online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas
deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que
aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas
deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas
resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas
seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis
de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas
tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas
uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas
deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1
euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas
descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso
segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas
en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas
en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas
en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas
en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas
en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas
en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea
españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea
mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas
en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas
en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de
tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas
en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo
casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo
fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo
peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana
mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas
españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa
mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas
espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports
fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa
españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa
hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga
pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1
bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para
ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas
favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc
barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas
final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del
rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final
europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final
mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas
finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula
1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro
nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia
españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas
futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas
futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas
futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas
futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos
olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas
futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos
trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas
ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de
la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador
f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas
ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores
mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana
la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona
real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas
golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis
casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para
hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas
gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a
eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas
handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas
handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas
hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy
pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra
paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas
juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas
jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings
league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas
la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas
legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas
liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas
liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas
liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas
liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real
madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas
madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas
madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid
campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana
la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester
athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas
mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas
seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador
eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador
eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas
mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb
hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como
funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas
multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas
mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial
campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas
mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula
1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial
moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp
nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba
all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba
finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba
para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba
pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana
4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl
pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online
boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas
online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas
online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas
online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas
online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online
juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas
online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas
osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real
madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over
2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas
paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para
el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa
league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar
dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas
para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para
hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa
league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la
copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de
hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas
partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de
futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos
mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas
peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas
playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas
playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas
polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por
internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas
por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas
prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos
por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que
siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a
segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas
quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara
la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas
real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico
champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid
campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid
girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real
madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real
madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas
real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas
real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid
vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real
sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas
resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas
roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby
mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas
seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras
en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras
gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas
seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras
para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas
seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal
paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla
juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla
real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas
sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10
hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas
tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas
tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas
tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas
tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de
golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas
uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc
ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas
ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia
barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas
venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela
bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas
villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal
bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas
villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales
futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas
y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas
y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina
uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile
apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico
apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona
apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de
madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid
apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid
apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid
apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid
apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona
real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona
vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs
espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid
apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis
apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas
online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono
apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono
apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono
bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de
apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono
casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de
apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida
apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de
apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas
de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de
registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro
apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas
sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos
bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos
casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de
apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos
de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas
de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos
en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis
apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de
apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil
colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas
para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas
seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora
apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas
yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de
apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora
de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de
apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular
momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga
apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras
de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras
de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos
de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa
apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa
apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa
apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores
cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas
online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros
gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa
de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas
bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa
de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions
league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de
apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de
colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de
apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa
de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas
deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas
en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas
deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas
peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito
minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa
de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa
de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas
españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa
league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa
de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas
méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas
nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa
de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas
online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de
apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de
apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de
apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa
de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa
de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa
de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas
caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas
apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo
5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas
apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de
apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas
bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas
boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas
de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de
apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas
de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos
sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas
de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de
apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas
de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas
copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas
de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas
con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas
en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas
deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas
deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas
deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero
gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas
de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de
apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de
apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de
apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas
de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas
española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas
de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de
apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de
apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas
de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas
de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas
de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas
legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas
de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores
bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas
méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas
de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial
baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva
ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas
ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online
argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online
ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online
en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas
fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online
nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de
apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas
Je suis epate par Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, cependant des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, Azur Casino est un endroit qui electrise. De plus la navigation est fluide et facile, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement super les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des recompenses continues.
https://azurcasino365fr.com/|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2
apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9
apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de
azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de
apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de
fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas
gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones
de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas
gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas
de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app
apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas
entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app
de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas
deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app
de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app
de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas
online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app
de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app
marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas
deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app
para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus
apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas
1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3
division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a
corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores
nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas
al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves
barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas
alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina
canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas
argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas
arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas
asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic
barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas
athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas
athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas
athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic
roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas
atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas
atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de
madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas
atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas
atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas
barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca
girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas
barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs
psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona
atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas
barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana
la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona
hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs
real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol
mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas
betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas
betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono
bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono
de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas
boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas
boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas
brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas
caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos
zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas
campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1
2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga
santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier
league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas
carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos
fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos
españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas
carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre
partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas
casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online
argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta
real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas
champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas
chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo
femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas
ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas
city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico
español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas
colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas
colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas
colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas
combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas
hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para
hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas
combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas
con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap
baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de
credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas
copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas
copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas
copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa
del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del
rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas
copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas
cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto
para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas
de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas
de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas
de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos
en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de
caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas
de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de
carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras
de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por
internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de
dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de
f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de
futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol
en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol
en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de
fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos
como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de
galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de
hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas
de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de
la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la
liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas
de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas
de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas
ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas
de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas
de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para
hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas
de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico
real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del
real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas
deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas
argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas
bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas
deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca
de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas
deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas
con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas
con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa
del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas
copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas
deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas
en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas
foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas
futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas
futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas
deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar
dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas
deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas
handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas
deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas
deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres
de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas
deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas
deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas
mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas
murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas
deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online
españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas
online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas
deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas
perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas
deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas
deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas
seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas
simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero
real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas
deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas
ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y
casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso
segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero
real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas
directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble
resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador
vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el
clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el
futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la
champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas
en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas
nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea
argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea
deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea
futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea
peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas
en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos
de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas
en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas
españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa
gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas
españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra
eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas
español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas
esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas
esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports
peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa
campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league
pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las
vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos
champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final
champions league|apuestas final champions
peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa
de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas
final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas
final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final
nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de
conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas
formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas
francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas
futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas
futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol
consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol
en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas
fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol
mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para
hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol
virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos
hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas
galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana
resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador
champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa
del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de
la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador
eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas
ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas
ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar
champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar
nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas
girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real
sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas
gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap
nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas
hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas
hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas
holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas
hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas
inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas
juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores
nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la
liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas
la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of
legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados
unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga
bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas
liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander
pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool
real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas
madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas
madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid
barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid
city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid
liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas
madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca
real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador
mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas
mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico
polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas
mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el
gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas
mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial
de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial
favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas
mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial
motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas
mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all
star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba
finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas
nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas
nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl
super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos
eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas
online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas
online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas
online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online
colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas
online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online
opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas
online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas
paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises
bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas
para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para
el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para
futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para
ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas
para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas
para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para
la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para
la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos
de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas
partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido
suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de
boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru
brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs
colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas
playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda
b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs
nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda
boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas
primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos
futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas
pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas
puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu
novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que
significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana
el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la
eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el
mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas
quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid
arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas
real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico
champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real
madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid
girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real
madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real
sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas
real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico
madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad
psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo
de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas
resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby
world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda
b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas
seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas
seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras
nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para
hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas
sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas
sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas
sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas
sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o
combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate
que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake
10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis
roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis
wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster
para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas
torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa
europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas
ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under
over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas
uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia
barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia
real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela
argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal
liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas
virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas
vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y
casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos
de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia
apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs
bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid
apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid
apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico
vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de
cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca
apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs
atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona
– real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de
apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid
apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona
sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol
apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis
apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog
apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas
tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida
marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono
casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas
gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de
apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa
de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro
apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas
deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos
apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos
casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de
apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos
casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas
sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de
apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida
de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de
apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos
paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas
de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil
colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas
deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora
apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas
apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas
de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas
deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora
de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora
poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para
apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora
stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular
apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas
deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias
apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos
apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos
apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de
caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos
de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas
futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa
apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de
apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa
de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de
apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de
apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de
mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions
league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa
de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa
de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa
de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas
del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca
de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de
apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas
deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas
peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas
deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa
de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa
de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas
ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso
mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de
apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de
apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa
de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas
nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial
del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de
apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de
apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de
apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa
de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa
de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas
sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de
apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de
apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la
suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas
apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas
apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas
deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas
apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas
eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales
españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas
nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas
peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas
5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas
de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas
de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por
registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de
apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de
apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de
apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por
registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de
apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap
asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de
apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia
españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de
apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas
de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de
apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas
deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de
apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas
deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas
en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas
deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas
deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de
apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito
mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas
de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas
de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas
de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas
en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas
equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas
de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas
española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de
apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas
de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol
españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas
legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales
mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas
madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas
mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas
minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de
apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de
apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas
de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas
en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas
de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas
de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de
apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de
apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de
apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online
mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online
venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas
para ufc|casas de apuestas payp
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15
euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2
apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que
significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9
apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas
deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas
deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas
deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas
perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones
de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app
android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de
futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app
apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de
apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de
apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas
colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de
apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de
apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas
futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de
apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para
apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas
deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps
de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas
deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a
colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al
tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos
equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina
colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas
argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas
argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs
colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina
vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas
athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas
athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas
athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas
athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico
barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico
campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas
atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas
atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs
barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas
bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto
acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto
juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas
barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca
vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico
de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas
barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas
barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas
barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas
barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona
psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real
sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs
madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas
basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol
mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas
betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis
girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas
betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas
betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas
billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono
bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de
campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas
boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil
colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs
colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas
caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos
hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas
caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas
campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula
1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas
campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas
campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas
campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas
carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas
carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de
caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos
hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos
en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre
partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino
gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino
online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas
celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas
champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs
colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas
ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia
uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas
combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas
combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas
copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa
del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas
copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial
de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas
corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas
de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo
canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como
funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas
de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas
de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas
de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas
de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por
internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas
de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de
futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de
futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas
de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas
de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de
futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol
sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos
online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas
de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas
de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas
de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la
liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas
de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la
ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para
hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas
ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de
peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de
sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas
de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del
boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del
dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas
del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del
real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas
deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas
1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas
deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas
baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas
barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas
deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas
deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se
juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas
con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas
consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa
libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas
altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas
de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas
de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas
deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del
dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas
deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas
deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas
deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas
españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas
estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa
league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles
de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro
futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol
colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas
deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas
golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas
gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas
la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas
legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas
mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas
mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas
deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas
deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas
deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas
deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas
online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas
para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido
suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas
deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas
que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas
deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas
deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para
hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas
deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas
deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis
de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas
deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a
segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso
primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas
dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble
oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas
en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras
de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas
en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas
mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas
en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea
peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas
en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis
en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de
mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo
argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas
españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas
españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana
el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana
mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas
españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas
españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas
españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol
barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas
eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas
eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa
hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas
f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas
f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1
monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas
faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final
champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final
copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de
copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa
league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas
finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol
en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas
fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol
español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas
futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas
futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol
telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas
galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas
gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas
ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas
ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador
del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial
f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores
mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas
ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe
valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas
girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona
real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles
asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis
con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis
sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y
ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas
holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas
hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra
paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas
juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas
kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas
la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league
of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas
legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas
liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas
de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas
liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid
atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid
barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas
madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas
masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo
goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas
mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas
mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas
momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial
de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas
mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas
mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp
eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales
de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba
consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba
para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas
nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas
nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas
nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas
nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas
online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas
online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online
deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online
espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online
futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas
online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas
online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas
open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas
osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over
under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas
paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas
para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el
dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para
eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas
para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas
para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para
hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions
league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa
marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas
partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas
partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol
hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas
partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas
perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru
paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas
peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff
ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas
playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet
para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas
predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas
pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos
tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas
puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la
champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana
la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará
el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas
real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid
betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas
real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester
city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas
real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas
real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid
vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas
real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real
sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas
real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real
sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de
bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda
b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas
seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas
seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy
pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas
sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla
madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas
sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas
significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas
sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis
atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas
tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis
seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas
tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas
trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas
ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas
ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc
telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas
us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas
valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia
real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela
ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal
betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal
manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas
virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta
a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas
y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas
y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia
apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos
apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic
osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico
de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid
apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico
real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca
apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca
madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico
apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona
atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa
de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona
real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs
athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol
apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal
apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best
america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis
madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono
apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida
apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono
bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono
bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono
casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono
de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de
bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono
de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono
por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa
de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas
sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de
apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos
casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos
casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos
de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos
de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis
casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de
apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito
apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot
de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para
hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de
cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos
apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas
seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de
futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas
deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para
apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular
cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular
stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera
de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras
de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras
de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico
de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono
bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono
sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa
apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa
apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de
apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de
madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas
beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono
sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras
de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas
champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia
en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de
apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa
america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de
apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de
peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa
de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas
deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas
españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas
deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa
de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa
de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa
de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de
apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de
apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa
de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de
apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa
de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas
nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real
madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa
de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas
online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa
de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas
peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas
que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa
de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso
minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas
sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas
valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la
suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas
apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas
deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas
deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas
apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso
minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas
legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas
mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas
apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas
peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas
barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas
bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas
de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas
champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas
ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas
de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas
de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de
registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas
de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de
apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de
apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas
de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago
anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas
de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de
peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas
deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de
apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas
deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de
apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas
españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas
de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas
deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas
de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas
de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de
apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de
apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas
españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas
de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa
2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas
f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula
1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas
fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas
de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de
apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales
en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas
de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas
de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de
apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores
cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas
de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas
en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de
apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de
apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de
apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas
de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas
de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas
de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas
paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas promociones|casas
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15
euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2
en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y
apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para
ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de
apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones
apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro
apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app
apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app
apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas
gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app
de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas
deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app
de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas
en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app
de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas
peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de
apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app
para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app
versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de
apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a
hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas
a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la
nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis
wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del
mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos
marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia
argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina
francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina
paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina
vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal
real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas
asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real
sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico
de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas
baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto
pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça
madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs
madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico
de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona
campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas
barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas
barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona
real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona
valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas
barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas
béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis –
chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis
girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas
billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de
bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real
madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo
femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil
uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos
hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar
de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas
calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas
campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1
2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp
2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas
campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos
de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos
hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de
caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de
caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos
en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas
casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas
casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league –
pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas
champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions
league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas
chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas
ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas
ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas
city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas
colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como
funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas
combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas
combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas
combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para
hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como
ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del
rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas
copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas
copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas
corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos
eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de
baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas
de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas
de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas
de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas
de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de
caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas
de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas
de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol
colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol
en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol
hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de
fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol
para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas
de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas
de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas
de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de
juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas
de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas
de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas
de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para
hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de
perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de
sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas
de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de
tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis
seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del
boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia
deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del
real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas
deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas
1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas
deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de
madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas
barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas
deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas
deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas
deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas
deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino
barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas
deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas
deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas
comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos
gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas
deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas
copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas
deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas
cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas
deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de
peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas
deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas
en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas
en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas
deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas
deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas
es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas
estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula
1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas
deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol
argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero
seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas
golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas
deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas
listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas
seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores
app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas
mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas
méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas
nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas
deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online
chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas
deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online
españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online
peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas
para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas
para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas
deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas
deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas
que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas
deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas
deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas
deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas
stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis
foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas
deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y
casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas
deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1
euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas
dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas
egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas
en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos
deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas
en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la
liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas
nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea
chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea
estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas
en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos
de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas
en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas
españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas
españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas
españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas
esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas
esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa
femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas
euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league
pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas
f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas
favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos
mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions
peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de
europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa
libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas
final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula
1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas
futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas
futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol
argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol
en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas
futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol
español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol
foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol
juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas
futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas
futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos
en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana
resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions
league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador
de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas
ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar
liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas
girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de
tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para
hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas
grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas
online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey
hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises
bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas
la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las
vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas
legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados
unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas
liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones
de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool
real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas
madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas
madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid
barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid
celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid
hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid
sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas
mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas
mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador
eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples
el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial
campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de
ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial
f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas
mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub
17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas
mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas
nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba
finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba
pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl
hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online
bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions
league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online
con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas
online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas
online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online
movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas
online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas
online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas
osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas
over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países
bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions
league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de
hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas
para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para
ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar
en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas
para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar
siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa
del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de
la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas
partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas
partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas
partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas
partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas
peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru
vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por
internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda
boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas
pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre
ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana
la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas
rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid
athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico
champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas
real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid
borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real
madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas
real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid
vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs
atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs
valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas
real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas
resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas
seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas
seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy
futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas
seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras
para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas
senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas
sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla
betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla
osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples
ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas
sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas
tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas
tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas
tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas
tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas
tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster
para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas
ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas
ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas
under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay
vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas
valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real
madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor
app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas
villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real
madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y
pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos
deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina
peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona
apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real
madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico
real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona
apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca
inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid
apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs
real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de
madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis
apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid
apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla
apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao
apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de
vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs
girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona
vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas
deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea
apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea
apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas
baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog
apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono
apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas
españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida
apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de
bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono
de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de
casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono
gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro
apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas
deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos
apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos
apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos
apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de
apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos
casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos
de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de
apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de
apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas
de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo
apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para
hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas
seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar
apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de
sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas
deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora
apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora
cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas
combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas
sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora
sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular
apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas
futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas
deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular
probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba
apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas
juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos
apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos
apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas
argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa
apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa
apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas
eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa
de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de
apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa
de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa
de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas
chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de
apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa
de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de
apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de
apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito
minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de
apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa
de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de
apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de
apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula
1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa
de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa
de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de
apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa
de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online
españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa
de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa
de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de
apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas
sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas
tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas
valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de
apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas
bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas
con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas
españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas
apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas
nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas
apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas
apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas
5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de
apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por
registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de
apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de
caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca
de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas
gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas
de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas
con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de
apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de
apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas
con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de
apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas
con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago
anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas
de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa
del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas
de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas
comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de
apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas
de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de
apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas
deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas
de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas
en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas
de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de
apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de
apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de
apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas
españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas
eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas
en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas
de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador
eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de
apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas
de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas
de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas
mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva
ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas
en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de
apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas
online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas
online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas
online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online
españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas
de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas
de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de
apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas
paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de ap
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
order provigil provigil in stores provigil online pharmacy provigil withdrawal symptoms a comprehensive view provigil sleepy
Je suis totalement conquis par Azur Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par moments des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Azur Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A noter la navigation est simple et intuitive, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des avantages uniques.
Poursuivre la lecture|
Je suis sous le charme de Lucky 31 Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Le bonus initial est super. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. En resume, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En plus le site est rapide et style, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements rapides.
Aller à l’intérieur|
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15
euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas
que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y
apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria
ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas
android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de
futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones
de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app
apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app
apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app
apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas
android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas
deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas
deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de
apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app
de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app
de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app
moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre
amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos
apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps
apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender
hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas
a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al
empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas
alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas
altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos
equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina
francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina
gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs
australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso
a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas
athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas
athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic
roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas
athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico
barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico
de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas
atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real
madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid
real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas
atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto
pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça
madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs
psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas
barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona
atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas
barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas
barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas
barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas
bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis
fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas
betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis
valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de
bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos
sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas
boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas
boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas
brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa
america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas
campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas
campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland
garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos
nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas
carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos
en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas
carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos
sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas
casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas
celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta
espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas
celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions
league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league
pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile
vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas
ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a
españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid
barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia
vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas
combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo
partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas
combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas
recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas
comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas
con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas
con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas
probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de
credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa
africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa
del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas
copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas
copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa
del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa
sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas
cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas
cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack
en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de
boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas
de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas
de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas
de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de
caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de
carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions
league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de
copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes
en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas
de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas
de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de
futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de
fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy
seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas
de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como
ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas
de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas
de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de
juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas
de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la
eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de
la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas
de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas
de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de
tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de
tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de
ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas
del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas
del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas
del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido
de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas
deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas
1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas
argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas
deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas
beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas
deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas
casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas
cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas
colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como
se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas
deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas
deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa
libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas
deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas
de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas
deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble
oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas
en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas
deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas
deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas
en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas
deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles
de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas
deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas
deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas
deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas
deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas
gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis
hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas
deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas
juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas
deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas
deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores
casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores
paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas
online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas
online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas
para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas
deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas
deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras
foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas
simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas
deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas
deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas
deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas
virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas
deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda
b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas
dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles
y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas
en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas
en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo
futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas
en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las
vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas
en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas
en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas
en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas
en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de
futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo
nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo
ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas
españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas
españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports
españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas
eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa
favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas
europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas
europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1
china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas
f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas
favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos
mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas
final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del
rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa
rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de
copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa
league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de
conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula
1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas
foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas
futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas
futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol
español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas
futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas
futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas
galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador
copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador
copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas
ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas
ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores
eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas
girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real
sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles
asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis
para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis
sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas
gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo
a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como
funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas
hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas
hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy
seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas
inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas
jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas
league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas
liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas
liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga
española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid
barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas
madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas
madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca
real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas
mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas
mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico
polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas
mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como
funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples
futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas
mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de
ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de
fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial
favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas
mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas
nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas
nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba
hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba
para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba
tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas
nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas
nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina
legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online
carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions
league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online
comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online
en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online
españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online
futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas
online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas
online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online
paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas
open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna
barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas
paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas
para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para
el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para
europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para
ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar
la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas
para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy
futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la
champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas
para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para
la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas
para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas
partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido
españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos
champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de
futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas
partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas
peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff
segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas
polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para
ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas
pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara
a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana
eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana
la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas
quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas
quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas
rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid
bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas
real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid
city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas
real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs
atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real
sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real
sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas
real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas
regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby
mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas
segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas
seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas
seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas
seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este
fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy
pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras
telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla
atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas
sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas
sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla
roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas
simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas
sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas
super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis
consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas
tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas
tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas
tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria
holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas
ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc
ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas
valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela
bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas
villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs
real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales
sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill
partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs
chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona
apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real
madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de
cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona
apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid
apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de
madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona
valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs
espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de
datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america
apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea
apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas
deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas
gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas
españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca
apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de
apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de
bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas
deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de
apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito
marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos
apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de
apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas
de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos
de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas
deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito
apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos
sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas
gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para
hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas
deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas
multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora
arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora
de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora
de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular
apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular
cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular
probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular
unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga
apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera
de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras
de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de
caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras
galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa
apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono
gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas
futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas
nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de
apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas
bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa
de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de
apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions
league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas
mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las
mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores
cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas
de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas
de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de
peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de
apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas
españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de
apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de
apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1
euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa
de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de
apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de
apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas
europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso
minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas
liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas
mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de
apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa
de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas
oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online
argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas
online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas
online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online
usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de
apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para
boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de
apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa
de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas
sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso
minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa
de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de
apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas
virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas
bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas
españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas
ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas
licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas
de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas
de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas
de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono
de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas
bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos
sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas
de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de
apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de
apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas
de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por
registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas
de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del
rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de
apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de
apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas
deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas
de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas
perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1
euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas
de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa
online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de
apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas
en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas
españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas
de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas
de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas
fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas
ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas
de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas
de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas
de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas
de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de
apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas
mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas
mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial
baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas
de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas
ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online
colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas
online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online
usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru
bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Je suis emerveille par Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour conclure, Azur Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, permet une immersion complete. Un atout les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des privileges personnalises.
https://azurcasinoappfr.com/|
Je suis emerveille par Action Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, mais encore plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour finir, Action Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. De plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, garantit des paiements rapides.
Commencer Г lire|
J’ai un faible pour 1xBet Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est simple et transparent, mais encore quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En bref, 1xBet Casino offre une experience inoubliable. D’ailleurs le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement top les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste la participation.
Visiter pour plus|
J’adore l’energie de Lucky 31 Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, toutefois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour faire court, Lucky 31 Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements securises.
Obtenir plus|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Lucky 31 Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, malgre tout des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour finir, Lucky 31 Casino assure un fun constant. En complement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement fun les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, garantit des paiements rapides.
VГ©rifier le site|
Je suis accro a 1xBet Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, neanmoins des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En resume, 1xBet Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le lien communautaire.
Commencer Г explorer|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Action Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, a l’occasion des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Au final, Action Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est simple et engageante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Lire les dГ©tails|
Je suis captive par Action Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par ailleurs plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En conclusion, Action Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement captivante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10
trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2
apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas
deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas
online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de
futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de
apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de
apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones
para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app
android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas
de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app
apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas
deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app
control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app
de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app
de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas
deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de
apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de
apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de
apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de
apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas
reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app
moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas
deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre
amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos
apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps
de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para
apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del
dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a
caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a
jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas
al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas
alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania
españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas
y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina
campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas
argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas
argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas
argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas
asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas
athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic
manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas
athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas
atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico
de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético
de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto
handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca
bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca
inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca
vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas
barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas
barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real
madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona
sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs
atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa
madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas
beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas
beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas
betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas
betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas
betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas
betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas
bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas
boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo
online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos
madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos
sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas
campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas
campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas
campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos
nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas
carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas
carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas
carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos
nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino
futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta
betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas
celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas
champions league|apuestas champions league –
pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas
champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league
pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas
ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour
francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas
clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas
colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas
de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas
futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas
recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas
combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades
de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de
credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa
argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de
europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del
rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del
rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de
hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas
corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto
nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol
para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas
de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como
funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos
españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas
de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos
por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de
caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de
carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas
de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de
ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de
esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas
de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de
futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol
en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de
futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas
de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol
peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de
galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de
galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de
hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de
juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la
europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba
para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema
como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas
del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de
hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de
hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas
deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas
1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas
deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas
deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas
deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas
deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino
online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas
con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero
ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas
deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas
copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas
cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas
de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas
de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble
oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas
deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas
es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas
deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas
faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas
deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas
deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas
deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas
deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis
con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas
deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas
libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas
liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas
deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas
deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores
cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas
mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas
deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas
deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas
deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas
online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para
ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas
deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas
promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas
deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras
hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas
seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas
simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas
sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram
españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas
deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas
y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas
deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas
descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la
liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas
dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble
resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas
dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas
draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas
el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas
en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo
futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos
deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas
en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las
vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas
en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas
en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas
en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de
tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas
en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas
en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos
de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas
españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas
españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa
inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas
euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa
sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league
pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1
bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas
f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de
ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito
champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc
barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final
champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa
europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa
del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas
final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina
betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas
fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas
fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas
futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas
futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas
fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos
olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para
hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas
galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas
ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa
del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador
eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga
española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador
nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas
ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe
valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas
girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador
eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf
masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas
gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis
regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y
ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap
baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap
nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas
holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas
inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos
en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas
kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas
la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas
legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados
unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de
campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas
liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool
barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid
barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas
madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas
madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas
madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas
faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para
hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas
mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas
méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas
méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas
mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas
momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como
funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas
mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas
mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial
de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas
mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de
rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial
ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial
sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba
all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para
hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos
hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl
pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas
online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas
online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas
online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas
online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online
mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico
golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas
paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas
países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de
hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para
eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas
para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas
para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas
para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para
ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas
para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas
para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos
de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido
colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas
partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos
csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas
partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas
plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff
ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff
segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas
predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos
futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos
nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos
por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre
ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la
champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas
quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas
real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas
real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid
betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas
real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real
madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real
madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas
real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad
betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas
recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas
rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas
segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas
seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras
calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas
seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras
futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para
ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises
bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas
sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas
sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas
sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla
manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas
sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas
sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas
super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas
tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis
pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster
para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de
golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc
hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas
uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay
vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia
betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas
valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas
venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas
villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales
colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales
sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas
y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y
pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina
croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina
peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico
en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic
osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid
apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs
real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico
madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona
casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real
madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia
apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de
vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona
apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base
de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea
apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog
apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono
apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida
marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de
bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono
de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro
casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro
apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas
deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos
apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas
sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas
apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de
apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas
de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas
deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de
apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de
apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos
sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas
de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia
apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para
hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador
de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas
seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas
multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora
apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora
de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de
apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping
apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular
apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular
apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular
momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de
cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos
con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de
galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos
apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa
apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono
gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa
apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa
apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa
apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas
nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de
apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa
de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas
bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de
apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas
boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas
carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de
apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas
mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las
mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa
de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa
de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa
de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas
deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas
deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas
deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas
deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de
apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de
apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de
apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa
inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de
apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de
apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas
ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales
en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa
de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real
madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de
apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de
apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online
paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online
usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago
anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas
para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas
perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas
sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo
de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas
tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas
venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa
oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas
apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas
con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas
apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas
deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas
esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas
legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas
nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas
de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas
baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas
de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas
caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas
de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de
apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas
con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas
con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de
apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas
con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas
con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de
apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas
de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas
de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas
con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas
deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas
deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas
de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas
online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas
perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas
de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas
en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas
de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas
en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas
de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa
nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas
de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas
fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas
de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de
apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas
legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas
de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas
de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de
apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas
de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas
de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas
de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas
online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de
apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas
de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online
nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online
usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de
apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas
I agree with you, thanks for an explanation. As always all ingenious is simple.
——
https://the.hosting/ru/help/vybiraem-prilozhenie-dlja-montazha-na-android
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10
trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2
apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2
en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5
euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre
ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades
de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america
apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android
apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas
online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas
en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app
apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app
apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas
entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app
casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app
de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app
de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de
apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas
deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de
apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app
de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app
de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app
de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app
de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para
apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para
apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para
hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control
de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas
deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a
hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta
del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100
seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas
a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas
a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la
baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves
barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del
mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas
argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas
argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina
gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas
argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal
real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic
barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas
athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas
atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico
campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas
baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto
handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas
barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas
barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca
real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas
barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas
barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana
la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas
barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona
madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas
barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona
villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona
vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket
hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol
pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas
betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis
real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis
valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay
hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas
billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono
de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas
boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas
boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil
vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas
caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas
caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas
calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas
campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas
campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas
campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos
nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera
de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de
caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos
sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de
galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino
gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online
argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas
celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas
celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas
champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league
2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions
league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile
venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas
ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas
clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de
fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para
hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para
mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas
con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de
debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas
copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa
del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de
hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas
de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto
nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack
en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo
online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos
como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas
de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas
de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de
caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions
league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de
deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas
de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas
de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de
futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de
futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas
de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas
de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas
de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas
de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos
online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos
online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de
la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la
liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas
de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para
hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos
de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros
en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de
sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas
de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas
de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas
de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas
del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del
día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido
de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros
gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas
deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico
de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas
deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas
deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas
deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas
deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas
cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas
deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas
com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas
como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas Con bono gratis; https://preprod.lourdes-Pireneje.pl/,|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas
deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos
virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del
rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la
mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de
baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas
deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas
deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas
en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas
deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro
futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas
futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas
ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis
sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas
handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas
legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas
seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas
mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas
murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas
ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online
chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas
deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas
online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago
paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para
hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas
deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas
deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas
deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram
españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas
deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis
hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas
tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas
valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas
deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas
descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias
seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas
directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas
doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund
barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador
vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas
en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas
en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras
de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas
en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas
en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas
en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas
en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea
estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas
en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas
en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas
en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania
eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas
españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas
españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas
espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas
esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports
lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa
españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1
canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1
hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de
ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos
champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc
barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas
final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final
de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa
league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas
finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas
fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia
argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol
online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas
galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas
gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas
ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del
rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas
ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas
ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador
mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial
f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores
eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar
liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona
athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana
la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores
eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf
masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis
casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas
gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis
sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas
gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas
grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas
handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey
hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas
hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas
hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos
online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league
americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga
hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales
españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1
peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva
pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas
liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga
españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas
madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid
barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas
madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs
barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas
mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas
maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores
casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas
mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas
mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas
mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial
de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas
mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas
mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp
nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas
nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas
nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas
nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos
eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online
champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online
comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas
online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas
online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas
online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas
online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas
online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises
bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países
bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para
el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la
europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas
para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del
rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa
league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas
partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido
colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas
partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas
partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de
boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas
peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas
playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas
playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet
para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas
por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones
futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas
pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas
puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas
quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana
la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el
mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara
la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas
real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real
madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas
real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de
madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas
real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid
betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid
campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas
real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid
girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid
osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid
vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico
madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real
sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real
sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas
recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas
resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas
roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas
ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas
segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras
calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas
seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol
hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas
seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras
para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para
hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras
para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas
sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla
betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla
inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla
real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas
sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas
sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito
minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero
real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo
copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super
bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas
tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas
tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas
tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas
tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos
de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa
europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc
como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas
villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas
valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas
villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas
villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas
virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta
españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y
pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs
chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina
vs francia apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas
deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic
osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de
madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs
real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas
apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs
real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona
atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg
apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real
sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona
vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas
chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis
madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas
ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono
bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono
bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida
marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas
de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida
apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca
apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por
registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono
sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas
sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos
casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos
casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas
sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis
casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos
sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo
apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas
seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas
de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas
multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas
sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de
apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de
apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de
apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para
apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas
deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora
scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading
apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular
apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas
deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad
cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades
apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga
apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos
apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de
caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de
galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras
de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico
de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas
chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas
españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa
apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa
apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de
apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de
apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa
de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa
de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa
de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de
apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas
con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas
con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas
de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas
de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real
madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas
deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito
minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas
en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas
española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas
esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa
league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula
1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso
minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales
en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga
española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa
de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa
de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa
de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de
apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa
de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de
apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa
de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa
de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa
de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de
apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de
apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de
apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas
apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas
apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas
españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas
apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas
españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas
de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras
de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas
champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas
con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono
sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas
con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas
con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago
anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal
en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de
caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de
apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de
apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de
apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas
de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas
de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas
en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de
apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas
en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas
en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de
apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas
de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas
de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de
futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa
alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa
licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas
española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas
con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas
eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas
formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de
apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de
apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas
de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas
de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas
mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas
mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de
apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas
nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas
online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas
de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas
de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas
de apue
Trending Testing News – Trendy topics ko simple tareeke se cover karta hai.
Good post. I learn something new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon every day. It will always be helpful to read through articles from other authors and practice something from their sites.
RUSSIAN PIDOR
Je suis captive par Azur Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est clair et efficace, en revanche des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En resume, Azur Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. D’ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, facilite une immersion totale. A mettre en avant les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je ne me lasse pas de Azur Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, a l’occasion plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En resume, Azur Casino assure un fun constant. Pour ajouter le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un point cle les transactions en crypto fiables, offre des recompenses regulieres.
http://www.casinoazurfr.com|
Je suis bluffe par Azur Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est simple et transparent, par contre plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour ajouter la navigation est simple et intuitive, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un avantage les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Explorer le site web|
J’adore le dynamisme de Lucky 31 Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, mais plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En resume, Lucky 31 Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et energique, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement attrayant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui motive les joueurs.
Poursuivre la lecture|
J’adore l’energie de Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est simple et transparent, de temps en temps quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En fin de compte, Action Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement fun les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des bonus constants.
Visiter pour plus|
Je suis captive par 1xBet Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est simple et transparent, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En resume, 1xBet Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour completer le design est tendance et accrocheur, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un bonus les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Aller Г la page|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Lucky 31 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par contre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et fluide, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement super les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui stimule l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Je suis epate par 1xBet Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, mais encore des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En fin de compte, 1xBet Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A mentionner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, renforce le lien communautaire.
Touchez ici|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Action Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est simple et transparent, rarement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, Action Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A mentionner l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un point cle les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des bonus constants.
Visiter le site|
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos
para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que
significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos
de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo
para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones
apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas
gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de
apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de
apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones
para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app
android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas
deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas
entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas
de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app
de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas
deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas
argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas
deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app
de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de
apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app
de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de
casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas
deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app
para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app
para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps
de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas
deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas
1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a
corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores
nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al
barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al
tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas
altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos
equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas
antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia
argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina
canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina
croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises
bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina
vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs
peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera
division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas
athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas
atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico
campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de
madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid
real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real
madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas
baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas
baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas
baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca
bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas
barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs
psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas
barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas
barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas
barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas
barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas
barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona
valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas
barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas
beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis –
chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis
fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas
betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis
valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas
bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas
bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos
sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo
de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo
hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas
brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos
hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos
zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas
campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference
league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas
campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas
campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas
campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula
1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp
2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial
baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas
campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de
futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera
de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas
carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras
caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas
carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras
de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino
gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta
eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta
madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real
madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league
– pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas
champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas
champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas
chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas
chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city
madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas
colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de
fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas
combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas
combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para
mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de
ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa
argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa
davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del
rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey
final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa
del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa
rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de
1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto
hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas
de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de
blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas
de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas
de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de
caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas
de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos
juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online
en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino
online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas
de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas
de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de
fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de
fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol
para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de
futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol
sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas
de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de
hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos
online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de
la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de
la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba
para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de
sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de
sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas
de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de
tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo
tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas
del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas
del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del
partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del
rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de
madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas
deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino
online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions
league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas
deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas
deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas
deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas
copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa
mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas
deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas
de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de
tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero
ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas
en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas
deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas
estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas
deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas
formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas
deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas
deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas
deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas
handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas
libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas
liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas
mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas
multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas
ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online
argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online
mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas
online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas
deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar
dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido
suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas
que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas
deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas
deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas
deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas
deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas
simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas
sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas
tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis
foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas
deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas
deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a
segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas
dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas
directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles
y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas
ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas
en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas
en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la
eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas
en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas
en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis
de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas
en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa
alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas
españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas
españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas
españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español
oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas
esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas
esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas
eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas
eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa
final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas
eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas
europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas
f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de
ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos
champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas
final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa
del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final
copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa
league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final
rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales
de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina
betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas
futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol
argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol
en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas
futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol
foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol
juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol
para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos
pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa
del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa
libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas
ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador
la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial
f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas
ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona
betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona
real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas
gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis
regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis
sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap
nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda
vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy
pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises
bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas
jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la
liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas
mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends
mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas
legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas
libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga
de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander
pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea
de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico
champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid
barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid
barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid
campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas
madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas
madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas
seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas
masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas
mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas
méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas
mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas
mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas
multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas
mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial
campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de
baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas
mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial
femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial
ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas
mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba
all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta
noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas
nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba
pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl
semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina
legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online
boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de
caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online
ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas
online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas
online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis
sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online
net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online
seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas
online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas
osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas
over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago
anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos
qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia
de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido
de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas
para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para
hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos
de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas
peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff
ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas
playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por
internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar
dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas
predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer
con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas
quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas
quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid
arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid
girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real
madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas
real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas
real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas
recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados
eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas
rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas
segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras
en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas
seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol
hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para
este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para
hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras
para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras
ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises
bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla
atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas
sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla
gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas
sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla
real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas
sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito
inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas
sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema
calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas
stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl
favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta
roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas
tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de
mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis
hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas
tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera
division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria
holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas
uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas
ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas
valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia
real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor
app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal
liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs
real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a
españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william
hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y
juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos
de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba
apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico
apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile
apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico
apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic
barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de
madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico
madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter
apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid
apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de
apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs
atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid
apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas
nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas
sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida
marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono
casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono
de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono
de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono
de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono
por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa
de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas
colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de
apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas
de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de
apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos
de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de
bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos
de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de
apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas
deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis
sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de
apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador
de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de
apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora
apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir
apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora
de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de
apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora
de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para
apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas
apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular
unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga
apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera
de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de
caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos
apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas
argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas
barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono
gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas
futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas
nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa
apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa
de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa
de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas
bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas
cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas
champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas
altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las
mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa
de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa
de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa
de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas
en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas
deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa
de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito
5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas
en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de
apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas
españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de
apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas
futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales
en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa
de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa
de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas
mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas
nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real
madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online
chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas
online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas
online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para
boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa
de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa
de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de
apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de
apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas
vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos
sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas
apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas
apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas
apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso
minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas
apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas
apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas
españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas
de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas
de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas
de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de
apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas
de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas
caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino
online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas
de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono
de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas
de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas
de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia
española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas
con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas
de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de
apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas
de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de
apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas
en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de
apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo
1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas
de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de
apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas
en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de
apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa
inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas
españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas
esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas
formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas
de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas
ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de
apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de
apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de
apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas
madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas
mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5
euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas
de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas
en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas
ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online
deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas
online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas
online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas
online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas
paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas
Je suis enthousiasme par Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, de temps a autre des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En somme, Azur Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Notons aussi le site est rapide et immersif, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, garantit des paiements rapides.
Voir maintenant|
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas
que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara
apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba
apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas
android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para
hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones
apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas
de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app
apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app
apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas
sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de
apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de
apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas
peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de
apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de
apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app
de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app
de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app
para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas
en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre
amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps
apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps
de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer
apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas
deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas
a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis
wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas
alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas
altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas
argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina
francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas
argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina
méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas
argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas
argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso
a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic
manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic
real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas
atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético
copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid
gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas
atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico
real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto
pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas
barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas
barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona
atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas
barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas
barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona
osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas
barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas
beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis
real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas
betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay
hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas
bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas
bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas
boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas
caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos
hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas
caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions
league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas
campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del
mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas
campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga
santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas
carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos
sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas
carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos
sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre
partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino
gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas
celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta
espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas
celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas
champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league
2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league
pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas
chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile
venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas
ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas
clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia
brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas
colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas
combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas
futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero
real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas
con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas
probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas
con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa
africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa
brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey
pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas
cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de
1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto
para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de
boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de
caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de
caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos
en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de
caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas
de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos
pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera
de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos
online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de
casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de
colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de
deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas
de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas
de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas
de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de
futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para
hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas
de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol
seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de
galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas
de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas
de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas
de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de
la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas
de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de
futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros
en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema
como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de
tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis
en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de
tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de
todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del
dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas
del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas
deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas
deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas
deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico
de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas
deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas
para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas
deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas
consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas
deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas
deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de
nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas
en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas
deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas
en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas
deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas
esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas
f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas
foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia
argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas
gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas
gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas
deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la
liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas
deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas
madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas
mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas
mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas
nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas
online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas
deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar
dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de
hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas
promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico
hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas
rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras
para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram
españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas
deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas
valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas
y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas
deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos
pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a
segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas
dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y
triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas
ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto
uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas
en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de
futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo
pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas
en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la
champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas
en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas
en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea
colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea
deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas
en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea
peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas
en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas
en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas
en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas
en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos
de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra
eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas
españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas
español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas
espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas
euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas
eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas
euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas
europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas
europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1
canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1
las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas
favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas
final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa
europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas
final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas
final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa
europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales
nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula
1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas
fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas
futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol
en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol
foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol
juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol
pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas
gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de
la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador
f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador
mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar
liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas
girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana
la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas
goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada
barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis
con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas
gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas
handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas
hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra
paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas
kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas
la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of
legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas
licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga
de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de
hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real
madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca
hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas
madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas
madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de
ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas
mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las
vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas
mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas
multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el
gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas
mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial
balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial
ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial
de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas
mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas
mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas
mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas
nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas
nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas
nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas
nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl
pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online
bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online
caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online
comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online
en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol
españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas
online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online
net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online
paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas
online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para
champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido
de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para
ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la
champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para
ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para
hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas
para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para
partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido
champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos
champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos
de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru
brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas
pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas
playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff
segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs
nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por
sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones
futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas
pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos
deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos
tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana
el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la
champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas
quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara
la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid
arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid
atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas
real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas
real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas
real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid
vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs
atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas
real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs
betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real
madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad
athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real
sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas
segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda
división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas
seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol
hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras
hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba
hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas
seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla
atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la
liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla
juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real
madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas
significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que
significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo
copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl
favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas
amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas
tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis
en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis
itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas
tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis
wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para
hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas
trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas
ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas
ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas
uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas
valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor
galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal
manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales
futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas
vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas
y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas
y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia
apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico
barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico
madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs
real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca
madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona
atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona
atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona
real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona
vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos
cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas
chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas
de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono
apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas
españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono
bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono
casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas
gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de
bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca
apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito
apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito
casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida
apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos
casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas
deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas
de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos
de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos
en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos
gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos
registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos
sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas
deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil
peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador
de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas
seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de
sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora
apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas
seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora
arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de
sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas
multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de
apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje
apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas
deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora
scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular
apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas
apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular
probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular
unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de
apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio
de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos
de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa
apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa
apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca
de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa
apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa
apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa
de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de
apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las
mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas
copa america; groxery.Kreativejohnys.com,|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas
de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas
del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de
mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas
en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas
deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de
apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de
apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa
inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de
apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales
en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa
de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de
apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa
de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de
apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa
de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online
peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas
pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa
de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa
de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa
de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa
de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa
de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa
de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas
caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas
colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales
españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas
apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas
ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas
peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas
asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas
5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de
apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de
apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas
ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono
por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas
con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos
sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de
apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de
apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de
apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas
de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de
apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas
de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas
de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas
de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas
de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas
en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de
apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas
de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1
euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas
en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas
de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas
de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas
de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de
futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de
apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas
de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas
eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de
apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de
apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas
de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de
apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas
de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de
apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas
de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas
de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas
de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas
de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para
ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que
significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de
cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo
para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas
en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas
online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de
apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app
apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre
amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control
apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de
apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas
deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas
peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de
apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas
en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app
de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app
marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para
apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer
apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos
apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas
de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps
de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas
a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la
baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas
al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz
hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y
bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos
equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes
del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas
argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas
argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto
paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas
argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina
vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real
madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic
sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas
atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas
atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas
atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de
madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético
de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real
madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas
baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas
baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas
barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca
inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca
vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas
barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona
campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas
barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas
barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas
beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real
madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar
online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos
sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas
boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas
brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil
vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos
españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos
sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas
campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas
campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas
campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas
campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas
campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas
carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas
carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de
caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de
caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas
carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas
casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos
online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas
celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league
– pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions
league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions
pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour
francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico
español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas
colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia
vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas
combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas
combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero
real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas
copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas
copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas
copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa
del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa
del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas
cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de
baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas
de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo
online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos
en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas
de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas
de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de
caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras
de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de
casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de
deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula
1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas
de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas
de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas
de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de
futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de
galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey
sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos
deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas
de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la
europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas
de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de
nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de
sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas
de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis
en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para
hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de
todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido
de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas
deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas
10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2 (Bebe)|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas
deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas
deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono
de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas
casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas
deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas
com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como
se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas
deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos
virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas
deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas
deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de
nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas
deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas
deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas
deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas
deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas
deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas
deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas
deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas
foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas
foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas
futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas
gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas
interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas
deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas
deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb
hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online
argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru
vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas
real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas
resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras
para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas
sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas
stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas
deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas
deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas
deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas
deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas
descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas
descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas
dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas
division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas
dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador
vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas
empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas
en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de
caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas
en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas
en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la
nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las
vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas
en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas
en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas
en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas
en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis
de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo
fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas
en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos
de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania
eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa
francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa
gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa
italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas
español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas
esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports
fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas
esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas
estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa
españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas
euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas
f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1
las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de
ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas
favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos
champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos
mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas
final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas
final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas
final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final
del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas
final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales
de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina
betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas
fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas
foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia
españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano
nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol
champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos
en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos
pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana
colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa
america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas
ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas
ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas
ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana
uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas
goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas
granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas
gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas
gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas
handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como
funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas
hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda
argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas
hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra
paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos
olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league
americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas
la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas
las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas
legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas
liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga
de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga
española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas
lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca
hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas
madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana
la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid
sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca
osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas
mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de
golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico
polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas
mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas
momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas
multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas
mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial
clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial
de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas
mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas
mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas
mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas
nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba
playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl
las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas
nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online
argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas
online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online
caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas
online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas
online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online
mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online
net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas
online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online
sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real
madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over
2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises
bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia
de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para
el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas
para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas
para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para
ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para
hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la
champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para
la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas
para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas
partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de
futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas
perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas
peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru
vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff
nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas
playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet
mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal
uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones
futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos
futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer
con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana
eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana
la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas
rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas
real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid
atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas
real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real
madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas
real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs
atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas
real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas
registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada
tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas
ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras
futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas
seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas
seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy
fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas
seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas
seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas
sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real
sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas
significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas
sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas
sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas
sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema
calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10
hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas
tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis
femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis
pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland
garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas
tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas
tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de
tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas
ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas
ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas
villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas
uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us
open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas
valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas
venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas
villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas
villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a
españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de
futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia
apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas
deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united
apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de
madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico
de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid
apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador
de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona
apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs
real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona
apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona
atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid
apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona
vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs
girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs
sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base
de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona
apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio
de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog
apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono
apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas
sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa
de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas
de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono
de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por
registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de
apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito
apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos
bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas
sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de
apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de
apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot
de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil
peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para
hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de
apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora
apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora
apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas
yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de
apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora
de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje
apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora
para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora
scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular
apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas
combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular
momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades
apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas
deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos
apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de
caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos
apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas
atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas
bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas
peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa
de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas
bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de
apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa
de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas
carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de
apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores
cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de
apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de
españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa
de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de
mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa
de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas
online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de
apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa
de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas
española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa
de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de
apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa
de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas
nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de
apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa
de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de
apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online
venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para
boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas
que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de
apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas
valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas
virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas
apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas
apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas
deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas
mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas
online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas
barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de
apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino
online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas
de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas
com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas
con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono
de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas
de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos
sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de
apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de
apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de
apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de
apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas
de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de
apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas
en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de
apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de
apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas
deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1
euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1
euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas
de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas
en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de
apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de
apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas
de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de
apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa
online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas
de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa
league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas
fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas
de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas
gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas
de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales
en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas
de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de
apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo
5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas
de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva
ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online
en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de
apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de
apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online
peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apue
The swapping tokens tools are accurate charts and stable performance. The dashboard gives a complete view of my holdings.
I personally find that skyler here — I’ve tried testing new tokens and the reliable uptime impressed me.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Dadasdas Click News – Updated topics ko simple aur engaging style mein cover karta hai.
Regіstrіere dich jetzt und sіchere dir das Willkоmmеnspаket: bіs zu 100 Frеіspіеle und bіs zu 1950Еur Воnus!
Тоp Spіеle und sofоrtіge Gewіnnе аuf
https://playquantum.shop/bvkp5qt
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Casinozer Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, en revanche des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Casinozer Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, facilite une immersion totale. A noter les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des recompenses continues.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis epate par Casinozer Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Globalement, Casinozer Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A signaler les evenements communautaires dynamiques, cree une communaute vibrante.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Casinozer Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, neanmoins quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Casinozer Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Ajoutons que le design est moderne et attrayant, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement super les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages sur mesure.
En savoir plus|
Je suis completement seduit par Mystake Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par moments quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Globalement, Mystake Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En bonus le site est fluide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement super les transactions en crypto fiables, garantit des paiements rapides.
AccГ©der Г la page|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Mystake Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, par ailleurs des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Mystake Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En extra le design est moderne et attrayant, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, cree une communaute vibrante.
https://mystakecasinoappfr.com/|
Je suis completement seduit par Pokerstars Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, occasionnellement plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En conclusion, Pokerstars Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un element fort les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Ouvrir le site|
Je suis emerveille par Stake Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, cependant plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Globalement, Stake Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A mentionner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des avantages uniques.
Avancer|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Stake Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, toutefois des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En resume, Stake Casino merite une visite dynamique. En complement le design est style et moderne, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires engageants, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Parcourir le site|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas
deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis
apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a
partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos
de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo
para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para
hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de
apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas
en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas
online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas
sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas
deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas
android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas
deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre
amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa
de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app
de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas
deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas
colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de
apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas
sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de
apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de
apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para
apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app
para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control
de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps
de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas
mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10
euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a
corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas
al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves
barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas
alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas
ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas
anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia
argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas
argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana
el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina
vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas
athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas
athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico
campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético
de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid
real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid
champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto
pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca
athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas
barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca
hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça
madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas
barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas
barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona
villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona
vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa
madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas
béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol
pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis
– chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas
betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis
sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy
colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar
online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia
real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino
olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas
caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos
madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas
caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas
campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa
del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas
campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga
santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas
campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera
de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de
galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de
caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de
caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas
champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas
champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league
2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile
venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas
ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas
ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas
city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas
como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas
mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para
esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas
combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas
seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero
real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas
con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas
copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa
argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas
copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del
rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa
sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas
cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1
euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas
de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de
boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas
de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas
de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se
juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas
de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de
caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de
carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos
online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa
america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula
1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol
en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de
futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol
online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas
de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol
para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas
de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de
galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas
de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas
de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la
nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de
partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas
de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de
sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis
hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de
tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas
de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas
del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del
día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas
del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del
sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros
gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas
deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas
deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas
deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas
com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas
deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas
deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas
deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de
nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de
peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas
en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas
en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas
deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas
deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas
estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas
eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas
foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas
deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas
hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas
deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas
deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas
deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas
nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas
deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas
online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para
ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs
ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas
promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas
deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real
madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas
deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras
para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas
sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas
deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas
stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas
deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas
ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas
deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas
y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com
foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a
segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero
real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas
directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor
juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas
doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs
venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas
en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas
en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas
en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos
virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas
en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas
en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas
en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas
en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas
en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo
argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas
españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas
españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas
españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa
inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises
bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol
villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports
peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas
eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa
hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas
europa league hoy|apuestas europa league
pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1
bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas
f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de
ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas
favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos
mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions
peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas
final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final
de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del
mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas
final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas
final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas
finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas
foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas
futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas
futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas
fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol
español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol
eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol
foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas
fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol
mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas
futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos
online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador
copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador
copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas
ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del
mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas
ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador
nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas
ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas
girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas
goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas
golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas
gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas
gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis
sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y
ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas
handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas
online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas
holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter
barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos
en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos
online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings
league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga
hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas
las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas
legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas
leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga
de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas
liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid
arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid
barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas
madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid
gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid
osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas
madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas
mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo
goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas
mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas
multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial
balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de
clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas
mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial
formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto
gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas
mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas
mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales
de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas
nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas
nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas
nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba
pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas
nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas
nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online
boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas
online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online
golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas
online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas
online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online
sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas
online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna
real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas
over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas
para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para
eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar
dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la
liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas
para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para
los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas
partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos
csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas
paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas
peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a
primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff
segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por
internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera
division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas
psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos
tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que
es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a
segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas
quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará
el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid
athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico
champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas
real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real
sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real
madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real
madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real
sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas
registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas
roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas
segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda
division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas
seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy
futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras
nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras
ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas
senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla
athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas
sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas
simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas
sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas
sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas
sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas
super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga
argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas
tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa
davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas
tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas
tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas
tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas
torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas
uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc
como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc
online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas
us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid
barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor
app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor
galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal
betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas
villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas
virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas
y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina
peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs
chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester
united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real
madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico
de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de
madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid
apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real
madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca
apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca
madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca
vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona
apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de
apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real
madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis
apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona
vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid
apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis
apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas
online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas
gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida
casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa
de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de
bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de
casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono
de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca
apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por
registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito
apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca
apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos
casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas
nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de
apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de
casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis
apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos
gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo
apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador
cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas
seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador
de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas
deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora
apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora
apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas
de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora
de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora
de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para
apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping
apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular
apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular
momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo
de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de
caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de
caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de
madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca
de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas
deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa
apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas
nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa
de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa
de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas
betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono
por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa
de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas
colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas
mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas
con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa
de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de
futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas
deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas
deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito
minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de
apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa
de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de
apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de
apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso
mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa
de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de
apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas
nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa
de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas
online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas
online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de
apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de
apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa
de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo
de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de
apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial
de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas
caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas
españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas
españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas
golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas
legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas
apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas
baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de
apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas
de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas
de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions
league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de
apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas
con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de
apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas
con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de
apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas
de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas
con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta
en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas
de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de
apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas
de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas
en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas
deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas
en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas
deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas
legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas
de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito
mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas
de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas
en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas
de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas
de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas
españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de
apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de
apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de
apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas
eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas
de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de
apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5
euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas
de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de
apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas
de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas
de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de
apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas
de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de
apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online
ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas
de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas
de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas
online españa|casas de apuestas online mas
fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online
nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas
de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas
pago paypal|casas de
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de
apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2
apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas
que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a
partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas
deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas
android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de
fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de
fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de
apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas
deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de
apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas
colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app
de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de
apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas
peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas
de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para
hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas
mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para
apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia
apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a
caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas
alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas
nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas
anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina
campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas
argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina
vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas
arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas
asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas
athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas
athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas
atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto
nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs
juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas
barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de
madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas
barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de
liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana
la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas
barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas
barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona
real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas
barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona
vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket
hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis –
chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas
betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis
vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas
bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de
campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas
boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas
caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos
zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas
campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de
champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas
campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas
campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas
campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas
campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato
f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas
carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos
hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino
futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino
madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino
online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta
barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta
madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas
champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions
league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions
league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league
pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas
chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo
femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas
ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas
city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas
colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas
combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas
combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta
semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para
mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para
hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero
virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de
ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de
debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas
copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas
copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de
1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto
para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas
de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como
se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas
de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de
colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de
futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de
futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol
español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de
fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol
para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de
futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol
seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol
sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de
galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey
sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas
de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la
copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas
de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para
hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema
como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de
tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas
del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid
barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas
del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas
del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10
euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas
app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas
deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas
beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas
casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas
colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas
con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas
consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas
copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas
deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas
deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero
ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas
deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas
en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas
deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias
seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas
deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro
tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas
deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas
deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol
colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas
deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas
deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos
olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas
deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga
española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas
deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas
deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas
nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas
deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online
chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas
deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas
online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para
hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de
hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas
predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que
aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas
regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas
deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas
deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras
para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas
deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas
deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas
deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de
mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas
deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas
valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas
deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas
dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas
directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas
doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones
venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas
en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de
caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino
online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos
online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas
en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la
nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas
en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea
deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas
en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea
mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas
en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los
esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de
mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo
futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania
eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas
españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana
eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas
españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises
bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas
espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports
colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports
lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas
euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga
pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas
f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas
f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles
de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para
ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas
fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions
league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa
de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa
libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final
de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas
final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final
rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas
finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas
fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas
foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano
nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol
hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol
pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol
virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos
hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas
ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del
rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la
eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del
mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas
ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas
girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la
liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam
de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas
gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis
puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas
gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap
asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas
hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas
holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas
impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos
en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador
sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la
liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas
las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends
mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas
legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas
liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga
de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga
españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas
liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas
madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid
barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas
madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas
madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid
gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas
madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs
barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester
athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas
mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas
seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor
jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas
méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples
como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas
mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas
mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial
ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas
mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial
formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas
mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas
nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl
playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas
nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos
eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online
bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online
caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online
ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de
caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online
esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas
online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas
online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online
mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas
osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real
madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas
over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas
paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises
bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas
para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el
partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas
para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para
ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la
ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas
para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar
la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas
para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para
hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas
para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para
la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas
partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas
partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas
partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru
vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas
playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet
para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas
portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones
futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas
pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg
barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas
puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas
que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas
quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas
quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas
real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid
athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico
champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real
madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas
real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real
sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas
real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid
vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas
real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs
sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas
real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas
real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas
registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas
retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world
cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda
b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras
foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras
gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de
semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras
para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas
seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas
semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla
atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas
sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla
celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas
sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas
sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla
valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito
minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas
sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas
super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas
tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa
davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis
hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas
tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas
topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa
champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia
topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay
vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas
valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal
barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas
villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester
united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales
colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales
sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas
y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas
y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas
y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs
colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina
vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid
apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid
real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico
madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador
de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca
bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça
madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona
– real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa
de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de
datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis –
chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla
apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de
tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono
bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono
bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida
casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de
apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida
casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono
de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por
registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas
deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas
colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos
apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos
bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas
de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas
gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de
apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa
de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de
apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos
sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot
de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador
cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de
apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora
apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas
combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora
de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de
apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora
poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas
futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular
cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba
apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos
apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos
apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de
caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas
argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono
bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono
sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa
apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores
cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa
apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa
de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico
de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de
apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono
por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de
apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas
cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas
ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores
cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa
de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de
caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa
de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de
peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa
de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de
apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas
peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas
europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de
apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga
española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas
segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas
méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa
de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del
real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de
apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online
españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago
anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de
apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa
de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa
de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso
minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa
de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia
en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas
españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas
licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas
apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas
apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas
de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono
bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos
sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas
de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de
mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de
apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas
de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de
apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas
con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas
con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de
apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de
apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de
apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas
de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas
deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas
deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de
apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas
de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas
españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de
apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas
en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas
en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas
de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa
inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas
españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas
de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula
1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas
futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas
ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas
legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas
seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores
cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas
nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas
online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas
de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de
apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de
apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas
de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de
apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online
venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas
paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Hey guys… something spicy coming.
private cam show made simple. Watch now, chat instantly, and explore exciting Worldwide content.
п»їhttps://pussycats.me
Pretty component to content. I simply stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to say that I get actually loved account your weblog posts. Anyway I’ll be subscribing in your feeds and even I achievement you get entry to consistently quickly.
J’adore la vibe de Pokerstars Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus initial est super. Le service client est de qualite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, malgre tout plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour finir, Pokerstars Casino merite un detour palpitant. A noter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
I am truly happy to read this website posts which carries plenty of valuable data, thanks for providing these kinds of data.
Je suis accro a Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, bien que quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En somme, Pokerstars Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement captivante, facilite une experience immersive. Un point cle les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, cree une communaute vibrante.
http://www.pokerstarscasino366fr.com|
Je ne me lasse pas de Pokerstars Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Pokerstars Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fluides.
Lancer le site|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Mystake Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, a l’occasion des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En somme, Mystake Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, renforce le lien communautaire.
Naviguer sur le site|
Je suis fascine par Casinozer Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, cependant des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En somme, Casinozer Casino assure un fun constant. En plus la navigation est fluide et facile, booste l’excitation du jeu. A noter les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
J’adore la vibe de Mystake Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour faire court, Mystake Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A noter l’interface est simple et engageante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce la communaute.
Cliquer maintenant|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinozer Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour conclure, Casinozer Casino garantit un amusement continu. En plus l’interface est lisse et agreable, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un bonus les options variees pour les paris sportifs, cree une communaute soudee.
Lire plus|
Je suis epate par Casinozer Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, malgre tout plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En bref, Casinozer Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Par ailleurs le design est style et moderne, permet une immersion complete. Un atout les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, garantit des paiements rapides.
Avancer|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was great. I do not know who you are but certainly you’re going to a famous blogger if you are not already 😉 Cheers!
New Horizons Hub – A clear guide to discovering valuable opportunities easily.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
When I initially commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove people from that service? Cheers!
The interface is trustworthy service, and I enjoy cross-chain transfers here. The mobile app makes daily use simple.
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis
marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas
que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto
se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar
y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre
topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de
apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para
hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones
apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas
android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas
perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones
de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app
android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app
apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas
deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app
de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de
apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas
online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app
de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app
moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para
apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de
futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps
para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer
apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10
euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas
a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a
jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas
al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis
wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos
equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas
anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas
anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia
argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina
españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia
cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina
gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas
argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas
argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso
a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas
athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas
athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic
real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic
valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas
atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético
copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de
madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real
madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto
handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas
barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas
barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs
madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona
athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona
atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de
liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana
la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas
barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona
psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas
barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas
barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas
betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas
betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis
valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas
bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia
real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo
español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas
boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas
caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos
madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas
caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions
2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference
league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas
campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp
2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas
campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de
futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos
hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de
galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras
de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras
de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos
sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta
barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions
hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league
– pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league
hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions
league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas
chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas
chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas
clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real
madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia
brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas
de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas
combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para
hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas
recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para
hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa
brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del
mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas
copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del
rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas
copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa
sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas
bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas
de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas
de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las
vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de
caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas
de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas
de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas
de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas
de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de
esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula
1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de
futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol
en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol
mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de
fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy
seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas
de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas
de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de
hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de
juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas
de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas
de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas
de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas
ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema
como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de
ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de
hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas
del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas
deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas
10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas
argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de
madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas
barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos
de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas
casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas
deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas
deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como
se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas
deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas
copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del
dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble
oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas
deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas
en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas
deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas
foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas
deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas
ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas
deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas
libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia
españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas
listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores
casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas
mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas
nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas
online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas
pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de
hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas
deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado
exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas
deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas
deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas
tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas
tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas
tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas
ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas
deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y
casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com
foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso
a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de
honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble
oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas
en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas
en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas
en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas
en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas
en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas
en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas
en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos
de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas
en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas
en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas
españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa
francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas
españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas
espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports
fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports
peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas
eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa
hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas
euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league
hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas
euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas
f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las
vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de
europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas
final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia
nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula
1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano
nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas
futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol
mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas
futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador
champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador
copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador
europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana
uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de
liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas
golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas
grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas
gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas
gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas
hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre
hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas
hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las
vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales
en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas
liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de
baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas
liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas
madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid
barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas
madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas
madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid
celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana
liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas
madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters
de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo
goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas
méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas
mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas
momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas
multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial
baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas
mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas
mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas
mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas
mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas
mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba
campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba
finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas
nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba
tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas
nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas
nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas
ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono
bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas
online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas
online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas
online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas
online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online
nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas
online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online
sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna
barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas
over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises
bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas
para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para
el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas
para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la
liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas
para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la
champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas
para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los
partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa
marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions
league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de
futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas
peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas
playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por
internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por
ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas
pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas
promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos
tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos
nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que
es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas
quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas
quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas
quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas
rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid
atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real
madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid
bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas
real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid
manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas
real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real
madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs
atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas
real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real
sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby
mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas
segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras
baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras
eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas
seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas
seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas
seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras
tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas
senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla
campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas
sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas
sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas
sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas
sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas
stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas
tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas
tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa
pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis
retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera
division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas
ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas
ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas
uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas
valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real
madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas
valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela
argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas
villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales
colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de
hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de
futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro
nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay
apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia
apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real
madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid
apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada
de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca
madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs
real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter
apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona
sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs
villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea
apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono
apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida
apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida
casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de
apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida
apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida
casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono
de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de
apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro
apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito
apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa
de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos
apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos
apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas
de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de
apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de
apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de
apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas
de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de
apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas
para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos
apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora
apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora
de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora
de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora
de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular
apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas
apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular
cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de
apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad
cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de
cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales
de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera
de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera
de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de
caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras
galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa
apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono
sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa
apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas
nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de
apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de
apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa
de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas
bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de
apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de
mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas
champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de
apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de
apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las
mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa
de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa
de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de
fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca
de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de
apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de
apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de
apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de
apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5
euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1
euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de
apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa
de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de
apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1
euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales
en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa
de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa
de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa
de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de
apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa
de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa
de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas
online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de
apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de
apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real
madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de
ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de
apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de
apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas
apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas
colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas
apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas
apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas
mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas
ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas
apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas
de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas
de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas
bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de
apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions
league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas
de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de
apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de
apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas
de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas
con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas
de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas
de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de
apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas
de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de
apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas
deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas
de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas
deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas
deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas
de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas
peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas
de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas
en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas
en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas
en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de
futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa
alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas
de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas
con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de
apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de
españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas
ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1
euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas
legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de
apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas
de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas
de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de
apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de
apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas
de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas
online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas
online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de
apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas
online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online
españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas
de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online
nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online
usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas
I value the responsive team and fast transactions. This site is reliable.
The exploring governance process is simple and the clear transparency makes it even better. The mobile app makes daily use simple.
Terrific post but I was wondering if you could write a litte more on this topic? I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit more. Kudos!
Good day, colleagues! I recommend reliable databases for Xrumer and GSA Search Engine Ranker. They come at low cost, are updated regularly, and help you save resources and time during SEO efforts.
You can view the information on the website https://dseo24.monster/vip-base-for-xrumer-and-gsa-ser/
You can choose any language on the website. You can use LTC, USDT, TRX, ETH, BTC, SOLANA and other money.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Pokerstars Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par moments des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En resume, Pokerstars Casino offre une aventure memorable. Pour ajouter la navigation est claire et rapide, permet une immersion complete. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages uniques.
Explorer davantage|
Официальный интернет-сайт компании : http://ruptur.com/
Highly descriptive article, I enjoyed that bit. Will there be a part 2?
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own weblog and was curious what all is required to get set up? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very internet savvy so I’m not 100% positive. Any tips or advice would be greatly appreciated. Appreciate it
I was skeptical, but after a year of trading, the low fees convinced me. I moved funds across chains without a problem.
J’adore la vibe de Stake Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. Globalement, Stake Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A souligner le design est tendance et accrocheur, facilite une experience immersive. Un plus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, cree une communaute soudee.
Cliquer maintenant|
Je suis enthousiasme par Stake Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Globalement, Stake Casino offre une aventure memorable. A noter le site est rapide et engageant, booste le fun du jeu. Un avantage les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Aller plus loin|
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your website. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more enjoyable for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a developer to create your theme? Exceptional work!
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Pokerstars Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par moments des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En bref, Pokerstars Casino merite un detour palpitant. A signaler la navigation est simple et intuitive, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement super les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, assure des transactions fluides.
Lancer le site|
Je suis totalement conquis par Stake Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est transparent et rapide, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En bref, Stake Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A noter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, booste le fun du jeu. Un atout le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, renforce le lien communautaire.
Entrer sur le site|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Casinozer Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En conclusion, Casinozer Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons aussi l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, cree une communaute soudee.
Naviguer sur le site|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
J’adore l’energie de Mystake Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, mais encore des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Mystake Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A souligner le site est rapide et immersif, apporte une energie supplementaire. Egalement super les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des paiements securises.
Essayer maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Mystake Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, parfois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Au final, Mystake Casino assure un fun constant. En plus l’interface est simple et engageante, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Apprendre les dГ©tails|
Je suis completement seduit par Casinozer Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, offrant des tables live interactives. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, par contre des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En resume, Casinozer Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, renforce la communaute.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis epate par Pokerstars Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, toutefois des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Globalement, Pokerstars Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En complement la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, permet une immersion complete. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, renforce le lien communautaire.
Commencer Г explorer|
Hi there, I discovered your web site via Google whilst searching for a comparable matter, your web site came up, it seems to be good. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Hi there, simply changed into alert to your weblog through Google, and located that it’s truly informative. I’m gonna watch out for brussels. I’ll appreciate if you proceed this in future. Lots of people shall be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
I’m not sure exactly why but this blog is loading incredibly slow for me. Is anyone else having this problem or is it a problem on my end? I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Project Inspiration Hub – Discover practical projects and creative ideas for daily fun.
I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is attractive, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an impatience over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come further formerly again as exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this increase.
Нотариальный перевод быстро – ближайший перевод документов. Нотариальный перевод документов в Самаре. Срочно, качественно, недорого. Любые языки. Гарантия принятия. Звоните сейчас!
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, rarement plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En conclusion, Pokerstars Casino assure un fun constant. En extra l’interface est lisse et agreable, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un atout les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des privileges personnalises.
Voir les dГ©tails|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, occasionnellement plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour finir, Pokerstars Casino merite une visite dynamique. De surcroit le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des recompenses continues.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
Je suis accro a Stake Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service client est excellent. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Globalement, Stake Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En extra la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement attrayant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges personnalises.
Visiter en ligne|
Je suis totalement conquis par Mystake Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, en revanche quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Mystake Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A signaler la navigation est claire et rapide, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, garantit des paiements securises.
Aller sur le site web|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Casinozer Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Globalement, Casinozer Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour ajouter la navigation est simple et intuitive, apporte une energie supplementaire. A signaler le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui stimule l’engagement.
VГ©rifier le site|
Наследственные документы точно – перевод документов цена самара. Перевод личных документов. Самарское бюро. Нотариальное заверение. Срочно и качественно. Конфиденциально.
Je suis totalement conquis par Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Au final, Mystake Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement top les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des avantages uniques.
Voir la page d’accueil|
Je suis captive par Casinozer Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, quelquefois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Casinozer Casino assure un fun constant. De plus la navigation est fluide et facile, booste le fun du jeu. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui motive les joueurs.
https://casinozercasino777fr.com/|
Потребность в изготовлении дубликатов регистрационных знаков может возникнуть у любого автовладельца https://kamaz1981.ru/the_articles/izgotovlenie-dublikatov-nomerov-na-avtomobil.html. Существует несколько распространенных ситуаций, когда эта услуга становится просто незаменимой.
When it comes to expanding living space in your property, one of the most effective and practical solutions is to build an accessory dwelling unit, or ADU. These structures, also known as granny flats or in-law suites, are small, self-contained homes that can be built on the same lot as a primary residence. They can be used for a variety of purposes, such as providing a home for aging parents, a private space for adult children, or a source of rental income. However, the success of your ADU project largely depends on the quality and expertise of the builders you hire. In this regard, finding the best adu builders is paramount to ensure that your project is executed flawlessly. These professionals have the necessary experience and skill set to navigate the complexities of ADU construction, from securing permits to designing efficient floor plans and selecting high-quality materials. They understand the unique challenges that come with building ADUs, such as maximizing space and ensuring privacy, and they know how to address these issues effectively. Moreover, the best ADU builders are those who prioritize communication and transparency. They keep their clients informed at every stage of the project, ensuring that their vision and preferences are reflected in the final product. They are also upfront about costs and timelines, helping homeowners avoid unpleasant surprises down the line. It’s important to remember that building an ADU is a significant investment, and as such, it’s worth taking the time to find the right team for the job. By choosing the best ADU builders, you can ensure that your project will be a success, adding value to your property and enhancing your quality of life. Therefore, before you embark on your ADU project, make sure to do your research, ask for references, and choose a builder that aligns with your vision and expectations. With the right team on your side, you can turn your dream ADU into a reality.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
https://tenchat.ru/media/4046976-kak-ya-vzyal-perviy-zaym-onlayn-i-ne-popal-v-dolgovuyu-yamu-chestniy-razbor-mfo-2025
Your Growth Path – Daily motivation and advice for cultivating consistent personal improvement.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15
euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2
en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2
que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas
que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas
android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas
deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones
de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones
de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar
seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de
futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas
deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas
entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas
de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas
android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de
apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas
en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas
sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app
de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas
gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app
para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app
para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus
apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2
division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a
la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas
al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas
alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso
campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y
bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas
nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas
argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina
colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas
argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas
argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina
paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs
australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas
argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas
athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic
manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic
real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas
athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas
atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de
madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas
atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico
madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas
bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto
nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas
barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas
barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça
hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas
barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real
madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca
vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas
barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas
barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real
sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas
bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis
fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis
mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas
betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis
valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo
de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas
campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions
league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la
champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas
campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula
1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas
campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp
2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial
baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato
f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas
carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas
carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera
de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas
carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos
en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras
de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas
carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas
carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre
partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino
futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino
online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas
celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta
madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions
foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas
champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas
ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city
real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs
argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas
mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas
nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para
hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas
combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras
para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas
con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas
con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas
copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa
brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa
del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey
futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey
pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial
de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas
cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de
baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de
caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos
como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador
y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas
de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de
casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa
america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas
de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de
europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas
de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol
colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas
de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de
futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol
para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol
pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de
futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas
de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy
seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas
de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de
la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la
eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga
bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas
ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas
de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de
sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis
de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas
de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de
ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del
clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas
del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia
futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas
apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas
deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono
sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas
deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas
deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas
deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas
deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas
copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la
mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de
peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas
en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas
en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas
es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas
deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas
estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles
de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas
foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol
argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas
deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero
seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas
gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas
deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la
liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres
de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas
deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online
por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para
hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas
deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas
peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru
vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas
pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas
rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas
deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas
deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas
deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas
valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas
deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a
segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso
primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas
diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero
real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo
futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft
nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas
ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el
clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas
en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de
futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas
en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la
nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea
deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea
estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas
en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos
de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos
de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas
en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas
en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo
tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas
españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas
españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el
mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas
españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas
españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra
eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises
bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas
espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas
esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas
euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa
españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga
baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas
europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas
f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1
monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para
ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas
favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos
mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions
league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final
copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final
copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del
rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final
eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1
pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas
foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia
españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas
futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas
futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas
futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas
futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas
futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol
hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas
futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos
pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la
eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador
europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga
española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial
baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar
eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana
la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona
real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf
pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas
gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas
gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por
registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a
eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas
handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy
futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas
hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter
barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos
olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas
la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las
vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas
legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas
legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga
de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas
liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool
real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid
barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca
supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas
madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas
madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real
madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas
seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas
mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas
mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial
brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial
de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas
mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas
mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba
consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba
gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas
nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas
nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas
online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas
online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online
colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online
de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas
online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna
athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna
sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos
ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para
champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para
el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas
para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas
para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas
para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para
la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido
españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas
partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de
futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas
paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru
brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas
peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso
a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia
argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por
sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas
primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas
pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas
prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por
tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que
significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana
eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas
quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas
quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid
arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico
champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético
de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real
madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid
betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid
manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid
vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real
sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas
hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas
resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma
barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world
cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas
segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas
seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras
futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras
hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras
para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas
seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla
campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la
liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas
sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla
manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real
sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas
simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas
sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema
trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake
10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas
tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de
mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis
seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas
tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway
cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa
champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas
ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas
ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay
colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal
bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas
villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales
sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de
hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de
azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas
y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina
francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina
vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic
barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real
madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona
apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real
madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico
vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca
inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid
apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid
apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao
apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona
vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best
america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas
online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog
apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas
gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa
apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa
apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de
bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de
registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por
registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro
casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca
apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de
apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos
casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos
casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas
sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas
deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de
bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida
de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de
casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis
apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos
sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas
gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil
vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas
seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora
apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas
multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora
apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de
apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de
apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para
apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular
apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas
combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas
deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos
apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos
de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos
apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas
barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa
apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas
nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de
apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa
de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de
apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono
sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas
cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa
de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas
colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa
de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa
de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de
apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas
deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito
5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1
euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de
apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de
apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de
apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1
euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa
de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa
de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas
méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas
mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas
oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa
de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas
online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de
apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas
pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para
ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas
peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa
de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de
apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real
madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas
ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas
golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas
apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas
apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5
euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas
de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono
de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de
apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas
de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas
de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas
con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas
de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas
de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas
de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas
con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas
con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas
de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas
deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas
en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas
de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas
deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de
apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de
apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de
apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas
de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de
apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas
españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas
de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de
apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas
futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas
de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de
apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas
legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas
de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas
mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas
de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas
de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas
españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas
de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de
apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de
apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas
online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas
online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de
apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas
de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin de
J’adore le dynamisme de Coolzino Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par contre plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour faire court, Coolzino Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En bonus le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un avantage les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui motive les joueurs.
Tout apprendre|
BreachDatabase – Exposed or Safe? Scan & See Instantly!
Think you’re safe? Think again — the dark web never sleeps, but BreachDatabase keeps you ahead.
Search across 33 billion compromised credentials with 50 million daily updates, all in seconds.
Use BreachDatabase’s account compromise checker to scan your email and see if you’re at risk.
Experience full protection, instant reports, and verified clean data downloads — all for just $2.
Scan now: https://BreachDatabase.net
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Coolzino Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par ailleurs des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Coolzino Casino assure un fun constant. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A mettre en avant les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Explorer le site|
Je suis captive par MonteCryptos Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, mais encore des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En bref, MonteCryptos Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Par ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, cree une communaute soudee.
Aller sur le web|
J’adore le dynamisme de Lucky8 Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, bien que des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, Lucky8 Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour ajouter la navigation est fluide et facile, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des paiements securises.
Parcourir maintenant|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour MonteCryptos Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, parfois des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En bref, MonteCryptos Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A souligner le site est fluide et attractif, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fluides.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
Je suis accro a Lucky8 Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, en revanche quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En somme, Lucky8 Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement captivante, apporte une energie supplementaire. A signaler les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce la communaute.
Apprendre comment|
Je suis sous le charme de NetBet Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots fluides. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, mais des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En bref, NetBet Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A souligner l’interface est simple et engageante, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un plus les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, renforce le lien communautaire.
Passer à l’action|
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Stylish Choice Daily – Quick access to trendy items that make shopping simple and fun.
Je suis emerveille par Coolzino Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En fin de compte, Coolzino Casino offre une aventure memorable. A souligner la navigation est intuitive et lisse, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un point cle les paiements securises en crypto, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Explorer davantage|
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans
dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé
paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age
paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide
aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de
paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme
paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris
sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris
sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse
de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif
sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli
de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli
paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris
sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris
sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de
paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif
en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris
sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris
sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de
bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans
justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris
sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris
sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a
faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce
paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce
paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner
paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris
sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis
paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis
sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll
management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris
sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de
bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de
depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus
en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans
depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris
sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif
en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif
sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet
paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris
sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une
cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul
combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris
sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des
cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris
sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris
sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de
mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi
paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une
cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash
out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris
sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de
cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code
paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo
paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot
paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris
sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris
sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné
pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris
sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment
analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner
au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment
ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment
calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris
sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris
sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche
avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment
etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie
sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire
des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris
sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris
sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les
paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment
faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne
les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes
dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les
paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand
oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout
les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au
pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner
au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment
gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner
aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs
sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans
les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de
l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent
avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des
paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner
en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner
sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris
sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les
paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner
un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari
sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris
sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment
marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche
les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent
les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment
parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de
paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris
sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote
pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari
sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes
paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris
sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur
de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari
sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif
des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris
sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris
sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les
cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap
paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes
paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris
sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris
sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari
sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris
sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil
paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif
tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils
de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris
sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils
paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote
a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de
pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote
minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça
marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif
explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif
france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif
moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes
de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris
sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot
5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe
les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche
avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb
paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs
hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis
paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les
gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de
gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement
sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd
hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce
week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements
sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire
des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire
fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer
les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll
paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de
paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum
paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris
sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux
pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari
sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant
paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100
euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros
par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner
a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari
sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent
pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif
a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner
au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup
d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace
aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris
sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie
avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie
avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les
coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris
sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris
sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris
sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif
application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5
gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris
sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram
paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap
1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris
sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap
pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap
paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris
sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors
arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif
france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu
de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu
paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux
de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif
gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs
en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris
sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris
sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris
sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise
des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la
méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse
cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de
paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site
de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris
sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux
paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les
applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les
gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs
sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris
sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris
sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari
sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les
paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les
paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les
plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au
paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse
cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites
de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites
de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1
paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des
champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris
sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste
pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris
sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris
sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris
sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic
calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris
sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris
sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris
sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match
arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match
interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match
reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris
sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur
app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli
pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli
paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur
application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de
paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris
sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur
application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris
sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de
paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote
site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur
offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de
bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre
paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur
pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur
paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif
en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur
site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur
site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site
de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif
canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur
site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site
de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur
site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif
international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs
en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site
pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site
paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site
paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif
france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris
sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site
pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur
strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur
technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour
gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de
paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure
appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris
sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes
paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris
sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante
paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode
infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au
paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif
foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif
tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris
sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum
depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum
pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris
sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante
pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante
paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode
match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif
hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau
paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site
paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris
sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de
paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris
sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari
sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de
bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris
sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre
de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue
site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre
pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris
sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé
cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris
sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire
des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris
sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack
de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100
euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif
abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif
algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari
sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif
avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari
sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif
combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari
sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe
du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au
cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif
en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif
en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif
faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des
jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif
france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari
sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif
gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a
tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari
sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif
handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari
sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif
match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari
sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari
sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari
sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif
remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari
sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif
rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans
argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari
sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps
reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top
14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france
sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris
sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris
sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif
a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris
sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif
argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris
sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif
au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris
sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris
sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif
avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif
basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif
belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique
france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif
bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris
sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus
sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre
son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur
non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur
remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris
sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif
combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif
comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment
gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif
comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris
sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris
sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif
dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris
sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris
sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec
paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne
france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris
sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris
sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris
sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif
euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue
des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris
sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif
foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe
du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot
suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football
americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif
forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise
des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris
sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france
argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif
france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france
usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif
gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif
gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap
1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris
sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey
nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris
sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le
match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris
sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris
sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise
des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris
sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les
plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris
sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif
ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris
sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif
match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif
match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris
sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif
match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif
meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris
sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris
sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple
2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif
multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba
conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris
sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif
offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre
bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om
psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus
de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus
ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris
sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd
hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif
pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg
inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris
sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif
remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris
sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris
sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6
nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du
jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans
carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris
sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans
depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si
un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris
sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris
sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris
sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif
systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif
systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour
gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris
sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif
tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis
roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif
ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via
paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs
abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs
astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris
sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs
conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris
sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris
sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous
les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs
ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs
ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match
interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans
argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris
sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris
sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine
paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif
au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari
sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse
cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris
sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou
moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif
remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris
sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic
paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif
du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et
aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg
inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris
sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg
paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu
un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans
les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que
signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut
dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les
paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer
paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel
est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est
le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel
pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris
sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif
rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris
sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle
est la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de
paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket
paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris
sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari
sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif
multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris
sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris
sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris
sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante
paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse
paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel
paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse
de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil
paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif
avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site
de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de
parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris
sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de
paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de
paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de
paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris
sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec
neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris
sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif
canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site
de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris
sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors
arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site
de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui
accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris
sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris
sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris
sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site
de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de
paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site
pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif
comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris
en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros
offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris
sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris
sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris
sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif
bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif
france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris
sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif
remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site
paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site
paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris
sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse
paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris
sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris
sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites
pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites
paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris
sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris
sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris
sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris
sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3
4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme
paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système
paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de
paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel
paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tab
was reading earlier might as well drop this here basic outline, fyi only. saw this earlier: more no endorsement.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
дизайн интерьера спб недорого студия дизайн интерьера петербург
Grow Your Potential – Helpful guidance to unlock your inner potential and confidence.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
дизайн интерьера онлайн дизайн интерьера спб
fantastic publish, very informative. I ponder why the opposite experts of this sector do not notice this. You should proceed your writing. I’m confident, you have a huge readers’ base already!
Configuration loli video
afpo.eu/357
go.euserv.org/1as
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
This website definitely has all of the info I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Hello there, You have done a great job. I will certainly digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m confident they will be benefited from this site.
lost track online again and thought i’d share pretty neutral, fyi only. dropping here: more fyi.
Определение цвета по фото – сервис определения цвета по картинки. Technguides – отличный сайт для определения цвета пикселя бесплатно.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Hi! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
scrolling through random stuff and thought i’d share basic outline, still maybe worth a look. leaving a note: reference as is.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
I like the valuable information you provide in your articles. I will bookmark your weblog and check again here frequently. I am quite certain I will learn lots of new stuff right here! Good luck for the next!
Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found that it’s truly informative. I am gonna watch out for brussels. I’ll appreciate if you continue this in future. Lots of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
lost track online again and thought i’d share just generic content, still maybe worth a look. found this: reference as is.
Fantastic site you have here but I was wanting to know if you knew of any discussion boards that cover the same topics discussed in this article? I’d really like to be a part of community where I can get advice from other experienced people that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Appreciate it!
Modern Style Spot – Find curated trendy products that make shopping convenient and enjoyable.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
I’m really impressed with your writing skills and also with the layout on your blog. Is this a paid theme or did you modify it yourself? Either way keep up the nice quality writing, it is rare to see a great blog like this one these days.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Hey there! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a group of volunteers and starting a new initiative in a community in the same niche. Your blog provided us useful information to work on. You have done a outstanding job!
Stylish Choices Hub – Quick access to fashionable items that elevate your everyday look.
I am regular visitor, how are you everybody? This article posted at this web site is genuinely good.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
You can certainly see your enthusiasm within the article you write. The sector hopes for even more passionate writers such as you who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. All the time go after your heart.
I like the helpful information you provide in your articles. I will bookmark your blog and check again here frequently. I am quite sure I’ll learn plenty of new stuff right here! Good luck for the next!
Hello! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting sick and tired of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at options for another platform. I would be fantastic if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
We stumbled over here coming from a different website and thought I might as well check things out. I like what I see so i am just following you. Look forward to looking into your web page repeatedly.
Affordable Treasures – Find hidden gems and budget-friendly options today.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
It is the best time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I have read this post and if I could I desire to suggest you few interesting things or suggestions. Perhaps you could write next articles referring to this article. I want to read more things about it!
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
http://suplementar.prg.ufpb.br/index.php?qa=6936&qa_1=%CE%B5%CE%BD%CE%BF%CE%B9%CE%BA%CE%AF%CE%B1%CF%83%CE%B7-%CE%B1%CF%85%CF%84%CE%BF%CE%BA%CE%B9%CE%BD%CE%AE%CF%84%CE%BF%CF%85-%CF%87%CF%89%CF%81%CE%AF%CF%82-%CF%80%CE%B9%CF%83%CF%84%CF%89%CF%84%CE%B9%CE%BA%CE%AE-%CE%BA%CE%AC%CF%81%CF%84%CE%B1-findycar
Do you have a spam problem on this blog; I also am a blogger, and I was curious about your situation; we have created some nice procedures and we are looking to trade strategies with other folks, please shoot me an e-mail if interested.
dealspotmarket – Shopping was easy and prices were very fair.
Browse latest fashion – Found a couple of eye-catching picks fast, very user-friendly.
Trend Explorer Daily – Easily navigate popular categories and find trendy items quickly.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Asking questions are truly good thing if you are not understanding anything entirely, except this post presents fastidious understanding yet.
savvyvaluehub – Prices were excellent, shopping online was a breeze.
Discover top fashion finds – Found several attractive and trendy items quickly, browsing smooth.
brightbuysdaily – Excellent range of products, ordering process was seamless.
Hi, after reading this amazing article i am also glad to share my knowledge here with mates.
For most recent news you have to visit internet and on the web I found this web site as a best site for most up-to-date updates.
https://e-art.com.ua/svitlo-yake-dumaie-chomu-bi-led-tse-ne.html
joyfulgiftsstore – Loved the gift options, site navigation was very easy.
Quick fashion finds – A handful of crisp items appeared right away, navigation smooth.
If you wish for to increase your knowledge just keep visiting this web site and be updated with the most recent news update posted here.
stylemarket – Great trendy collection, navigating the site was effortless.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
bestbrightshop – Shopping was effortless, pages loaded quickly and selection was good.
https://best-bankrotstvo-kaluga.ru
Thanks for one’s marvelous posting! I seriously enjoyed reading it, you will be a great author.I will make certain to bookmark your blog and will often come back later in life. I want to encourage you to continue your great job, have a nice morning!
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
trendcentralhub – Great fashion items, smooth ordering and quick delivery.
Urban style link – Found multiple fashionable items fast, layout user-friendly.
happystore – Found perfect products easily, delivery felt fast and consistent.
marketfindscenter – Excellent product range, navigation felt smooth and fast.
Cùng với hệ thống bảo mật đạt chuẩn SSL 256-bit và đội ngũ hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7, j888slotlogin.com nhà cái từng bước xây dựng được hình ảnh một nhà cái trẻ nhưng cực kỳ bản lĩnh.
Cùng với hệ thống bảo mật đạt chuẩn SSL 256-bit và đội ngũ hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7, j888slotlogin.com nhà cái từng bước xây dựng được hình ảnh một nhà cái trẻ nhưng cực kỳ bản lĩnh.
Cùng với hệ thống bảo mật đạt chuẩn SSL 256-bit và đội ngũ hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7, j888slotlogin.com nhà cái từng bước xây dựng được hình ảnh một nhà cái trẻ nhưng cực kỳ bản lĩnh.
Genuinely no matter if someone doesn’t understand afterward its up to other visitors that they will help, so here it happens.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
chictrendhub – The website layout is stylish and easy to navigate quickly.
Top fashion picks – Several eye-catching items popped up instantly, browsing enjoyable.
marketchoice – Found a lot of interesting items, prices seem good and browsing was effortless.
Kudos! Loads of info.
Feel free to surf to my homepage https://mail.ru/
It’s fantastic that you are getting ideas from this paragraph as well as from our discussion made at this place.
homepickcorner – Wide selection of home products, navigation felt smooth and intuitive.
joyhubgifts – Found great gifts, very satisfied with both price and quality.
trendzone – Great selection of city styles, navigating the site was effortless.
Thanks for finally writing about > %blog_title% < Loved it!
globalfindsoutlet – Quick navigation and effortless ordering, really liked the selection.
joyhomehub – Loved the discounts, website made shopping very smooth.
Thank you for another wonderful article. The place else could anyone get that type of info in such a perfect approach of writing? I have a presentation subsequent week, and I am at the look for such information.
Check fashion items – A few interesting styles were easy to find immediately, layout clean.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
казино официальный
modernfashionfinds – Smooth site layout, fast loading pages, and enjoyable shopping experience.
I take pleasure in, lead to I found just what I used to be looking for. You have ended my four day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
smilecornerstore – Loved the friendly assistance and the quality of items.
Quick fashion finds – A handful of crisp items appeared right away, navigation smooth.
chicfinder – Loved exploring the items, shopping process was fast and easy.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Thanks to my father who informed me about this weblog, this website is in fact amazing.
ко ланта ко лант
trendfusionhub – Stylish pieces at great prices, delivery was super fast.
trenddealhub – Great discounts available, shopping felt effortless and fast.
Urban trend finds – Several standout options appeared right away, browsing easy.
fashionpulse – Nice daily finds, exploring the website was smooth and fast.
Thanks for finally talking about > %blog_title% < Liked it!
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Daily Streetwear Spot – Discover fashionable urban wear curated for a modern lifestyle.
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris
sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif
football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris
sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de
paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris
sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif
tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse
de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse
paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris
sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app
paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif
avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif
sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli
paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse
paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de
parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris
sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris
sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia
paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris
sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris
sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif
offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif
paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans
justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris
sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire
des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les
paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi
paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications
paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris
sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans
depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot
paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce
paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris
sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce
pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces
paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis
sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis
tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll
paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris
sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash
paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue
sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de
paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans
depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif
belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris
sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif
sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris
sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus
site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif
gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers
paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris
sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris
sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul
double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise
paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul
pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris
sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris
sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur
paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer
cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer
roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs
paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris
sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement
meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code
promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif
sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site
paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de
temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris
sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris
sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les
paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment
arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au
paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment
ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer
gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris
sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre
les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de
paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris
sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment
faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment
faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment
fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les
cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans
les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs
grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner
a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a
tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au
pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup
sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au
paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner
au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner
aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris
sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner
dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de
l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris
sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif
foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses
paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les
paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au
pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris
sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris
sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment
marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les
cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment
miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris
sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris
sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris
sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les
cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes
paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur
de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de
côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur
de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur
site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus
paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif
cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes
paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre
paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif
en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site
de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites
paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris
sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre
les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris
sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte
financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil
paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des
champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif
tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris
sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris
sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris
sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils
paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote
a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote
de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari
sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote
paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote
paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris
sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris
sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif
rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme
paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les
paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains
paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot
minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb
paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt
minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de
jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains
des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans
un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement
sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif
paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris
ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote
paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap
paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a
face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des
paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune
paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de
paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier
excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains
paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris
sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les
paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des
jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris
sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france
pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne
paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant
pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris
sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris
sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000
euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris
sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner
a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner
argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au
pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner
au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner
aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris
sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner
de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari
sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner
pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif
foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses
paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum
paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif
impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains
paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs
imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll
paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll
paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris
sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris
sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap
5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris
sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap
européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap
paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris
sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap
paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris
sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris
sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur
gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif
gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de
paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de
paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux
paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs
en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur
blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu
paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote
paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la
martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la
meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner
paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le
meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris
sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus
gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17
secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs
pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les
bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains
de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont
ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris
sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les
meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris
sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari
sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris
sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer
gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris
sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris
sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de
paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris
sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris
sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise
paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris
sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris
sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse
paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel
gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel
gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot
sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel
prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel
prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris
sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs
en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale
paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou
reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu
tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match
suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de
paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli
de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de
paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris
sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris
sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris
sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris
sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur
offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue
paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre
paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris
sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur
promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site
de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site
de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif
en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur
site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur
site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris
sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris
sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site
paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors
arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif
rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris
sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris
sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique
pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure
appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris
sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif
android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures
cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris
sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs
application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote
paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif
en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs
sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au
paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris
sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode
pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise
moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant
maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari
sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple
paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris
sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba
paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau
site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris
sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau
site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites
paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de
paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli
pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre
bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu
paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif
belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro
paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris
sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre
paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris
sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement
paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris
sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris
sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de
mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte
paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100
remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie
aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec
wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas
titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif
comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote
match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari
sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif
du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne
au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari
sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari
sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari
sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise
des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france
italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari
sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari
sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le
plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue
1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari
sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari
sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif
mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari
sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari
sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif
pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari
sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari
sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif
sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari
sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari
sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari
sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis
abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie
sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie
sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif
pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris
hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris
sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100
euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris
sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif
application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres
prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris
sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif
aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris
sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket
coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket
prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris
sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris
sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris
sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot
belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris
sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris
sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue
pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris
sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris
sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris
sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif
comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris
sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif
coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris
sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris
sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris
sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris
sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne
cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne
gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne
suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif
et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa
league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue
des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris
sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca
marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris
sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif
foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris
sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france
argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif
france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris
sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris
sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner
argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris
sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif
gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris
sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris
sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif
handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif
joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif
joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise
des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester
champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour
gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris
sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif
ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des
champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif
ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif
match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match
annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du
jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif
match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif
meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris
sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif
mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins
de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif
moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2
3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif
multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple
explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris
sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif
nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris
sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre
de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif
paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris
sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier
paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif
pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic
foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris
sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg
inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris
sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte
le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif
rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif
remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris
sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif
rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans
argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif
sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur
ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris
sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse
légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du
jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris
sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif
technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris
sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis
gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif
tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc
france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif
vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif
victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris
sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris
sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris
sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs
conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs
du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris
sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne
gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs
en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner
à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs
jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris
sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue
europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris
sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris
sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs
stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir
riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner
sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris
sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris
sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros
gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris
sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus
grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus
ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité
cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo
pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo
site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic
de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic
paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic
paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris
sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris
sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris
sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg
om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris
sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur
se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1
en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris
sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie
dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que
signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie
gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut
dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris
sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel
est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est
le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari
sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site
de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif
est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel
paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus
rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la
meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris
sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les
plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris
sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle
paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris
sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement
paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris
sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur
mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris
sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris
sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris
sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris
sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris
sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur
systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris
sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris
sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site
de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site
de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site
de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors
arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site
de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de
paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site
de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de
paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site
de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif
bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif
comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site
de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de
paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris
sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris
sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de
paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris
sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site
de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris
sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de
paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans
carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif
suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris
sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site
pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif
100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site
pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif
hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris
en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100
euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site
paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec
bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site
paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif
canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris
sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris
sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site
paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement
cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site
paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site
paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site
pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites
de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés
en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de
paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris
sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites
paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot
paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot
paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique
paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques
football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de
paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie
paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner
au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris
sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote
paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme
pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme
paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau
de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris
sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif
gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau
gestion bank
trendpulsehub – Website is fast and responsive, found my desired items quickly.
What a data of un-ambiguity and preserveness of precious knowledge about unpredicted feelings.
Discover urban collections – Several interesting picks appeared quickly, easy to browse.
trendhunterstyle – Pleasant experience, pages loaded fast and navigation was simple.
fashionlane – Enjoyed exploring trendy collections, the site loaded quickly and easily.
Go for details: https://www.salesforce.com/trailblazer/h5606puhol7nvddztv
Usually I do not learn post on blogs, however I would like to say that this write-up very forced me to check out and do so! Your writing taste has been amazed me. Thank you, very nice post.
New loli po*rn
afpo.eu/357
go.euserv.org/1as
chiccornerhub – Excellent deals and a wide variety of styles.
Check this style collection – Found several appealing fashion picks quickly, browsing was smooth.
giftjunction – Lots of useful gifts to choose from, shipping felt efficient.
familystylecorner – Quick and easy to shop, the variety was impressive.
Flourish & Grow Hub – Practical tips and inspiration to support your daily personal growth.
Skip to details: https://www.gamespot.com/profile/npprteam12/
Heya this is somewhat of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding expertise so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
Не упустите возможность сделать ваш праздник незабываемым, выбрав идеальный ресторан под банкет https://banket-restoran.su/ в нашем ресторане!
Правильный выбор места проведения банкета в значительной степени влияет на общее впечатление от праздника.
blsp at
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
shopcentralbig – Excellent deals and effortless checkout, very satisfied.
trendemporium – Nice assortment of items, browsing today was effortless.
Good blog you have here.. It’s difficult to find good quality writing like yours nowadays. I seriously appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
urbanoutlethub – Wide selection of urban items, shopping process felt natural.
SoftStone Hub Store – Smooth site, great selection, and delivery arrived promptly.
trendseasonhub – Loved the seasonal styles, browsing the site was quick and easy.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
fashionhubdaily – Enjoyed exploring the collection, site navigation was smooth.
Daily Dream Builder – Practical strategies to help you visualize, plan, and achieve your goals.
hunterbuyinghub – Pleasant experience, pages loaded quickly and navigation was simple.
onyx-55
fashionflarehub – Trendy items are amazing, website experience is smooth and fast.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
fashionflare – Great selection of outfits, checkout process was seamless.
Wild Sand Online – Trendy products, easy-to-navigate site, and very fast order processing.
Goal-Setting Inspiration – Practical tips and guidance to turn your dreams into achievable actions.
Soft Cloud Favorites – Enjoyable navigation and the site layout is simple to follow.
Lunar Harvest Corner – Finding products is easy and the shop feels welcoming.
Bright Flora Market – Items are easy to locate, and the site feels inviting.
trendbuycenter – Loved the selection, navigating the site was very simple.
timelessharborboutique – Fast-loading pages and organized products for effortless browsing.
urbanshopperhub – Very pleased with products, pricing is excellent and affordable.
urbanpick – Enjoyed exploring the collection, the site loaded quickly and was easy to use.
bs2best at ссылка
Fresh Wind Boutique – Beautifully presented items and a very smooth checkout flow.
live cam rooms free video chat
??????????????????????????
Modern Harbor Spot – Navigation feels natural and items appear without delay.
Creative Ideas Hub – Discover fresh ideas and projects to spark your creativity every day.
Hey, respected followers!
I’d like to tell about latest developments from the world of European sports.
Lately in Italy is developing a real growth of sporting activity.
Especially it’s worth to mention excellent achievements in football.
The national football league delivers impressive performance. Fixtures occur with huge intensity.
Clubs battle for every point, providing an captivating atmosphere at stadiums.
Spectators are thrilled by what’s happening!
Also it’s worth to point out the growing popularity of volleyball and basketball. Rising athletes are confidently making their mark, displaying superb performance.
In conclusion Italian sport is undergoing a unprecedented growth!
Follow the news and enjoy the contests!
uniqueoutletcentral – Smooth browsing and quick checkout, really liked the selection.
Full Circle Corner Picks – Smooth and intuitive navigation throughout the site.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
fashionvaultonline – Trendy products are amazing, browsing is smooth and hassle-free.
бонуси казіно бонусы казино
savemorehub – Great bargains available, website felt responsive and quick.
BrightWind ShopNow – Items looked amazing, and the entire shopping flow felt effortless.
Timber Grove Spot – Items load quickly, and shopping is stress-free.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
happydealshub – Excellent variety of items, shopping process felt effortless.
trendspotstore – Items arrived quickly, and the checkout process was seamless.
Harbor Calm Corner – Shopping felt calm and simple thanks to the neat design.
fashionjunction – Loved discovering new trends, checkout was fast and user-friendly.
Silver Moon Shop – Excellent selection, user-friendly site, and the order arrived promptly.
calmspace – Everything felt organized, exploring the catalog was hassle-free.
Modern Ridge Picks Online – Navigation is smooth, and products are easy to explore.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
glamtrendstore – Trendy items arrived quickly, delivery service was excellent.
bestdealcorner – Pleasant experience, pages loaded quickly and items were easy to find.
Daily Self-Improvement Spot – Tips to nurture habits, focus, and intentional achievements.
Timberwood Picks – Products load quickly and finding what I need is easy.
avani koh lanta krabi resort 4
BrightMeadow Deals – Fast, smooth, and everything showed up exactly when expected.
??????????????????????????????????
Aurora Essentials – Finding what you need is quick and the displays are appealing.
valueemporiumhub – Smooth browsing and great products at reasonable prices.
chicvault – Browsing through products was seamless and visually pleasing.
trendworldcentral – Smooth browsing and fast checkout, really liked the selection.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/ybddma6j
леса строительные Аренда строительных лесов для отделочных работ: Аренда строительных лесов для отделочных работ – это оптимальное решение для выполнения качественной отделки фасадов и внутренних помещений. Леса обеспечивают удобный доступ ко всем участкам, позволяют разместить необходимые инструменты и материалы, а также повышают безопасность выполнения работ. При выборе лесов для отделочных работ важно учитывать высоту, конфигурацию объекта и особенности выполняемых задач.
fashionemporium – Loved browsing the collection, shipping was consistent and speedy.
Origin Peak Boutique – Loved the trendy items, checkout was smooth, and my order arrived quickly.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Whispering Trend Emporium – Quick exploration and products are simple to locate.
Open Plains Picks Online – Navigation is easy, and the site is visually clear.
fashioncrazehub – Loved the fast delivery and wide collection.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/uk-UA/register?ref=XZNNWTW7
dealjunction – Lots of deals to explore, site loads quickly and efficiently.
trendpickhub – Convenient to find stylish pieces, checkout was smooth.
freshchoicehubzone – Smooth interface with well-organized items, very pleasant to browse.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
SoftBlossom Corner Store – Lovely products, smooth online experience, and quick ordering process.
Replika Uhr Herren Kollektion
Daily Fashion Scoop – Stay updated with the hottest fashion trends and stylish selections.
dailybargainhub – Loved the selection of daily offers, everything arrived perfectly.
Coastline Picks – Browsing is smooth, and everything is neatly arranged.
video production services in Cortina
Sunwave Essentials Picks Hub – Exploring products is comfortable and pages load quickly.
hometrendstore – The site loads quickly, and the collection is interesting.
uniquefashioncentral – Smooth browsing and quick checkout, really liked the collection.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
fashionpick – Browsing is seamless, and the site feels organized and responsive.
костюмы спортивные Трикотажные изделия – краеугольный камень современного гардероба, предлагающие беспрецедентный комфорт и универсальность. Толстовки, худи и свитшоты – это не просто одежда, а заявление о стиле, отражение непринужденной элегантности и активного образа жизни. Они идеально подходят для создания многослойных образов, занятий спортом или просто для уютного времяпрепровождения дома. В динамичном мире моды, эти вещи подтвердили свою вневременную привлекательность.
NobleRidge Styles – Loved the modern collection, site worked flawlessly, and shipping was fast.
Kind Groove Spot – Navigation is smooth, and the store feels welcoming.
процедура банкротства сроки проведения Процедура банкротства имеет свои плюсы процедуры банкротства физического лица, такие как избавление от долгов и прекращение начисления процентов и штрафов. Однако, важно понимать, что проведение процедуры банкротства – это сложный процесс, требующий юридической грамотности и опыта. Проведение процедуры банкротства должника должно осуществляться под контролем квалифицированного юриста. Необходимо четко понимать процедура банкротства сроки проведения, чтобы быть готовым к длительному процессу. Процедура банкротства физических лиц по кредитам имеет свои особенности, которые необходимо учитывать. Процедура банкротства физического лица в суде требует подготовки документов и участия в судебных заседаниях. Процедура банкротства физического лица пошаговая инструкция поможет сориентироваться в этапах процедуры. Процедура банкротства физического лица через суд – основной способ проведения процедуры. Процедуры банкротства должника физического лица регулируются законодательством о банкротстве.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/5fye7y59
Positive Mindset Spot – Strategies for cultivating positivity and self-assurance.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Blue Grain Corner – Easily discovered quality items and browsing felt intuitive.
процедура банкротства физического лица в суде Компетентное ведение дела – залог успешного завершения процедуры банкротства физического лица через суд. Важно доверить процедуры банкротства должника физического лица опытным юристам, специализирующимся на банкротстве. Компания должна иметь безупречную репутацию. Только так можно быть уверенным, что процедура будет выполнена в соответствии с законом и все ваши права будут защищены.
freshgiftoutlet – Very easy to shop, found exactly what I wanted.
chicfashionzone – Easy to move through categories, products are clearly displayed.
Kindle Wood Choice – Excellent variety, smooth checkout, and my order arrived quickly.
прогнозы на футбол Привлечение новых игроков и удержание существующих – это важная задача для букмекерских контор. Бонусы букмекеров и промокоды букмекеров – это эффективный инструмент для мотивации игроков и повышения их лояльности. Бонусы могут быть представлены в виде фрибетов, надбавок к депозиту, кэшбека и других интересных предложений. Важно внимательно изучать условия получения и использования бонусов, чтобы избежать недоразумений. Следить за новостями о ставках на спорт – это важный аспект успешного беттинга. Оперативная информация о травмах игроков, изменениях в составах команд, погодных условиях и других факторах, способных повлиять на исход матча, позволяет принимать своевременные решения и увеличивать свои шансы на выигрыш.
Dream Harbor Boutique – Everything loads smoothly, and items are well organized.
списание долгов по кредитам физических лиц банкротство В лабиринте финансовых затруднений, когда долговое бремя угрожает стабильности, банкротство физических лиц выступает как законный механизм избавления от непосильных обязательств. Однако, это сложный процесс, требующий четкого понимания правовых норм и взвешенной оценки всех рисков. Определяющим фактором часто является банкротство физических лиц сроки процедуры, зависящие от ряда обстоятельств, включая сложность финансового положения должника и оперативность работы судебных органов.
Поможем уличшить позиции сайта в поисковой выдачи за счет увеличеник ссылочной массы Хрумером 23
Погнали в ТОП
списать долги через банкротство В непростых финансовых обстоятельствах, когда бремя долгов становится непосильным, процедура банкротства физических лиц может стать спасительным кругом. Однако, прежде чем решиться на этот шаг, необходимо тщательно изучить все аспекты и нюансы, связанные с данной процедурой. Важным вопросом является определение сроков процедуры банкротства физических лиц, которые могут варьироваться в зависимости от сложности дела и загруженности судебной системы.
ORBS Production https://filmproductioncortina.com is a full-service film, photo and video production company in Cortina d’Ampezzo and the Dolomites. We create commercials, branded content, sports and winter campaigns with local crew, alpine logistics, aerial/FPV filming and end-to-end production support across the Alps. Learn more at filmproductioncortina.com
topfavstore – Fast and simple shopping experience, pages loaded quickly.
Wild Horizon Value Store – Lovely items, easy site navigation, and order processing was seamless.
shoppickzone – Layout is neat, products are easy to locate, and browsing is effortless.
Bridgetown Trends – Products are displayed clearly, and the site is simple to navigate.
https://geltaxi.ru/taxi-krasnodar-kislovodsk
Pgsiam777
https://www.soft4led.com/why-jimmy-kimmel-is-the-man-of-the-youtube-era/
Video equipment rental Milan Full-service production company in Milan: Managing every aspect of the production process, ensuring a smooth and efficient workflow from start to finish.
https bsme at
valueandstyle – Great range of items, placing an order was effortless.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Grand Style Deals – Products load well, and finding what you need is simple.
curioushub – Browsing was effortless, and all products were easy to explore.
pragmatic slot
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
https://techfily.com/motherhood-and-music-how-having-a-daughter-transformed-kehlanis-life/
Trendy Market Hub – Discover stylish products that make your shopping quick and enjoyable.
blsp at check
Future Groove Picks – The layout is modern, and finding items is effortless.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/3w8c5xxm
Morning Rust Finds – Browsing was seamless and products are easy to find and appealing.
growthselectionhub – Smooth navigation, fast-loading interface, and items are clearly displayed.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
lucky88
https://pro-dacha.com/2025/08/21/kak-podgotovit-pochvu-pered-posevom-gazonnoy-travy-20250821.html
Urban Peak Selection – Browsing is smooth and products are easy to find.
Trendy Style Spot – Handpicked fashion items to elevate your style effortlessly.
EverPath Market – Smooth browsing and simple navigation make shopping enjoyable.
motivatedpick – Fast navigation, clear product display, and shopping was effortless.
Dawncrest Boutique – Items are easy to explore, and the site feels inviting.
https://ecchc.economics.uchicago.edu/2021/11/30/issue-brief-the-impact-of-hr-5376-on-biopharmaceutical-innovation-and-patient-health/comment-page-666/#comment-35369
https://cincinnatitaiwanesechurch.org/ru/kupit-gashish-bot-taraz-analog-stima-gid_3953.html
Lunar Wave Boutique Picks – Smooth and comfortable shopping experience with a clean layout.
Хочешь развлечься? купить альфа пвп федерация – это проводник в мир покупки запрещенных товаров, можно купить гашиш, купить мефедрон, купить кокаин, купить меф, купить экстази, купить альфа пвп, купить гаш в различных городах. Москва, Санкт-Петербург, Краснодар, Владивосток, Красноярск, Норильск, Екатеринбург, Мск, СПБ, Хабаровск, Новосибирск, Казань и еще 100+ городов.
urbancorner – Smooth interface, quick page loads, and browsing felt natural.
1win not int один вин официальный сайт 1win
Starlit Style Spot – Items are easy to locate, and browsing is smooth.
казино з бонусами казино з бонусами
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Value Shop Daily – Quick access to deals, offers, and savings to make shopping simple.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Timberline Choice – Fast navigation and a visually appealing store make shopping pleasant.
девочки по вызову спб Снять шлюху СПб: Забудьте о стереотипах и насладитесь обществом привлекательной и обаятельной женщины, которая знает, как доставить удовольствие и поднять настроение.
urbancornerhub – Clear layout, easy to browse, and pages respond quickly.
FutureGardenOutlet – Fast-loading pages and clear menus made finding items effortless.
сульфаминовая кислота оптом Сотрудничество с РТХ – это гарантия стабильного и успешного развития вашего бизнеса в динамичном мире современной промышленности
ca do bong da tren mang
Бывает, что нужна помощь не только с входной дверью: кто-то заказывал вскрыть шкафчик замок спб, вскрытие замка шкафа спб, вскрыть велосипедный замок тросовый спб или вскрытие навесного замка гараж спб. Плюс у охотников периодически всплывает вопрос открыть оружейный шкаф спб без повреждения. Во всех этих случаях важно, чтобы мастер не просто вскрыл, но и предложил адекватную замену. В этом плане удобно, когда есть поставщик фурнитуры, как https://avers-zamki.ru/, где можно сразу подобрать новый замок, защелку или цилиндр, а не ставить первую попавшуюся дешевую личинку.
item finder – I moved through the site easily; everything was clearly arranged.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
shop new horizon – Browsing felt effortless and products were easy to view.
golden boutique access – Browsing felt natural and product sections were easy to follow.
birchlanehub – Smooth layout, browsing items feels comfortable and intuitive.
Daily Fashion Hub – Explore popular categories with ease and enjoy a fun browsing experience.
timberlineatticstudio – User-friendly interface, perfect for exploring ideas and experimenting.
EverBranchCollectibles – Navigation is simple and smooth, images are clear.
blacksprut
грати слоти грати слоти
ігри онлайн казино ігри казино
Sun Meadow Outlet – The site is well-organized and fast, making product discovery smooth and convenient.
Wonder Peak Corner Picks – Items are simple to find and the layout is clean.
shopcornerhub – Interface is smooth, and discovering products was straightforward.
kasyno mostbet mostbet
CTO Timber Selection – Simple design and smooth browsing created a nice overall experience.
collection hub – Nicely structured layout made exploring different categories effortless.
new grove collection – Well-arranged products and responsive design made browsing simple.
установка натяжного потолка Натяжные потолки: Идеальное решение для вашего дома
artisancentral – Smooth and simple navigation, browsing was very convenient.
tallbirchoutletlane – Products are clearly presented, navigating the store is quick and simple.
horizon hub link – Smooth interface and well-organized items enhanced browsing.
BotSync, занимаемся автоматизацией бизнеса делаем умные, чат боты для Telegram на N8n https://sorted-booth-08732357.figma.site
BlueStone Emporium – Loved how organized everything was and easy to explore.
growzonehub – Interface is user-friendly, making exploration of products simple.
collection portal – Everything was laid out clearly, helping me find what I wanted easily.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
urban collection hub – Fast pages and tidy layout made browsing pleasant and easy.
aplikacja mostbet aplikacja mostbet na androida
ігри казіно ігри казино
brightbrookmarket – Smooth browsing, everything is logically placed and easy to find.
pragmatic slot
найкращі слоти слоти безкоштовно
ігри в казино онлайн ігри казино
oficjalne kasyno mostbet kasyno mostbet
shop golden collection – Smooth navigation and neatly displayed products improved browsing.
Cozy Wood Outlet – Navigation felt intuitive, and the overall vibe of the site made browsing enjoyable.
Northern Mist Picks – Fast-loading pages and clear product images helped me browse efficiently.
NewGroveEssentials Storefront – Everything was clear and easy to access, making browsing enjoyable.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Sun Meadow Marketplace Online – Clear structure and intuitive menus made browsing effortless.
collection hub link – The layout was clear and made browsing through everything feel effortless.
shop coast hub – Items are visually appealing and the interface is user-friendly.
https://topicterritory.com/1xbet-promo-code-today-pakistan-2026-e100/
a href=”https://growyourmindset.click/” />growthcentral – Pages are responsive, products are neatly arranged, and browsing is effortless.
a href=”https://brightnorthboutique.shop/” />brightnorthernstyle – Simple layout, browsing through items feels quick and pleasant.
artisanbayhub – Navigation is intuitive and product pages are neat, made browsing easy.
soft access – Clear categories and tidy design made shopping seamless.
бездепозитные бонусы казахстан за регистрацию в казино с выводом
https://www.tai-ji.net/board/board_topic/4160148/7494496.htm
Northern Mist Studio Shop – Clean pages and organized products made browsing effortless.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
https://www.diigo.com/item/note/bndqh/3w6e?k=e0588ee9e21a61232573125e52ea9470
Coastal Ridge Collections – Enjoyed browsing through items; everything is easy to locate.
Wild Shore Online – Clean design and easy navigation made discovering items effortless.
soft access – Clear sections and tidy design made browsing effortless.
Unlock Daily Growth – Explore actionable tips to boost your skills and overall potential.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/mursurtj
свежие новости беларуси и мира новости беларуси и мира
affordable selection – Items were priced well and the site was easy to move through.
Lunar Peak Trends – The site is easy to navigate, and products are a pleasure to explore.
homeselection – Products are clearly displayed, and moving through categories was effortless.
mountaintrailhub – Smooth navigation, items are clearly presented and easy to explore.
женская обувь dsert купить онлайн Женская обувь екатеринбург – возможность приобрести модную и качественную обувь в вашем городе.
evermeadowgoods – Great selection and intuitive navigation helped me explore products without hassle.
Bright Timber Finds – Simple interface and good product range made browsing a pleasure.
MountainMistStudio Deals – Items were easy to locate, making the visit comfortable.
Mountain Wind Hub – Clean menus and smooth interface made finding products easy.
shop moonfall – Items are well displayed and navigating the site felt intuitive.
классическая женская обувь Женская обувь натуральная кожа черная – классика, неподвластная времени, универсальное решение для любого гардероба.
Urban Seed Essentials – Fast browsing experience with a neat, organized layout.
Check Out The Gallery – A very pleasant shopping session was had due to the uncluttered layout.
Modern Fable Choice – Products are easy to locate, and the layout is simple.
build hub – The interface is simple and browsing different sections is seamless.
softrosehubstore – Intuitive pages with organized layout, shopping was simple and enjoyable.
greenoutpostlanehub – Clean layout, products are easy to browse and well organized.
sunset corner – Fast loading and clean layout made exploring products effortless.
everymomentzone – Pages load quickly, and exploring products felt natural.
https://pedol46928.wixsite.com/1xbet-promo-code/post/1xbet-promo-code-2026-1x200free-130-deal
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом
EverRoot Haven – Neat interface and attractive visuals made shopping enjoyable.
BoldCrest Treasures – Loved browsing through the variety; everything was easy to locate.
root studio – Items loaded quickly and navigating sections felt effortless.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
ремонт стиральных машин недорого мастер по ремонту стиральных машин
ремонт стиральных воронеже дому https://master-stiralok-vrn.ru/
https://cybrvrs3.mn.co/posts/94432141
Golden Branch Collection – Products were easy to view, and the interface felt efficient.
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наша продукция:
Лента из прецизионных сплавов для упругих элементов 1.9×120 мм СП22 ГОСТ 14117-85 Купите ленту из прецизионных сплавов для упругих элементов по выгодной цене на Редметсплав.рф. Высокая прочность, устойчивость к коррозии и отличная эластичность делают этот материал идеальным для различных отраслей. Предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции и подробную информацию для правильного выбора.
Seasonal Finds – Products are easy to locate and the site is user-friendly.
create your future – Pages load quickly and navigation feels natural and intuitive.
goldenrootstore – Very easy to browse, and product images are clear and appealing.
Fresh Meadow Studio – The layout is clear and exploring items is very easy.
Street Fashion Daily – Explore curated urban wear and stay ahead of the latest trends.
Outlet Link – Browsing was a joy; the clear sections helped me locate interesting things with ease.
Urban Pasture Market – Browsing the inventory was simple and the site feels very responsive.
BrightStone Crafts – Clean layout and clear images made browsing effortless.
аренда горизонтальных строительных лесов аренда строительных лесов для отделочных работ
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
choicepick – Pages load quickly, items are organized, and browsing is natural.
Timber Crest Hub Online – Well-laid-out pages and logical menus made product discovery effortless.
pine emporium – Clear categories and smooth navigation made shopping enjoyable.
Howdy very nice website!! Man .. Excellent .. Superb .. I’ll bookmark your site and take the feeds additionally? I’m glad to search out so many helpful information right here within the publish, we want work out more techniques on this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
https://fasindo4d.com/melbet-kazino-sloty-2025-obzor/
Создать ИИ презентацию по тексту
Evergreen Boutique – Navigation is intuitive and products are well presented.
green picks – The layout is calming and made browsing effortless.
rarestylehub – Neatly organized pages and intuitive navigation, shopping was pleasant.
cozycorneremporium – Everything is neatly organized, site feels pleasant to browse.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Lunar Harvest Picks – Browsing was pleasant thanks to clear sections and fast page loads.
brightwinterstore – Products look appealing and navigation is smooth — a good shopping experience.
Your Flourishing Path – Advice and resources to support daily growth and goal achievement.
Cozy Cabin Hub – Loved the clean layout and effortless product browsing.
EverWild Collection – Clean interface and fast-loading products made the shopping experience enjoyable.
удалённая работа Удалённая работа для подростков: первые шаги в карьере. Подростки могут найти простые задания в интернете, такие как написание текстов, обработка фотографий или помощь в социальных сетях. Это отличный способ заработать первые деньги и получить опыт.
Your Next Find – The site’s excellent organization is matched by its impressively quick load speeds.
shopcentral – Easy to navigate, items are organized and simple to locate.
shop wild timber – Fast-loading pages and intuitive navigation made browsing effortless.
Silver Moon Picks – Fast navigation and clear presentation made shopping enjoyable.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
работа на удаленке без опыта Фриланс: свобода и независимость. Фриланс – это отличный вариант для тех, кто ценит свободу и независимость. Биржи фриланса предлагают множество заказов для копирайтеров, дизайнеров, программистов и других специалистов.
True Horizon Online – Items are easy to locate, and browsing is seamless.
discover lakes – Products were easy to navigate through and the interface felt inviting.
sunrisehilllanehub – Smooth layout, browsing items feels comfortable and intuitive.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/ysdu82em
brightwillowboutique – Clean design and easy layout helped me find interesting items fast.
удаленная работа в интернете Как найти удаленную работу: полезные советы. Используйте специализированные сайты, группы в социальных сетях и обращайтесь к рекрутинговым агентствам. Не бойтесь рассылать резюме и участвовать в собеседованиях.
Iron Valley Treasures – Organized pages and crisp visuals helped me browse quickly.
Daily Dream Builder – Practical strategies to help you visualize, plan, and achieve your goals.
Shop MidRiverDesigns – The layout felt polished and made browsing categories simple.
онлайн работа без опыта Онлайн работа бесплатно: возможности без вложений. Многие онлайн-платформы предлагают бесплатное обучение и возможность заработка без вложений. Воспользуйтесь этими возможностями, чтобы начать свою карьеру в интернете.
Whitestone Corner Picks – Smooth and fast browsing makes shopping enjoyable.
rusticridgeboutique – Pleasant browsing experience, items are easy to view and site feels well structured.
Moor Picks – I could easily navigate and explore all product options.
shophubzone – Navigation is effortless, and all products are neatly arranged.
PureEverWind Online – The uncluttered pages and simple checkout made everything feel smooth.
shop the crest – Neat layout and intuitive interface helped me find items effortlessly.
Hey! I know this is kinda off topic however , I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest writing a blog article or vice-versa? My blog addresses a lot of the same subjects as yours and I feel we could greatly benefit from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free to send me an e-mail. I look forward to hearing from you! Awesome blog by the way!
https://topvngroup.com/2025/10/26/melbet-oficialnyi-sait-registratsiya-2025/%20https://sogo77.com/melbet-obzor-2025-bukmeker/
fashionhilllane – Layout is tidy, and shopping feels comfortable and intuitive.
silverlookhub – Intuitive design and neatly displayed products, shopping was easy.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
brightfallstudio – Enjoyed browsing here, items seem well curated and easy to explore.
Soft Feather Market Shop – Clean layout and intuitive navigation made browsing quick and pleasant.
bright corner – Navigation flows naturally and items are neatly presented.
Silver Moon Marketplace – Items are displayed neatly, making browsing simple and quick.
https://forums.siliconera.com/threads/a-global-wildlife-photography-hub-and-tour-resource.133322/
PineHill Access – The store feels organized and uncluttered, making browsing quick and simple.
createzone – Browsing was quick and enjoyable, with all products easy to find.
Sunny Slope Corner – Quick to locate items and the layout feels friendly.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
https://hamster.ru/board/post.php?mode=post&f=3264
pathway picks – Browsing felt simple and I came across good items without any effort.
sereneforesthub – Smooth shopping experience, items are well arranged.
Check Out The Shoppe – Shopping was a delight thanks to the great product photos and tidy design.
Everdune Goods Online Picks – I liked how quickly I could move through different categories.
winter hub – Items loaded quickly and categories were easy to explore.
DeepBrook Picks – The organized layout and product clarity made finding items fast.
Бонусы казино
Your personal character will speak volumes to the players you influence https://dailysport.co.ke/my-quick-review-of-online-casinos-kenya/
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
boutique corner – Well-structured layout and clear sections enhanced the shopping experience.
Moon Haven Outlet – Easy-to-use navigation and neat layout made shopping stress-free.
If you like handy online tools, check this out,
I came across this free AI-powered calculator that gives instant, accurate results for everyday tasks — from finance to fitness.
It’s part of the SmartCalc collection — built for speed, accuracy, and simplicity.
Try it here:
SmartCalc Online Tool
No signup, no ads — just clean and simple calculators that actually work.
If you like data-driven tools or quick results without spreadsheets, this is worth a look.
Give it a try and see what you think!
coastalmistcollection – Products are easy to locate, and navigating the site is simple.
sunwave picks – Fast pages and neat categories made browsing enjoyable.
Timeless Harvest Store Link – Easy-to-follow layout with items clearly presented for a smooth experience.
freshcornerstore – Pages are clean and browsing feels natural, very smooth experience.
Vibe Online – Products are easy to find and the navigation feels natural.
silver picks – The site looked very polished, and moving through categories felt natural.
Good to see you here. let’s dive into something that might surprise you.
Explore winter fresh gaming built for consistency, clarity, and smooth slot performance. A refreshing option for Canadian players.
п»їhttps://besthotcasino.ca
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
Наши товары:
Кольцо из драгоценных металлов платиновое 3х2х4.5 мм ПлПд95-5 ТУ Широкий выбор высококачественных кольц из драгоценных металлов. Элегантные украшения, созданные талантливыми мастерами. Уникальность и изысканность в каждой детали. Возможность заказа персонального кольца по вашим пожеланиям. Подчеркните свою индивидуальность с нашими кольцами.
TrendyLivingCorner – Easy to browse, content is interesting and lively.
FashionSelectOnline – Stylish pieces with a smooth shopping process, really enjoyable today.
Wild Coast Workshop Shop – Clean layout and varied items made browsing enjoyable.
Everfield Furnishings – The site runs smoothly and the product presentation is easy on the eyes.
moon hub link – Smooth browsing and organized products enhanced the experience.
вскрытие замков спб
BrightMoor Collection – Very organized pages, which made finding items simple.
SunCrestCrafthouse Storefront – Clean interface and neat layout made shopping smooth.
рейтинг онлайн казино
lunarboutique – Very user-friendly layout, shopping feels effortless.
wild river picks – Clear layout and neat presentation made shopping enjoyable.
everpeakcorner – Clean interface and clear product display helped make browsing smooth and easy.
Выводил 7k казино деньги несколько раз уже. Все приходит в срок, без задержек и комиссий скрытых.
shop hub – Browsing was straightforward and the pages loaded fast with a clean layout.
Short piece of writing but pretty helpful overall.
Rustic River Finds – Quick loading times paired with inviting visuals made the experience enjoyable.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Maintaining a cipro online is essential for overall well-being, helping you stay energized and balanced in daily life. By making informed choices, you can improve your physical and mental state while boosting long-term vitality. Whether you’re exploring new wellness strategies, adopting nutritious eating habits, or discovering the benefits of exotic superfoods, prioritizing health leads to a more fulfilling lifestyle. Stay informed with expert insights and evidence-based recommendations to make the best decisions for your body and mind.
https://pfo.volga.news/715679/article/na-chto-obrashat-vnimanie-pri-vybore-korotkoj-shuby.html
Soft Leaf Marketplace – Easy navigation and clear visuals made selecting products stress-free.
GlamourFinds – Browsing was effortless and the products are very trendy and appealing.
安全かつだまさずに暗号カジノの公式ウェブサイトを見つける方法 https://un-wa-mawaru.com/free-casino-gaming-bonus-2/
studio picks – Navigation flows naturally and items are easy to view.
https://redfordtheatre.com/wp-content/pages/bonus_code_promo_1xbet.html
TrendyLifeUpdates – Loved the fresh posts, engaging content and smooth navigation.
Check Out The Store – Exploring the product range felt completely seamless due to the smart organization.
Lush Art Hub – Smooth interface and organized sections made finding items fast.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
urbanclovercollective – Products are logically arranged, making exploring simple and fast.
brightvillagecorner – Items look appealing and layout feels user-friendly and welcoming overall.
urban corner – Clean layout and quick loading made browsing hassle-free.
wildmeadowemporium – Tidy layout with fast-loading pages, browsing was simple and enjoyable.
Visit TallPineEmporium – The interface was tidy, making exploring products effortless.
fashion picks – The whole site carries a good vibe and the items are displayed in a tidy, easy-to-view manner.
лицензирование 1С ЗУП ПРОФ для компаний Нс Диджитал Франчайзинг 1С Бухалтерия, продажа и разработка продуктов 1с
Fresh Pine Picks – Simple design and clear visuals helped me browse effortlessly.
Soft Blossom Studio Link – Browsing felt calm and well-structured, with a soothing aesthetic.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/fj5ftj8y
бездепозитные бонусы казино в казахстане
shop sunlit boutique – Smooth scrolling and fast pages made browsing comfortable.
Каждый камлок (Camlock) состоит из двух частей, которые образуют замок кулачкового типа https://telegra.ph/CHto-takoe-kamlok-i-kak-on-rabotaet-12-04
EasyPurchaseSpot – Smooth browsing and very fast checkout, highly satisfied.
Harbor Living Online – Browsing felt natural and stress-free thanks to the clean layout.
https://www.chambers.com.au/forum/view_post.php?frm=1&pstid=46690&pstcl=0&kwd=&page_rtn=201
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Check Out The Collective – Browsing was quick and hassle-free thanks to the great range and smart design.
TrendyLivingGoods – Very happy with my purchase, smooth browsing and ordering experience.
shop stone picks – Clean interface and fast pages made exploring simple.
https://forum.yurclub.ru/forum/post.php?mode=post&f=57547
wildleafhubstore – Items are well arranged, shopping feels quick and intuitive.
шкафы купе на заказ по индивидуальным размерам недорого в москве Встроенная мебель для гостиной: Стильное и функциональное решение для вашей гостиной – встроенная мебель, изготовленная по вашим размерам и с учетом ваших пожеланий.
product portal – Fast response times and an organized interface made it a pleasant visit.
Свежая кракен тор ссылка публикуется в проверенных источниках с датой последнего обновления для информирования пользователей об актуальности адреса.
беларусь новости правда зеркало новости беларусь
unique marketplace – The clean structure and fast loading made scrolling through items enjoyable.
Lush Grove Emporium – Clean layout and intuitive interface helped me shop efficiently.
shop soft picks – Items loaded quickly and the layout was easy to follow.
MoonView Portal – The modern layout helped me browse products quickly and easily.
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris
sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif
forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris
sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide
pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris
sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour
paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris
sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris
sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse
pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris
sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli
de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli
pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif
avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli
paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme
paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil
paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie
sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de
paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris
sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif
belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris
sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris
sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris
sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris
sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour
gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris
sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent
facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce
gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris
sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour
gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces
paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif
foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis
sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh
signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros
paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif
gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique
paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue
sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de
paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot
paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus
paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif
retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus
sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris
sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris
sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi
une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote
pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture
paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris
sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage
cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris
sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur
paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer
cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer
probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris
sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs
paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash
out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif
en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris
sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site
paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser
un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris
sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris
sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné
paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment
arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment
arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au
paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris
sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment
calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de
paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip
paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner
au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des
parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment
faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris
sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire
pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour
gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie
sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent
les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes
dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent
les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment
fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner
a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment
gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment
gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris
sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment
gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec
les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent
sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des
paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement
au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les
paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout
le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris
sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment
jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer
aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les
paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment
marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris
sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment
ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au
paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont
calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les
paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari
sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site
de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur
de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur
paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari
sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris
sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris
sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif
site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris
sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des
paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les
handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris
sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris
sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil
paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris
sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil
pour paris sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller
en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils
pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote
a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote
de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote
maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif
comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris
sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris
sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris
sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif
psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif
tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte
paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris
sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote
paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris
sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche
avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris
sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif
definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains
paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris
sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement
sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement
sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs
paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes
paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a
face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité
gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum
de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris
sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise
des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2
paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris
sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france
pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france
pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris
sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris
sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne
au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros
par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris
sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros
par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris
sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari
sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent
avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner
argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris
sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris
sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de
l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner
de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec
les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris
sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de
l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur
les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner
paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec
les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les
paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari
sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris
sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont
ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de
mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris
sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe
telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris
sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap
en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif
basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap
paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris
sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel
paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de
paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris
sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux
de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux
paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris
sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de
caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur
décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris
sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris
sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la
meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la
méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner
paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché
des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de
paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le
meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif
du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les
10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets
pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs
pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers
paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont
ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications
de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs
bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs
paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs
site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari
sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris
sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs
les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus
gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris
sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés
en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1
paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise
paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des
sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris
sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris
sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris
sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris
sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel
gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel
gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris
sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour
paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel
variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les
paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché
des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des
paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale
paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris
sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu
tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match
paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match
suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués
paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme
paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app
de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de
pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur
appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur
appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris
sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur
bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur
bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris
sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote
pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur
forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner
au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus
paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif
aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif
foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic
paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site
de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif
forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de
paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site
de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur
site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif
belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur
site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif
france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site
pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur
technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur
technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli
pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli
paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure
offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure
strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures
cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs
application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs
applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs
paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site
de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante
paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode
paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode
pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot
paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise
minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris
sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante
parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul
paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau
site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre
bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris
sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif
belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre
de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de
bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre
paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement
paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris
sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris
sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris
sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari
sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif
combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça
marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari
sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de
france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari
sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari
sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france
belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif
france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les
coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner
des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari
sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur
absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif
ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari
sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif
match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif
mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o
jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif
prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg
inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari
sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari
sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte
bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari
sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour
gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie
sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie
sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris
hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques
paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros
offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100
offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris
sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif
abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif
analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif
application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent
virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif
au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec
argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif
avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris
sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus
bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus
sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris
sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur
blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur
remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris
sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif
combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du
jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment
gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur
cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil
gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif
cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif
coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de
rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris
sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris
sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec
paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne
belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne
comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris
sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans
depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif
espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et
hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif
euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des
champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif
foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot
comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif
foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif
foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif
foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris
sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif
forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à
coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif
gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris
sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans
depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris
sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap
0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1
0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap
explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris
sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur
blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant
le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare
forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les
18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris
sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue
europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris
sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif
match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif
meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2
3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif
multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris
sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif
multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif
nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre
bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre
de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif
plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou
moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif
pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic
foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris
sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris
sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg
inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif
remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue
des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif
rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif
sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif
sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris
sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne
joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif
site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris
sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif
sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris
sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris
sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif
temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif
tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris
sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland
garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris
sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris
sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris
sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs
belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs
comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe
du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris
sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne
france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs
en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs
euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à
tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris
sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors
arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris
sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue
2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris
sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre
bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris
sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs
sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs
tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent
paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de
l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les
paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus
gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris
sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris
sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus
grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse
somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif
remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos
paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif
tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris
sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris
sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics
paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif
gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter
paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris
sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est
ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que
signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les
paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris
sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg
en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap
paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer
paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel
est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de
paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est
le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris
sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de
paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli
de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris
sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris
sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle
paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris
sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement
paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement
cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement
paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur
de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris
sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent
paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris
sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris
sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot
paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb
paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris
sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur
systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide
paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris
sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse
paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif
avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif
gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de
parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris
sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif
avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de
paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris
sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site
de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de
paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif
en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site
de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif
gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site
de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de
paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif
offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif
qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse
en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans
carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans
depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec
paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris
sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site
des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100
euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site
pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne
sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site
paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif
1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec
bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site
paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif
depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris
sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif
hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif
nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif
remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site
paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif
sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris
sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors
arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris
sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de
paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites
de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de
paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites
de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs
arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so
foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot
paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris
sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de
paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris
sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de
suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris
sportif|tableau paris sportif|tableau paris
Wild Ridge Hub Online – Well-laid-out categories and tidy design made finding products simple.
BrightGroveHub Goods – The streamlined layout helped me jump between pages without delay.
SmartSelectionCorner – Very neat and organized, navigation was quick and simple.
cloud picks – Neatly displayed items and smooth scrolling made browsing effortless.
wavecornerstore – Pleasant layout, items are easy to locate and browse.
wild treasures – Clean categories and intuitive browsing made shopping comfortable.
Got locked out in Tampa and figured I’d drop this here in case it helps someone else.
I used a local locksmith from this site:
https://tampa24hrlocksmith.com/
They offer round-the-clock mobile service in Tampa FL for:
– Vehicle lockouts and lost car keys
– House / apartment lockouts
– Changing keys after a move
– Small business / office locks
The tech didn’t take long to arrive, explained the cost up front and there were no hidden fees at the end.
If you lose your keys, it’s worth saving this:
**https://tampa24hrlocksmith.com/**
Posting this because it’s hard to tell which locksmiths are real and which are sketchy, and this one actually did the job without turning it into a circus.
Savanna Goods Hub – A comfortable browsing experience with well-displayed items throughout.
grovecornerstore – Well-organized layout and fast loading, shopping was smooth and simple.
this online store – The site felt clean and easy to move around, which made browsing surprisingly pleasant.
UrbanStyleMarket – Smooth browsing experience, excellent variety of items.
Coastline Goods – Simple layout and visible product shots made browsing straightforward.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/mrfcwwkh
shop harbor collection – Navigation was effortless and items were well displayed.
https://bahchisaray.org.ua/index.php?showtopic=37884
Mountain Sage Corner Shop – Smooth navigation and organized pages made shopping fast.
We buy household appliances in St. Petersburg and the Leningrad Region продать ноутбук. We buy tumble dryers.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наши товары:
Кольцо из драгоценных металлов палладиевое 30х3х5 мм ПДСР-40 ТУ Широкий выбор высококачественных кольц из драгоценных металлов. Элегантные украшения, созданные талантливыми мастерами. Уникальность и изысканность в каждой детали. Возможность заказа персонального кольца по вашим пожеланиям. Подчеркните свою индивидуальность с нашими кольцами.
EverForest Design Hub – Lots of interesting options, and navigating through categories felt natural.
https://www.animaljobsdirect.com/profiles/7565327-melmybetcode-com1
LearnWithPassion – Creative approaches to make discovering new ideas exciting.
stream hub link – Smooth interface and well-organized products enhanced browsing.
brightstonecollective – Items are logically arranged, making exploration quick and easy.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
установка 1С Бухгалтерия КОРП для ИП Нс Диджитал Франчайзинг 1С Бухалтерия, продажа и разработка продуктов 1с
timberford shop – Browsing was smooth and products were easy to locate.
discover finds – Everything appeared tidy and well-structured, making browsing pleasant.
Shop EverCrestWoods – Everything felt neatly organized, making browsing pleasant from start to finish.
Wild Meadow Goods – Easy-to-use design and clear visuals made shopping stress-free.
shop true pine collection – Smooth navigation and clearly presented items improved shopping.
TrendyGlobalOutlet – Really easy to order, found some great bargains.
Бесплатный инструмент просмотра и анализа блокчейнов https://cryptoexplorerhub.com/
Silver Maple Corner Shop – Organized layout and smooth navigation made shopping quick.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Всё лучшее здесь: https://medim-pro.ru/kupit-spravku-ot-sportivnogo-vracha/
wave corner – Clean design and quick loading pages made exploring products easy.
Autumn Mist Deals – Everything looked neatly organized with helpful descriptions throughout the page.
softleafemporium – User-friendly interface, shopping flows smoothly and comfortably.
BuySmartCenter – Affordable and excellent quality products, extremely pleased.
sunridge store – Browsing was easy and products were well organized.
Джекпот вчера пересекал 2 миллиона рублей примерно. Такие суммы привлекают много игроков сюда.
browse creations – Clean look, easy browsing, and products positioned beautifully across the pages.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
trueharborlane – Tidy layout and organized listings, browsing felt effortless.
Lunar Wood Marketplace – Simple design and well-organized products made exploring smooth and enjoyable.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/3ms3sts6
moonfield access – Fast-loading items and intuitive design made exploring effortless.
Hello to all, how is the whole thing, I think every one is getting more from this website, and your views are pleasant in favor of new visitors.
forticlient mac download
TrendOnlineSpot – Nice design with clear categories and smooth browsing experience.
NextLevelGrowth – Motivating and informative, makes skill improvement seem achievable.
Informationbreach – Your Email May Already Be Exposed
Your inbox isn’t safe anymore. Hackers mail, stolen logins, and email vulnerability are spreading fast — and your email address on the dark web could be the next target.
Informationbreach scans 33B+ breached passwords and 50M new records daily to reveal if your account has been compromised. Instantly check email in dark web, detect hack email account attempts, and verify credentials security before damage happens.
Run a real-time exposure check, see if someone has hacked into your email, and secure your identity with accurate results — not guesses.
Full access is just $2 — unlock everything, stay protected, and take control before hackers do.
Scan Email Now: Email dark web
|
field store – Well-arranged items and simple layout made exploring easy.
oakcollectivestore – Items are logically arranged, and navigation is effortless.
EverHollow Essentials – The site felt light and fast, and all category groups were logically arranged.
forest treasures – Simple layout and fast response times helped me browse efficiently.
this shop – The design feels modern and browsing around was quick and comfortable.
wildgroveemporium – Items are well arranged and navigation feels intuitive — nice overall experience.
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
поставляемая продукция:
Медное двухраструбное колено под пайку 180 градусов 12х9х0.6 мм 8.6х10.6 мм твердая пайка М2РМ ГОСТ Р 52922-2008 Купите надежные медные двухраструбные колена под пайку от ведущего производителя. Обеспечьте эффективное отопление и водоснабжение с прочными и устойчивыми к воздействию внешних факторов коленами из меди.
future finds hub – Browsing was intuitive and products loaded quickly.
Studio Crest – The catalog was structured well and easy to follow.
FindDealsFast – Everything looked clean and the savings were displayed in a way that made sense.
DeterminationZone – Uplifting and practical content, steps are straightforward and encouraging.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
https://store.mantung.com.hk/index.php?route=journal3/blog/post&journal_blog_post_id=11
farm fresh hub – Clean layout and well-categorized items made shopping enjoyable.
a href=”https://pureforeststudio.shop/” />foreststylehub – Fast navigation with well-laid-out pages, shopping felt natural.
Shop EverWillow – A cozy layout with everything logically placed, making browsing simple.
BrightPetal Studio Shop – Clean navigation and product clarity made my shopping smooth.
Lunar Branch Selection – Fast site speed and tidy layout improved the browsing feel.
shop wild boutique – Smooth scrolling and fast pages made finding items easy.
бездепозитные бонусы казахстан за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения
This page definitely has all the information I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
fortinet vpn download
Here’s
a simple
redirect endpoint
to check how various browsers and servers react to 301 redirects
.
It’s just for verifying how redirects behave in different conditions.
In case you’re doing similar routing diagnostics, you can check it too
:
https://plu.sh/ytqk8
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Vine Hub – Navigating through the products was fast and enjoyable.
Your Pathway Start – The layout caught my attention and the vibe was positive throughout.
Free video chat emerald chat log in find people from all over the world in seconds. Anonymous, no registration or SMS required. A convenient alternative to Omegle: minimal settings, maximum live communication right in your browser, at home or on the go, without unnecessary ads.
Оригинальные медикаменты для потенции жена с другом
deltaweaveemporium – Products are easy to find, and the interface is comfortable to use.
Soft Forest Studio Hub – Clean interface and easy navigation helped me shop quickly.
BrainBoosters – Clear instructions and fun exercises, highly recommended.
DailyFashionFresh – Great lineup of fashion items with a light, easy browsing feel.
MoonGrove Gallery Shop – The site looked very polished, and navigating through pages was quick and smooth.
I was able to find good info from your content.
Qfinder Pro download
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
https://lebanonhub.app/blogs/737999/Les-Diff%C3%A9rents-Types-de-Codes-Promo-1xBet-et-Leurs-Objectifs
Посмотрел 7к казино игровые автоматы в демо, выбрал любимый слот. Потом уже на реальные деньги начал давить.
EverMapleCrafts Finds – The site felt well-arranged, helping me browse comfortably.
Казино ловит клиентов честно, без обмана и подводов. 7k онлайн правила прозрачные, нет скрытых условий.
Wild Spire Picks – Fast loading and clear presentation made finding products enjoyable.
Guided Path Spot – Checked it out today; the insights were warm and genuinely encouraging.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наша продукция:
Медная однораструбная редукционная переходная муфта под пайку стандартная 66.7х53.6 мм твердая пайка М3РМ ГОСТ Р 52922-2008 Приобретите высококачественные медные однораструбные редукционные муфты под пайку от Редметсплав для надежного соединения трубопроводов. Гарантированная прочность и устойчивость к коррозии. Идеальны для различных систем отопления, водоснабжения и прочих технических целей.
Brightline Collection – Well-structured layout and good visuals made selection easy.
urbanwillowlane – Tidy layout and organized listings, browsing was simple and fast.
Modern Trend Hub – Great browsing speed and a clean presentation of fashionable choices.
LifeNavigator – Content inspires reflection and browsing felt smooth.
SimpleSavingsVault – Nice deals and moving between pages was effortless.
FashionTrendsOnline – Fast delivery, trendy items, and excellent quality.
FashionStopCenter – Enjoyable browsing experience with clearly displayed items.
Silver Hollow Hub – Elegant structure and organized product listings make browsing effortless.
Moon Glade Finds – Browsing was fast and stress-free thanks to the clear layout.
Creative Bundle Gifts – Spotted several cute items, and everything was easy to view.
BrightPeak Online – Clean design and simple navigation helped me browse quickly.
https://youslade.com/freebetpromoe
Urban Trend Sale – Liked the stylish finds here; pages were quick and checkout straightforward.
DiscoverPotential – Pleasant browsing and a good mix of items on display.
Explore PineCrestModern – Clean interface and organized displays improved browsing efficiency.
FashionExplorer – Trendy items showcased nicely, navigating pages was easy.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
https://chojnow.pl/forum/thread/view/id/1231781
ModernHomeVibes – Loved the stylish items, browsing and purchasing was very smooth.
Golden Ridge Gallery Site – Overall experience was smooth, with a neat layout that made exploring satisfying.
LearningPathCenter – Resources were clear and accessible, making study easy and smooth.
Gold Shore Selection – Pleasant navigation made discovering items effortless.
Какие бывают типы по дизайну человека? Управленческие компетенции. Где можно найти деньги в бодиграфе? Где деньги в дизайне человека. Дизайн человека не предсказывает будущее, а помогает описать уникальную природу каждого человека. Увеличивают продуктивность командной работы. Преимущества и уязвимости. Как получать деньги в свою жизнь без надрыва и сопротивления. Как вести за собой команду в условиях неопределенности.
https://ua-human-design-n-ru-cu.hdua.ru
Growth Discovery Spot – Browsed it today and found the layout simple and content uplifting.
https://open.substack.com/pub/codespromo1xbet/p/code-promo-1xbet-2026-bonus-vip-130?r=6z01qo&utm_campaign=post&utm_medium=web&showWelcomeOnShare=true
autumnlookhub – Fast-loading pages with intuitive navigation, shopping felt natural.
https://preschool.nafa.edu.sg/happenings/performances/nafa-arts-preschool-graduation-performance-wu-ruiqi-class-of-2023
City Trend Selections – Enjoyed the modern interface and the wide selection of fashionable items.
FashionNest – Loved exploring the site, everything feels well organized.
ModernLifeHub – Wide assortment of trendy products and navigation felt effortless.
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино 2025 с выводом без пополнения
DecorSelect Hub – Loved the polished feel of the design and the simple category structure.
ремонт замена стиральных машин https://remont-stiralok-vrn-24.ru/
Expand at the link: https://digital-marketing-agency09876.pages10.com/nppr-team-shop-the-ultimate-hub-for-social-media-marketing-mastery-73884638
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Football fans can explore a wide selection of matches from top European leagues betbonanza
Soft Pine Treasures – Well-organized pages allowed for fast and pleasant exploration.
SunlitValleyMarket Finds – Everything was organized clearly, helping me explore effortlessly.
LuckyBear — это яркое онлайн-казино, предлагающее игрокам множество азартных развлечений https://luckybear-cas.uno/
Soft Summer Portal – Soft colors and easy navigation made exploring items stress-free.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наши товары:
Полоса из платины и ее сплавов 0.25 мм ПлПд-10 ГОСТ 24718-81 Изучите разнообразие полос из платины и ее сплавов на сайте Редметсплав.рф. Наши высококачественные материалы обладают высокой прочностью, устойчивостью к коррозии и непревзойденными техническими характеристиками. Полосы из платины и ее сплавов применяются в ювелирном деле, медицине и производстве специальных деталей, гарантируя надежность и качество продукции.
LearnAndGrowDaily – Helpful insights and a very smooth browsing experience overall.
Antipublic – Stop Account Takeover Attempts Before They Hit You!
Your accounts may already be targeted by hackers. Antipublic scans 33B+ stolen passwords and 50M newly hacked datasets every day to detect account-takeover and unauthorized-access attempts in real time.
Find out if your email is being used in hacking activities, receive instant hack alerts, and shut down any takeover attempt before it succeeds.
Stay one step ahead of attackers for just $2 — activate your anti-hacking shield now.
Take Control Before Hackers Do: Username hack
|
ТутВот есть все: дешевые авиабилеты для прямых перелетов, посуточная аренда квартир, домов, гостиниц и отелей https://tutvot.com
TrendExplorer – Browsing felt seamless with plenty of interesting items.
Next Adventure Picks – Fun and engaging selection, and browsing through items was simple and smooth.
TrendVaultShop – Stylish items displayed nicely, navigation felt intuitive.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
TrendMode Collection – Stylish selections offered, and everything seemed to load instantly.
DailyGoodsMarket – Pleasant design, navigation felt natural.
a href=”https://evertrueharbor.shop/” />EverTrue Harbor Site – The clarity of the layout made checking out each section enjoyable and effortless.
ShopDiscover – Fast-loading site and easy to find interesting products.
Bright Pine Fields Market – The organized layout made finding items quick and effortless.
craftcorner – Intuitive design and tidy listings, shopping felt very natural.
Style Upgrade Spot – Had a pleasant time scrolling around; the layout felt clean and modern.
UrbanTrendSpotlight – Stylish selections, site layout is clean and browsing felt effortless.
ExploreInsightZone – Site felt intuitive and everything displayed quickly without any issues.
Style Deals Corner – Everything is positioned neatly, and the navigation creates a relaxed shopping flow.
From now on, you’ll no longer have to search for mirrors of the official website https://school-vposad.ru
https://pauladdavis.scholar.bucknell.edu/2017/10/29/fall-dance-concert-2010-bucknell/#comment-311685
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/uvt98s84
Normally I don’t write detailed posts, but right now I thought I’d share one recent session about a decent hit at an online casino.
I’ve been spending some time at nllalabet.com, mostly in the evenings and with low bets. I signed up because the first deposit bonus looked decent and the wagering conditions seemed not too bad compared to many other places. The registration process was quite easy: name and email and simple email verification, then I was able to start playing.
For my first deposit I kept it small and put a low amount into my balance. I headed to the slots section because that’s what I tend to play. I looked for most played games and picked a slot with a bonus buy feature, hoping for a good session.
At first it was up and down: a few line hits but nothing big and bonus rounds that paid almost nothing, and I was ready to log out because my balance was shrinking. Then things changed: I landed a strong bonus round with multipliers all over the screen, the slot kept hitting combinations and the multiplier boosted my balance way up. For me it was a really nice win compared to my regular sessions.
I didn’t keep spinning forever; after a few more small spins I decided to leave the game and send a cashout. The withdrawal process was as expected: the casino asked me to verify my account with ID card or passport. I sent everything the same evening, and the verification was accepted without any issues. After that the money was transferred to my payment method and I received it in a decent timeframe.
I’m not saying this casino is a miracle, and of course you can also lose, but in this case my experience was mostly good: transparent rules, decent support and no drama with the withdrawal. This is not a promise you’ll win: gambling always involves risk, so only gamble what you can afford to lose and don’t rely on it as income.
Our United States directory of gaming properties includes over 1500 casinos https://school-vposad.ru
Our United States directory of gaming properties includes over 1500 casinos https://school-vposad.ru
The concept of Roulette prediction has long intrigued mathematicians AI roulette prediction
DiscoverChic – Stylish products with a comfortable browsing experience overall.
DailyEssentialsHub – Wide range of products, browsing was smooth and simple.
TrendFinderHub – Great deals to explore, and browsing the site was quick and easy.
Lifestyle Corner Shop – The store feels welcoming, and the product selection is impressive.
Urban Wild Grove Collections – The site felt contemporary and well-organized, with easy navigation.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
ChoiceSelect Outlet – Nicely designed pages with a pleasant browsing flow today.
https://edex.adobe.com/community/member/ImnxkefDE
azino777 официальный сайт мобильная версия Хотите испытать удачу и получить заряд адреналина? Азино 777 приглашает вас в мир захватывающих азартных развлечений! Здесь вы найдете множество ярких слотов и других игр, которые помогут вам расслабиться и, возможно, выиграть.
InnovativeThoughtHub – Creative posts with a user-friendly interface and smooth scrolling.
https://mushlovesocial.com/blogs/100016/C%C3%B3digo-promocional-MelBet-ZEVS777-Bono-de-par-de-100-100
https://www.tapatalk.com/groups/techseo/1xbet-promo-code-bangladesh-2026-100-eur130-t16000.html
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наши товары:
Меднаядвухраструбная подвижнаямуфта под пайку76.1х2.6ммМ3рГОСТ 32590-2013 Выберите медные двухраструбные муфты под пайку от производителя RedmetSplav. Прочные и герметичные соединения для систем водоснабжения, отопления и газоснабжения. Долговечные и надежные муфты для любых видов работ. Подходят для использования в домашних условиях, коммерческих и промышленных объектах.
Создание сайтов — это процесс разработки и воплощения в интернете цифрового представительства компании, проекта http://prodvizhenie-saytov-moskva.ru/sozdanie-saytov/
TrendFreshHub – Items are appealing and the site navigation felt intuitive.
GrowFurtherNow – Motivating content and browsing through pages was smooth.
Happy Savings Picks – Lots of practical items and the site felt user-friendly.
sunnybayshop – Very user-friendly design, made exploring items enjoyable.
Quiet Plains Shop – Really liked the clean interface today, and products were easy to explore.
Check out the list of the best licensed online casinos in 2025 https://uronews.ru/
BlueHarborBloom Portal – Nice speed overall, with a visually pleasing and logical product layout.
DailyFindsHub – Attractive layout, effortless navigation throughout.
События Озёрск
https://news.ozrtech.ru
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Анонимная торговая площадка kraken darknet market внедрила escrow систему условного депонирования средств и мультиподписные кошельки для предотвращения кражи криптовалюты.
Нужна работа в США? стоимость курса трак диспетчера в америке с реальными кейсами : работа с заявками и рейсами, переговоры на английском, тайм-менеджмент и сервис. Подходит новичкам и тем, кто хочет выйти на рынок труда США и зарабатывать в долларах.
ModernDealsOutlet – Products displayed neatly, and navigating the site was simple and pleasant.
FreshBargainHub – Pleasant browsing experience with well-presented products.
PureHarborStudio Finds – Clear sections and fast-loading pages made exploring simple.
Contemporary Fashion Outlet – Easy to navigate and the collection felt fresh and stylish.
Trend Buy Hub Finds – Nice assortment of products, site loaded fast and browsing was easy.
Forest Picks Outlet – Enjoyed the refreshing product range and the smooth transitions between pages.
Уже месяц как играю тут, всё гладко. Менеджер поддержки помогал разбираться мне быстро.
Платформа совершенно безопасна для игры на деньги. 7k официальный шифрование хорошее, данные не сливают никому.
TrendZoneOnline – Clean and polished interface, items clearly displayed.
SimpleHomeVault – Great assortment of home items, site layout is clean.
FashionTrendSpot – Very happy with the speedy delivery and chic items, shopping was hassle-free.
Hub of Fashion Trends – User experience was smooth, and I found several attractive pieces.
wildorchardemporiumhub – Neatly organized pages with intuitive design, browsing was enjoyable.
Uwielbiasz hazard? nv casino online login: rzetelne oceny kasyn, weryfikacja licencji oraz wybor bonusow i promocji dla nowych i powracajacych graczy. Szczegolowe recenzje, porownanie warunkow i rekomendacje dotyczace odpowiedzialnej gry.
TAB Picks Online – Stylish items laid out clearly, browsing was simple and fast.
Rainy City Goods – The site ran well today, and everything looked organized and appealing.
Only top materials: http://business.sweetwaterreporter.com/sweetwaterreporter/markets/article/abnewswire-2025-12-4-the-ultimate-guide-to-buying-facebook-advertising-accounts-what-must-be-known/
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – идеальный вариант для вас.
поставляемая продукция:
Кольцо из драгоценных металлов палладиевое 200х50х1.5 мм ПдСр60-40 ТУ Широкий выбор высококачественных кольц из драгоценных металлов. Элегантные украшения, созданные талантливыми мастерами. Уникальность и изысканность в каждой детали. Возможность заказа персонального кольца по вашим пожеланиям. Подчеркните свою индивидуальность с нашими кольцами.
Silver Garden Online Shop – Seamless navigation and clean design made the store feel trustworthy.
Soft Grove Online – Well-organized sections and clean interface made shopping hassle-free.
CozyHomeMarket – Great assortment of items and the website feels intuitive.
MotivateDaily – Smooth design, uplifting articles, and convenient site flow.
The Sultan Games app provides users with a full range of gaming features and functions Султан Геймз
Trend Market Online – Browsing worked perfectly and the assortment of products was impressive.
Quick share for anyone interested,
I came across this free AI-powered calculator that gives instant, accurate results for everyday tasks — from finance to fitness.
It’s part of the SmartCalc collection — built for speed, accuracy, and simplicity.
Try it here:
SmartCalc Online Tool
No signup, no ads — just clean and simple calculators that actually work.
If you like data-driven tools or quick results without spreadsheets, this is worth a look.
Thought I’d share
Trend & Buy Shop Online – Loved the clean layout, finding items felt quick and smooth.
FreshCorner Market – Good variety of daily offerings with smooth page transitions throughout.
Rare Botanical Picks – Nice floral-themed pieces, and the smooth layout made exploring pleasant.
PickSmartHub – Loved the selection, everything I needed was easy to locate.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Timber Path Picks – Categories were intuitive, making the site straightforward to navigate.
Trend & Style Store – Loved the clean, modern interface, browsing was very smooth.
FreshSelectionSpot – Clean visuals, easy navigation, and enjoyable shopping experience.
v
Rare Finds Market – Items caught the eye, and page navigation was simple and quick.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
SimpleTradeSpot – Fast delivery and seamless navigation, I’ll definitely return for more.
FreshSelect Hub – A nice array of items with a simple, clean interface that’s pleasant to explore.
PureHarborStudio Portal – Organized sections and clear visuals made it easy to find items.
ExploreOpportunities Online – Clean layout and easy access to all resources made browsing enjoyable.
FashionTreasure – Smooth interface with fast-loading pages for effortless browsing.
EverNova Picks – The aesthetic was refreshing, and navigating through categories felt very natural.
Trend Choice Picks – Loved the layout, finding what I needed was smooth and fast.
Leaf Collection Market – Pleasant marketplace setup and quick, natural browsing throughout.
GiftHubOnline – Large variety of gifts, easy-to-navigate layout, and neatly arranged sections.
ремонт вертикальных стиральных машин https://remont-stiralok-voronezh-ceny.ru/
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/2v3azfwd
GreenHubSpot – Excellent assortment and intuitive site layout, shopping was easy and fun.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
Наша продукция:
Медный удлиненный двухраструбный отвод 90 градусов под пайку 15х11х0.7 мм 10.6х12.6 мм мягкая пайка М3т ГОСТ 32590-2013 Покупайте медные двухраструбные отводы 90 градусов под пайку на Редметсплав.рф. Надежные и долговечные отводы из высококачественной меди для систем водоснабжения, отопления и кондиционирования воздуха. Гарантированно надежные соединения, простой монтаж и оптимальное распределение потока.
Mostbet is a reliable online casino with a wide selection of slot machines, bonuses, the official промокод при регистрации mostbet
ExploreOpportunities Finds – Fast-loading pages with a clean interface and neatly presented items.
ClassicVault – Fast pages and well-organized items make shopping smooth and enjoyable.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Trend Spot Online – The trendy collection looks appealing with simple navigation throughout.
TCS Style Store – Clean layout with stylish products, browsing was smooth and enjoyable.
urbanstylehub – Pages are neat, made choosing products quick and easy.
DecorSelect Hub – Loved the polished feel of the design and the simple category structure.
Выберите тяговые АКБ, которые обеспечивают мощность, долгий ресурс и стабильную работу погрузчиков и штабелёров, помогая вашему складу работать быстрее, безопаснее и без простоев аккумуляторы для электропогрузчиков
Всё о камерах видеонаблюдения — полное руководство!
Приветствуем вас, уважаемые форумчане! Сегодня мы подробно поговорим обо всём, что касается видеокамер наблюдения. Мы поможем вам разобраться в огромном разнообразии предложений рынка и сделать правильный выбор оборудования для защиты вашего имущества и безопасности вашей семьи.
Почему важно установить систему видеонаблюдения?
Камеры видеонаблюдения становятся всё популярнее среди владельцев домов, офисов и коммерческих помещений. Они обеспечивают защиту имущества, предотвращают преступления и помогают контролировать происходящее даже дистанционно. Давайте рассмотрим самые важные аспекты выбора камеры и её установки.
Какие бывают виды камер видеонаблюдения?
Вы можете выбрать камеру исходя из ваших потребностей и условий эксплуатации:
– **Уличные** — предназначены для наружной установки, защищены от влаги и пыли.
– **Домашние** — компактные модели для внутренней установки.
– **IP-камеры** — позволяют подключаться к сети Интернет и просматривать записи онлайн.
– **Wi-Fi камеры** — удобны благодаря беспроводному соединению.
– **Камеры с SIM-картой** — работают независимо от интернета, передавая сигнал через мобильную сеть.
– **Миниатюрные камеры** — незаметны и подходят для скрытого наблюдения.
– **Поворотные камеры** — способны охватывать большие площади, поворачиваясь на 360 градусов.
– **Ночные камеры** — оснащены инфракрасной подсветкой для съёмки в темноте.
—
Как правильно выбрать камеру видеонаблюдения?
Перед покупкой обратите внимание на следующие характеристики:
– Разрешение камеры — HD/FullHD/UHD обеспечит чёткое изображение.
– Угол обзора — широкий угол позволяет видеть больше пространства.
– Наличие микрофона и динамика — возможность двусторонней связи.
– Датчик движения — экономия памяти устройства путём включения записи только при обнаружении активности.
– Питание — проверьте совместимость с вашим источником питания.
– Возможность удалённого доступа — управление камерой через смартфон или компьютер.
—
Установка и подключение камеры видеонаблюдения
Правильная установка и настройка камеры позволят вам эффективно пользоваться всеми возможностями системы видеонаблюдения. Рассмотрим ключевые моменты:
– Выберите оптимальное место для размещения камеры, обеспечивающее максимальный обзор охраняемой территории.
– Убедитесь, что камера защищена от погодных воздействий, если устанавливается снаружи здания.
– Настройте Wi-Fi соединение или кабельную линию подключения.
– Установите приложение для просмотра записей и управления камерой через мобильное устройство.
—
Где лучше всего приобрести камеру видеонаблюдения?
При покупке обращайте внимание на проверенные магазины и бренды. Рекомендуем выбирать оборудование известных производителей, предлагающих гарантии качества и поддержку клиентов. Обратите внимание на предложения крупных торговых площадок, таких как Ozon, Wildberries и специализированные магазины электроники.
—
Советы по установке камер видеонаблюдения:
– Изучите правила установки камер видеонаблюдения перед началом монтажа.
– Получите согласие жильцов многоквартирных домов на установку камер в подъездах и местах общего пользования.
– Позаботьтесь о защите личной жизни соседей, устанавливая камеры таким образом, чтобы избежать нарушения частной собственности.
—
Поделитесь своим опытом!
Расскажите нам о вашем опыте покупки и установки камер видеонаблюдения. Может быть, у вас есть советы или рекомендации для новичков? А может, вы столкнулись с проблемами при выборе или настройке оборудования? Оставляйте комментарии ниже, давайте делиться полезными советами вместе!
Автор:
Система видеонаблюдения
*Данная статья носит информационный характер и предназначена исключительно для ознакомительных целей.*
HomeStyleCorner – Neat interface, well-organized items, and enjoyable shopping experience.
RainySelectStore – Easy navigation and fast service, I’ll definitely be back.
FashionBuy Trends – Loved the seamless flow through the pages and the modern presentation.
UrbanSpotlight – Clean interface and intuitive navigation make finding items easy.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
aussenseiter wetten strategie
Here is my web blog: wett-tipps ai erfahrungen (Sal)
Trend Deal Shop Online – Loved the layout, browsing through offers felt seamless.
Home Essentials Point – The catalog felt neatly arranged, and pages loaded without any hassle.
Inspired Living Hub – Positive energy across the site and effortless browsing throughout.
FuturePath Corner – Modern pages with well-organized products make shopping simple and enjoyable.
Pin Up Casino is the official website of a well-known online casino for players from Russia https://khvochshovskayaschool.ru
Numerous games across various genres. Live casino with high-quality games https://xn--80aejyh.xn--p1ai
Sunrise Trail Studio – Easy-to-navigate pages with well-placed products create a pleasant experience.
Growth Vision Spot – Layout is neat and the pages respond quickly to navigation.
BrightHub – User-friendly site and well-presented products make browsing seamless.
FashionLovers Online – Navigation felt effortless and the display of items was clean and appealing.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
GiftIdeasCenter – Pleasant design, intuitive navigation, and unique product offerings.
Trend Fashion Online Store – Stylish layout with attractive items, exploring the site was seamless.
harborlookstore – Smooth navigation with tidy product pages, shopping was hassle-free.
City Style Deals – Modern urban pieces with smooth transitions and an easy-to-use layout.
Explore New Growth – Pleasant layout with fast load times and accessible content.
FuturePath Picks – Products arranged neatly with intuitive browsing for a seamless experience.
CityWishSpot – Lovely selection of items and a clean, user-friendly interface.
Best Value Picks – Fast loading and a reliable layout helped make browsing straightforward.
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наша продукция:
Проволока с заданным ТКЛР 0.056 мм 47НХ ГОСТ 14081-78 Купить проволоку с заданным ТКЛР с высокой прочностью и прочным защитным покрытием. Идеальный материал для строительства и производства. Широкий выбор диаметров и типов покрытий. Закажите у надежного поставщика.
Trend Life Hub – Appealing items and clear navigation, exploring the site felt easy.
Grand River Finds Online – Attractive products arranged neatly, providing a smooth browsing experience.
BrookCoastalFinds – Everything feels well sorted, and navigating through the store is quick and pleasant.
DailyOfferCenter – Clean pages, smooth navigation, and attractive product selections.
Sunrise Market Lane – Simple structure and neat product arrangement improve site usability.
New Perspective Horizons – Quick load times and the content felt meaningful and well-presented.
CrestHub – Stylish items easy to find with intuitive navigation throughout.
http://pisatel.forumbb.ru/forum/post.php?mode=post&f=1916
https://reklama-forum.ru/razum1st/10023-промокод-на-1xbet-при-регистрации-2026-1x200mad
Discover Fashion Hub – Liked how modern the interface felt, and the pages opened instantly.
Street Style Choice – Clean interface and user-friendly design with appealing urban styles.
GlobalRidge Picks Hub – Neatly arranged items and smooth navigation make browsing simple and pleasant.
Trend Market Online Store – Nice clean interface, navigating the site felt simple and fast.
Grand River Curated – Beautiful river-themed products, browsing is comfortable and enjoyable.
Stop switching between a dozen sportsbook apps and websites. Beika.app consolidates your entire betting experience into one sleek, powerful platform https://beika.app
Color Mea Finds Hub – Creative items showcased clearly, giving a pleasant and effortless shopping experience.
sunnytrendstore – Organized well and intuitive, shopping was fast.
https://sites.gsu.edu/nramirez5/2016/04/04/georgia-aquarium-gift-shop/comment-page-1171/#comment-177823
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
ChoiceFinderCenter – Neat interface, top-quality items, and pleasant browsing experience.
wetten anbieter
My page; sportwetten urteil
https://www.1001fonts.com/users/code-promo-1xbet-2026/
NatureVault – Smooth site performance with well-displayed rustic products.
FreshFit Outlet – Lots of appealing options, and every page loaded with no delay.
TCS Shop Online – Modern items displayed well, navigating around the site was easy.
Hidden Valley Collection – Attractive items displayed clearly, making discovery enjoyable.
FindMotivation Studio – Well-laid-out motivational posts with seamless browsing experience.
WildFuture Select – Well-structured items with a modern aesthetic create a refined shopping experience.
Next Adventure Hub – The site feels exciting, with an adventurous layout and smooth browsing.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
http://probki.vyatka.ru/content/reshenie-20102012#comment-35083283
CopperLaneSpot – Everything runs quickly, and the calm layout makes checking the deals enjoyable.
Надежный магазин сайт по продаже аккаунтов рад приветствовать вебмастеров в нашем ассортименте аккаунтов и знаний. Особенность этого шопа — заключается в наличии эксклюзивной вики-энциклопедии, где написаны актуальные гайды по заливу. Команда научим, каким образом грамотно прогревать рекламу, как избегать чекпоинты а также настраивать клоаку. Заказывая у нас, вы получаете не только логи, а также полную помощь саппорта, гарантию на валид плюс максимально приятные цены в нише.
Casino is a 1995 epic crime film directed by Martin Scorsese, adapted by Scorsese https://drrebenka.ru
FlowerFinds – Beautiful natural-themed items, easy to browse and site layout is clean.
https://top10seosecret.blogspot.com/2017/05/how-to-do-blog-commenting.html?sc=1760554334280#c5606776351345562025
FashionTrendHub – Stylish collections displayed nicely, smooth navigation and enjoyable browsing.
обновление 1С ERP 2 для компаний Нс Диджитал Франчайзинг 1С Бухгалтерия, продажа и разработка продуктов 1с
Daily Value Outlet – The site felt organized, dependable, and offered plenty of wallet-friendly picks.
TPH Online Store – Clean and modern layout, browsing felt effortless.
Highland Craft Picks – Items presented clearly, making exploration easy and pleasant.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наши товары:
Латуное внутреннее стопорное пружинное кольцо M31 33.4х1.2 мм ЛСд DIN 472 Выбирайте надежные и высококачественные латунные внутренние стопорные кольца по DIN для эффективной фиксации элементов механизмов. Широкий спектр применения, высокая прочность и долговечность. Идеальное решение для вашего бизнеса. Покупайте на Редметсплав.рф!
goldencrestyle – Smooth layout and tidy listings, shopping felt quick and pleasant.
Offer Highlights – Everything appears well-sorted, making it simple to check out the latest offers.
Fresh Buy Lane – Trendy selection presented neatly with smooth page flow and organized sections.
CozyCloverStore – Nicely presented cozy goods, with a layout that feels soothing and easy to explore.
Global Style Point – The interface felt intuitive, and the site ran effortlessly for me.
NorthernTreasure – Intuitive navigation with products arranged neatly for effortless browsing.
APS Seasonal Hub – Seasonal collections look appealing, and flipping through pages feels calming.
Simple Home Finds Online – Fast and smooth browsing with nicely displayed products.
top shopping corner – Selection looks fantastic, browsing feels effortless and quick.
TSO Trend Store – Well-laid-out sale items, moving through pages was very smooth.
High Pine Spot – Pine-inspired items displayed clearly, browsing feels natural.
DealFinderHub – Clear layout, solid deals, and fast, intuitive browsing experience.
Midday Marketplace Select – Organized sections and clean layout make shopping intuitive and simple.
Best Value Deals – Offers look organized and appealing, making browsing pleasant and efficient.
Fresh Home Hub – Modern layout with neatly displayed home items makes browsing smooth.
Cozy Autumn Studio – Fall-inspired selections look inviting, and site navigation is wonderfully simple.
ValleyValueMart – Items look well-presented with fair prices and an overall reliable feel.
your shopping corner – Products are well arranged, navigating feels easy and convenient.
Simple Living Picks – Intuitive navigation and well-arranged sections enhanced usability.
UGC Picks Online – Loved the selection today, navigation around the site was seamless.
Joyful Living Online – The site runs smoothly, looks bright, and the products feel inviting.
Ironline Market – Solid marketplace with dependable products and fair pricing throughout.
https://supermoto.bbforum.be/post51628.html#51628
QuickDealMarket – Fast navigation, easy-to-browse deals, and clean layout.
https://checksite.com
https://kyourc.com/therockpit
goldencrestyle – Smooth layout and tidy listings, shopping felt quick and pleasant.
Product Discovery Hub – Many good options stand out, and the interface feels clean and efficient.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
PromoFinds – Site loads quickly, and discovering discounts felt simple.
FashionFresh Market – Trendy displays and fast navigation make browsing effortless and enjoyable.
your fav finds – A clean set of finds with browsing that feels light and responsive.
FreshSeason Online – Intuitive interface and clean product arrangement allow effortless exploration.
UGC Picks Hub – Beautifully displayed gifts, browsing the site was effortless.
Trend & Style Hub – Stylish items presented clearly, with smooth navigation and pleasant browsing.
hub marketplace – Enjoyed browsing around; listings look consistent and quality-focused.
Iron Root Corner Shop – Well-laid-out selection, finding products is quick and easy.
shop daily growth – Selections seem useful, browsing feels effortless and quick.
uplift store – Selection looks motivating, site experience is clean and intuitive.
оригинальный фен dyson оригинальный фен dyson .
купить курсовую москва kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru .
купить курсовую работу купить курсовую работу .
http://timurka.rx22.ru/viewtopic.php?f=12&t=1077
TrendStylePick – Stylish selections displayed neatly, smooth browsing and easy navigation.
Odkryj legalny salon gier z licencją Totalizatora — poczatkowy bonus aż do 13 750 zł! Bezpieczna gra z licencją Totalizatora Sportowego — zainstaluj teraz i aktywuj pakiet powitalny! Oficjalna aplikacja Totalizatora oferuje paczę startową z dopłatą i spinami — zgodnie z prawem. Zaufany operator — Salon Gier na Automatach zapewnia ochronę środków i turnieje slotowe. Chcesz grać w automaty? Oficjalna aplikacja z licencją daje Ci start z dopłatą — pobierz teraz! Graj z Totalizatorem — Salon Gier na Automatach oferuje do 550 darmowych spinów i bezpieczeństwo płatności. Pełna ochrona gracza — pobierz aplikację i odbierz swój bonus!
divephotoguide.com
Budget Joy Hub – Pages feel responsive and the collection of value items is appealing.
Everyday Choice Outlet – Everything loads quickly, offering a very convenient browsing experience.
сколько стоит курсовая работа по юриспруденции kupit-kursovuyu-28.ru .
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Normally I don’t write detailed posts, but right now I decided to share what happened to me about a decent hit at an online casino.
I’ve been spending some time at nllalabet.com, mostly on weekends and with low bets. I joined because the welcome bonus looked okay and the wagering conditions seemed fair enough compared to many other online casinos. The signup process was pretty simple: basic details and a quick confirmation link, then I was able to start playing.
For my initial deposit I kept it small and added a low amount into my balance. I went straight to the slots section because that’s what I mainly like. I sorted by trending games and picked a slot with medium volatility, hoping for a good session.
At first it was pretty standard: small wins and losses and free spins with low payout, and I was close to giving up because my balance was getting low. Then the session flipped: I hit a big bonus with wilds all over the screen, the slot didn’t stop paying and the bonus feature boosted my balance far above my start. For me it was a big boost compared to my regular sessions.
I didn’t stay too long; after a few more small spins I decided to cash out and send a withdrawal request. The withdrawal process was nothing unusual: the casino asked me to complete KYC with some ID. I sent everything right away, and the verification was approved after a short wait. After that the money was sent to my wallet and I received it faster than expected.
I’m not saying this casino is a miracle, and of course you can also bust your balance, but in this case my experience was pretty fair: transparent rules, normal support and no excuses about cashout. This is just my personal story: there is always a risk in gambling, so only play with limits and remember it’s just a game.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Медно-никелевый лист 10x1000x2000 мм МНЖ5-1 Приобретите качественный медно-никелевый лист МНЖ5-1 размером 10x1000x2000 мм на Редметсплав.рф. Идеальное сочетание прочности и гибкости для различных проектов. Компания Поставка цветных и редкоземельных металлов и изделий из них гарантирует надежность и качество.
OfferPalace – Clean design and rapid load times make finding deals simple.
дайсон стайлер для волос официальный сайт с насадками купить цена fen-d-3.ru .
FashionWorld Select – Clean design and quick page loads made browsing very enjoyable.
your inspiration corner – Products feel uplifting, site layout makes browsing easy.
Majestic Grover Picks – Grover-themed items presented clearly, exploring the site feels natural.
daily fashion market – Fashion selections look attractive, browsing is quick and intuitive.
Wild Rose Collection Online – Lovely atmosphere with a few delightful discoveries along the way.
Fresh Trend Lane Hub – Clear visuals and organized sections provide a seamless shopping experience.
fantasy grove shop – The catalog feels inspired, and checking different sections is very easy.
заказать дипломную работу в москве https://kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru/ .
написание курсовых работ на заказ цена kupit-kursovuyu-23.ru .
PurePresentsHub – Organized structure, attractive products, and smooth site experience.
GlobalCrest Select – Attractive layout and clearly divided sections give a professional impression.
TrendHub Deals – A solid lineup of trendy products appears, and navigation is very intuitive.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
DiscoverDeals – Browsing is simple, with a user-friendly interface.
Trendy Modern Hub – Modern styles look great, with an easy-to-navigate layout throughout.
онлайн сервис помощи студентам онлайн сервис помощи студентам .
заказать студенческую работу http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru .
купить фен дайсон оригинал купить фен дайсон оригинал .
learnandexplore.click – Learning-focused items look appealing, site layout feels easy and smooth.
Modern Home Market – Loved the tidy structure and how quickly pages responded.
WildRose Goods – Warm and cozy atmosphere, found a few delightful surprises.
MidCity Online Store – Collections look great, navigation is intuitive and browsing is pleasant.
home essentials picks – Products look attractive and organized, navigation feels pleasant.
Premium Global Collection – Loved exploring here, items are well presented and diverse.
WildBrook Modern Works – Contemporary style throughout, browsing felt effortless and calm.
DailyShopDeals – Smooth browsing, great daily offers, and user-friendly interface.
Building Today Studio – Inspiring theme with organized sections and fast, easy navigation.
evercrest selection online – The store feels updated often, giving shoppers new finds to check out routinely.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Design Fashion Hub – Modern fashion options look appealing, and navigation flows effortlessly.
написание учебных работ http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru .
стоимость написания курсовой работы на заказ https://kupit-kursovuyu-23.ru .
InfoCentral – Clear presentation of resources and smooth navigation throughout the site.
authenticsupplyzone – AuthenticSupplyZone offers genuine items with a clean, easy-to-navigate layout.
Sunset Grove Lane – Inviting visuals and clean layout ensure a natural browsing experience.
WildRose Studio Online – Cozy and charming shop, found a few pieces worth exploring.
modern style corner – Products appear fashionable, everything is simple to find and organized.
Modern Look Hub – Clean, easy-to-navigate layout with well-arranged modern fashion items.
Midnight Trend Choices – Stylish selections available, shopping feels fast and enjoyable.
воронеж стиральных ремонт машин дому недорого https://remont-stiralok-vrn-24.ru/
Trendy Picks Hub – Fast page loads and an easy-to-follow layout made exploring enjoyable.
ValueOutletShop – Offers excellent discounts and a quick, easy shopping experience.
купить курсовая работа kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru .
Premium World Market – Enjoyed checking out the collection, everything has an international flair.
PositiveVibesOnly – Vibrant visuals, clean structure, and user-friendly flow.
Daily Fashion Choice – A neat variety of styles is displayed, and finding products feels simple.
http://atlantarp.forumex.ru/viewtopic.php?f=36&t=1920
LifeCompass – Quick loading pages and content feels organized and accessible.
Trendy Picks Studio – Modern, clean layout with well-highlighted items for a seamless shopping experience.
Evergreen Hub Selection – Product listings are simple to navigate, helping find items efficiently.
заказать курсовую работу https://kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru .
помощь в написании курсовой работы онлайн http://kupit-kursovuyu-23.ru .
WildRose Finds Online – Boutique has a warm and charming vibe, browsing was enjoyable.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
Наша продукция:
Медная крестовина под пайку 34х29х1 мм 23х25 мм мягкая пайка М1 ГОСТ 32590-2013 Узнайте о высококачественных медных крестовинах под пайку от Редметсплав. Гарантия надежности, прочности, отличной теплопроводности и простоты монтажа. Широкий выбор размеров и конфигураций для любых электрических соединений.
modern style zone – Selections are fresh, browsing feels intuitive and fast today.
MidRiver Collection Spot – Well-organized products showcased neatly, navigation is fast and intuitive.
TrendWaveHub – Modern fashion, smooth page flow, and effortless browsing.
Trendy Outfit Hub – Everything loaded instantly, and the overall selection looked solid.
заказать студенческую работу https://kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru .
Design Market Collective – Clean interface and well-chosen products made the browsing experience pleasant.
GoldenField Studio – Easy-to-navigate pages with neatly arranged products improve the user experience.
NatureGoodsHub – Pleasant layout, eco-conscious items, and easy browsing flow.
Modern Market Picks – Items are well-presented, and navigating between sections is seamless.
VisionPath – Content is presented clearly and browsing is simple and enjoyable.
naturallivingcentral – NaturalLivingCentral offers high-quality selections that are a pleasure to explore.
Everline Shop Online – Great assortment with a smooth interface that makes finding products simple.
WildWood Lane Hub – Clean layout with trendy products and effortless browsing throughout the site.
WildBrook Modern Designs – Stylish pieces throughout, the layout made exploring effortless.
gift ideas hub – The site showcases creative gift choices, and everything loads without hassle.
Modern Roots Curated – Items look appealing and well-organized, browsing feels natural.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Best Bright Choices – Simple, friendly browsing experience with clearly arranged categories.
ChicChoiceStore – Smooth browsing, trendy items, and intuitive site design.
WildRose Picks Online – Friendly and inviting feel, discovered a few special pieces.
Sustainable Home Studio – Easy to navigate and the product variety felt naturally curated.
помощь в написании курсовой работы онлайн http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru .
ChicFinds – Fast-loading pages and browsing through trendy items feels effortless.
UrbanWild Picks – Creative arrangement of items with a sleek interface provides effortless navigation.
Daily Shop Away – Pleasant design and a variety of items make the experience enjoyable.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Everwild Marketplace – Everything is nicely organized, creating a comfortable browsing experience.
UniqueGift Studio Lane – Lovely presentation of gifts and clear navigation create an enjoyable shopping experience.
MoonCrest Select – Attractive designs showcased well, exploring the store feels natural.
WildRose Goods – Warm and cozy atmosphere, found a few delightful surprises.
BestGiftSpot – Easy-to-browse gifts, fast page loads, and enjoyable shopping flow.
Purpose-Driven Modern Store – The selection feels intentional and stylish, navigating is simple and smooth.
Plains Trading Store – Well-structured pages and simple navigation improved the overall experience.
Top Tier Finds Store – High-end selections shown in a clean and accessible layout.
GiftSpot – Beautiful selection of gifts and the site is very easy to navigate.
fashion zone hub – Trendy selections are appealing, site feels quick and intuitive.
<consciousfashionhub – ConsciousFashionHub offers stylish, eco-friendly items that are simple to browse.
Wild Rose Picks – Boutique has a lovely atmosphere, found some special items easily.
Mountain Mist Collection Hub – Products displayed attractively, navigation feels smooth and quick.
TrendHavenShop – Attractive items, clear layout, and convenient navigation.
Curated Eco Commerce – Unique and charming pieces with a clean layout, exploring was a joy.
Motivate & Move – The site offers steady performance wrapped in empowering vibes.
Quiet Plains Market Hub – The site loaded fast, and browsing through sections felt very comfortable.
Everwood Supply – Well-organized supplies, loading quickly and making shopping hassle-free.
EverGlow Design Hub – Stylish layout with polished visuals and neatly arranged products for a professional look.
Premium Home & Style – Home and lifestyle products arranged thoughtfully with easy navigation.
WildBrook Modern Shop – Stylish and contemporary, navigating through the items felt smooth.
Unique Gift Corner Hub – Clear layout with neatly organized gifts makes exploring easy.
modern trend corner – Selections appear attractive, site navigation is clear and intuitive.
Добро пожаловоть в новое онлайн-казино Атом. На нашей площадке вас ждут тысячи интересных игр https://atomplay.top
WildRose Lifestyle Online – Cozy, inviting atmosphere, browsing revealed a few standout items.
Mountain Star Picks – Modern items arranged neatly, browsing is enjoyable and quick.
Curated Creative Finds – Colorful, interesting, and well-presented products, browsing was enjoyable.
ValueExpressStore – Easy browsing, attractive picks, and smooth site experience.
RainyCity Online – Lovely page design with fast navigation and nicely presented items.
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/hied/2020/10/29/self-care-saturdays/comment-page-99/#comment-389061
Elevated Daily Hub – User-friendly navigation with visually appealing layout.
Everyday Forest Goods – Affordable everyday items, browsing and finding products feels quick and easy.
Seasonal Trend Corner – The shop feels polished, loads efficiently, and keeps everything easy to find.
trend store picks – Items are well arranged, site navigation feels clean and simple.
UniqueValue Picks Online – Clear layout and value-focused product arrangement create an enjoyable experience.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
MoonGlow Boutique Hub – Minimalist layout with soft visuals ensures a smooth and appealing shopping journey.
стайлер для волос дайсон цена с насадками официальный сайт купить https://stajler-d-1.ru .
фен dyson купить оригинал фен dyson купить оригинал .
купить дайсон стайлер для волос официальный сайт цена с насадками https://stajler-d.ru/ .
timelessdiscoverhub – TimelessDiscoverHub offers unique items with a carefully curated classic feel.
Next Level Lifestyle – Each item feels modern, and exploring the store is smooth and enjoyable.
Mountain View Deals Hub – Great outlet items, navigating the site is easy and pleasant.
WildRose Studio Online – Cozy and charming shop, found a few pieces worth exploring.
Global Thoughtful Finds – Navigation is intuitive, the collection feels purposeful and well curated.
ValueOutletStore – Items are easy to find, navigation is smooth, and shopping is enjoyable.
RareFlora Market Hub – Attractive botanical style with responsive pages and smooth navigation.
Premium Home & Style – Refined layout with intuitive browsing and organized categories.
SunrisePeak Inspirations – The creative ideas showcased here feel uplifting and easy to browse.
fashion outlet finds – Pieces appear trendy, browsing is fast and very user-friendly.
noble boutique access – Browsing felt natural and product sections were easy to follow.
Forest Lane Hub – Lovely forest-inspired selection, making browsing smooth and pleasant.
фен дайсон цена официальный сайт stajler-d-2.ru .
UrbanChoice Lane Hub – Fast-loading pages with well-displayed items and intuitive navigation.
купить фен дайсон купить фен дайсон .
https://douploads.net/45seol3curp6
FashionChoice Picks – The assortment is well-curated, and moving through categories feels easy.
Colorful Fashion Place – The items display beautifully, and the overall navigation stays smooth.
Next Gen Home Essentials – Smooth navigation paired with innovative and stylish items.
дайсон официальный stajler-d.ru .
DealQuest Market – Everything is laid out logically, contributing to a smooth user journey.
Ever Forest Essentials – Browsing feels smooth, items are simple, clean, and appealing.
NameDrift Collections – Stylish selections offered, browsing feels natural and enjoyable.
taib29 is my new spot for quick bets. The site is straightforward, and depositing funds was hassle-free. I recommend taib29 to anyone looking for entertainment!
carefullychosenluxury – Carefullychosenluxury has an elegant selection that made browsing feel premium and fun.
BrightBudgetStore – Neatly displayed items, smooth browsing, and simple shopping.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Style Picks Marketplace – Carefully curated items with smooth interaction flow.
AchieveWithFocus – Great motivational content, moving through the site is effortless.
trusted value hub – Selections look strong, navigating is fast and easy.
Всё о камерах видеонаблюдения — полное руководство!
Приветствуем вас, уважаемые форумчане! Сегодня мы подробно поговорим обо всём, что касается видеокамер наблюдения. Мы поможем вам разобраться в огромном разнообразии предложений рынка и сделать правильный выбор оборудования для защиты вашего имущества и безопасности вашей семьи.
Почему важно установить систему видеонаблюдения?
Камеры видеонаблюдения становятся всё популярнее среди владельцев домов, офисов и коммерческих помещений. Они обеспечивают защиту имущества, предотвращают преступления и помогают контролировать происходящее даже дистанционно. Давайте рассмотрим самые важные аспекты выбора камеры и её установки.
Какие бывают виды камер видеонаблюдения?
Вы можете выбрать камеру исходя из ваших потребностей и условий эксплуатации:
– **Уличные** — предназначены для наружной установки, защищены от влаги и пыли.
– **Домашние** — компактные модели для внутренней установки.
– **IP-камеры** — позволяют подключаться к сети Интернет и просматривать записи онлайн.
– **Wi-Fi камеры** — удобны благодаря беспроводному соединению.
– **Камеры с SIM-картой** — работают независимо от интернета, передавая сигнал через мобильную сеть.
– **Миниатюрные камеры** — незаметны и подходят для скрытого наблюдения.
– **Поворотные камеры** — способны охватывать большие площади, поворачиваясь на 360 градусов.
– **Ночные камеры** — оснащены инфракрасной подсветкой для съёмки в темноте.
—
Как правильно выбрать камеру видеонаблюдения?
Перед покупкой обратите внимание на следующие характеристики:
– Разрешение камеры — HD/FullHD/UHD обеспечит чёткое изображение.
– Угол обзора — широкий угол позволяет видеть больше пространства.
– Наличие микрофона и динамика — возможность двусторонней связи.
– Датчик движения — экономия памяти устройства путём включения записи только при обнаружении активности.
– Питание — проверьте совместимость с вашим источником питания.
– Возможность удалённого доступа — управление камерой через смартфон или компьютер.
—
Установка и подключение камеры видеонаблюдения
Правильная установка и настройка камеры позволят вам эффективно пользоваться всеми возможностями системы видеонаблюдения. Рассмотрим ключевые моменты:
– Выберите оптимальное место для размещения камеры, обеспечивающее максимальный обзор охраняемой территории.
– Убедитесь, что камера защищена от погодных воздействий, если устанавливается снаружи здания.
– Настройте Wi-Fi соединение или кабельную линию подключения.
– Установите приложение для просмотра записей и управления камерой через мобильное устройство.
—
Где лучше всего приобрести камеру видеонаблюдения?
При покупке обращайте внимание на проверенные магазины и бренды. Рекомендуем выбирать оборудование известных производителей, предлагающих гарантии качества и поддержку клиентов. Обратите внимание на предложения крупных торговых площадок, таких как Ozon, Wildberries и специализированные магазины электроники.
—
Советы по установке камер видеонаблюдения:
– Изучите правила установки камер видеонаблюдения перед началом монтажа.
– Получите согласие жильцов многоквартирных домов на установку камер в подъездах и местах общего пользования.
– Позаботьтесь о защите личной жизни соседей, устанавливая камеры таким образом, чтобы избежать нарушения частной собственности.
—
Поделитесь своим опытом!
Расскажите нам о вашем опыте покупки и установки камер видеонаблюдения. Может быть, у вас есть советы или рекомендации для новичков? А может, вы столкнулись с проблемами при выборе или настройке оборудования? Оставляйте комментарии ниже, давайте делиться полезными советами вместе!
Автор:
Система видеонаблюдения
*Данная статья носит информационный характер и предназначена исключительно для ознакомительных целей.*
Glow Lane Online – Smooth layout with attractive items that make exploring enjoyable.
дайсон фен оригинал цена дайсон фен оригинал цена .
Fashion Daily Place – Daily fashion items are showcased well, browsing feels quick and effortless.
trendmarkethub – TrendMarketHub delivers stylish selections in a user-friendly, clean layout.
Intentional Living Marketplace – Navigation is easy and items reflect careful selection.
TallCedar Picks – Comfortable and inviting layout, found some nice products.
дайсон стайлер для волос с насадками купить официальный сайт цена http://stajler-d-1.ru/ .
NatureRoot Corner – Lovely natural items showcased well, browsing feels simple and convenient.
Modern Curated Goods – Items reflect careful selection, browsing was simple and enjoyable.
DreamVisionOutlet – Fast navigation, inspiring items, and a neat, clean interface.
ShareGrow Online – Friendly atmosphere with a tidy layout that makes navigation effortless.
дайсон официальный сайт стайлер купить http://stajler-d.ru .
Soft Petal Store Deals – Really loving the soft, calming vibe here; always stumble across something refreshing.
Modern Living Design Hub – Modern living products showcased in an organized, user-friendly setup.
ValuableLessonsHub – Informative content, and navigating the site was smooth.
Discover Trend Corner – The modern layout and fast-loading pages make exploring items enjoyable.
discover hub store – Selections are neat, site layout is intuitive and organized.
FDP Trend Hub – Stylish selections are easy to browse, site experience feels smooth.
>Forward-Focused Home Finds – Smooth interface and innovative selection make shopping enjoyable.
Wild Bird Creative – Impressive variety with intentional curation, very enjoyable browsing.
Goldcrest Corner – Neatly presented items make exploring the studio catalog simple and enjoyable.
Thanks you!
https://hop.cx
NightBloom Treasures – Beautifully displayed products, browsing here feels intuitive and pleasant.
Lifestyle Hub Premium – Enjoyed checking out the range, everything looks carefully chosen.
dyson сайт официальный в россии http://www.stajler-d-2.ru/ .
фен дайсон купить официальный сайт https://www.stajler-d-1.ru .
ElegantStyleStore – Shopping is simple, items are neatly displayed, and navigation feels natural.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
купить стайлер дайсон официальный сайт https://www.stajler-d.ru .
<Top Quality Marketplace – Well-curated items showcased with a clean layout and effortless browsing.
new deals shop – Offers look appealing, site navigation is fast and simple.
ModernTrendsVault – Loved the collection, site layout feels clean and intuitive.
Innovative Finds Market – Everything feels visually engaging, and browsing is effortless.
FCreative Studio – Loved the curated feel, everything was clear, organized, and pleasant to look at.
World Lifestyle Finds – The layout is clean, and exploring authentic items is enjoyable.
UrbanRidge Collection Online – Modern setup, enjoyable to browse and easy to navigate.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
FDS Bargain Spot – Trendy selections displayed clearly, browsing is convenient and easy.
https://www.wikidot.com/user:info/codde1xbet
topshopcentral – TopShopCentral delivers a curated range with clear details that make shopping smooth.
Global Design Treasures – Impressive selection, navigating through all the designs was seamless.
a href=”https://discoveryourpurpose.click/” />DiscoverLife Purpose – Well-organized pages and encouraging material provide a steady user experience.
Northern Peak Hub – Well-curated items, browsing feels quick and intuitive today.
<Golden Harbor Store – Dependable goods and smooth browsing create a simple shopping experience.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
ChicChoiceHub – Fast browsing, appealing products, and intuitive site design.
shop hot finds – Items appear appealing, site navigation feels intuitive and fast.
http://hard1russia.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=14&t=914
TimberCrest Finds Online – Gallery has a warm artistic feel, browsing is enjoyable.
Conscious Essentials Hub – Shopping is pleasant, thanks to quality items and ethical practices.
Fashion Finds Hub Online – Store showcases unique products, navigation is smooth and easy.
trendyshopzone – TrendyShopZone feels clean and professional with easy-to-use navigation.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Golden Root Corner – Well-laid-out root collection, making navigation fast and simple.
shop quality finds – Products look appealing, browsing feels natural and effortless.
WildShore Shop – Product variety is impressive, layout is intuitive and browsing is smooth.
BloomCorner Picks – A refreshing aesthetic combined with simple menus enhances usability.
WildRose Lifestyle Online – Cozy, inviting atmosphere, browsing revealed a few standout items.
сервисный центр по ремонту стиральных машин ремонт стиральных машин вызов
Artistic Essentials Shop – Every item feels curated, and navigating the store is smooth.
Urban Lifestyle Lane – Modern items displayed cleanly with smooth page transitions and easy navigation.
FLH Picks – Unique collections showcased nicely, shopping experience is smooth and easy.
Consumer Curations Studio – Clear interface with thoughtfully selected products, very enjoyable to browse.
SocialTreasureHub – Engaging products, fast browsing, and an intuitive layout.
handmadeandmodernhub – HandmadeAndModernHub showcases a balanced collection of artisan and modern items, easy to explore.
Быстрые займы под залог ПТС! Получите деньги за 1 час, автомобиль остается у вас смотреть
Grand Forest Picks Hub – Beautiful studio products, with an intuitive interface for effortless navigation.
HighlandMeadow Hub Studio – Relaxing design and smooth browsing experience throughout the shop.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Find the newest updates — http://hammill.ru/
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Труба профильная нержавеющая 30x30x1.5 мм AISI 304 шлифованная Покупайте качественную трубу профильную нержавеющую 30x30x2 мм AISI 201 с шлифованной отделкой на Редметсплав.рф. Прочная и элегантная нержавеющая сталь AISI 201 обеспечит надежность и стиль вашим строительным и дизайнерским проектам.
FLO Store – Fashion deals look attractive, shopping experience is smooth and intuitive.
фен dyson купить фен dyson купить .
qualityproductzone – QualityProductZone provides a delightful range of items that are easy to explore.
CreativeGlowStore – Clean design, unique products, and enjoyable, smooth browsing.
UrbanTrend Studio Lane – Organized layout with attractive items provides a pleasant shopping journey.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Bright Crest Online – Modern spacing and logical item placement make the browsing journey hassle-free.
top shopping corner – Selection looks fantastic, browsing feels effortless and quick.
Everglen Shop – Warm atmosphere overall, and scrolling through the products felt smooth.
BluePeak Finds – Modern aesthetic with a simple, enjoyable layout for exploring items.
Users benefit from the following benefits by logging into the platform through the current Mostbet mostbet az
Clickping Experience Store – Thoughtful layout with intuitive browsing and well-organized products.
Curated Premium Essentials – Every piece feels unique and browsing is intuitive.
Откройте мир развлекательных игр с Мелстрой Гейм – качественные и инновационные игровые решения для всей семьи https://melstroy-game.uno
Contemporary Studio Hub – Stylish items and smooth navigation, enjoyed exploring all the collections.
FPM Trends – Trendy market collections look fresh, navigating the site is simple.
TrendSpotDaily – Daily selections look appealing, pages load quickly, and shopping is effortless.
стайлер дайсон купить в спб http://www.fen-dn-kupit-1.ru/ .
shopandbrowse – ShopAndBrowse presents fresh products with simple, easy-to-understand details.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
https://makeagif.com/user/melmybetfree?ref=UVw8WE
Daily Hub Lane – Clear presentation of products, intuitive browsing, and fast-loading pages.
Soft Sky Studio Online – Relaxing tones and tidy layout make exploring effortless.
Curated Home & Design – Elegant product arrangement with smooth navigation and clear sections.
Modern Daily Essentials – Each product is thoughtfully chosen, and browsing is simple and fast.
Расскажем, в какой подразделение ты можешь попасть и какие выплаты за подписание контракта контракт на сво
Bright Style Trail – Featured items pop nicely, and the layout keeps everything intuitive.
Design Curations Hub – Products feel special and well-arranged, navigating the site was simple.
Fashion Trend Hub – Trendy collections appear fresh, shopping experience feels simple and enjoyable.
Здесь
глисты выходят комом
Kudos. I appreciate this.
luxury casino canada https://bhcmerced.org/canadian-casino-online/ no deposit casino canada
GoldenPeak Artisan Finds – A delightful mix of handmade pieces, presented in a calming, neat layout.
официальный магазин дайсон в москве fen-dn-kupit-1.ru .
Golden Meadow Lifestyle – Warm and inviting shop design, items feel thoughtfully chosen.
Daily Finds Corner – Neatly arranged products, simple navigation, and enjoyable browsing experience.
Curated Trade Center – A trade-focused marketplace with intuitive browsing and clear visuals.
Refined Lifestyle Picks – Easy browsing with high-quality products for daily use.
trendymarketcentral – TrendyMarketCentral provides a seamless and visually appealing platform for all shoppers.
Fashion Value Outlet – Items are well displayed, shopping feels easy and enjoyable.
designbuyzone – DesignBuyZone features carefully chosen selections that created a refreshing browsing experience.
Given the significant impact of data centers on job creation in the U.S., could the Indian government’s tax incentives and rebates on tech industries serve as a catalyst for job growth in the U.S., even without direct hiring of tech workers? Might this be a strategic move for U.S. companies to expand operations, particularly in light of ongoing global economic shifts? ()
EverLine Picks Online – Items show careful craftsmanship and an artisanal quality.
купить фен dyson купить фен dyson .
Search for affordable hotels by location, amenities, and real reviews https://gfoster.photo/2024/01/03/birmingham-december-2023/#comment-136025
Узнайте, какие выплаты положены служащим по контракту, на сколько лет заключается контракт контракт на сво
WaterEase Bright Shoppe – A calm interface with gentle highlights keeps browsing relaxed.
Crafted Modern Living – Products are stylish and functional, making shopping enjoyable.
Modern Comfort Store – A comfortable modern feel supported by straightforward navigation.
FuturePath Online Hub – Cleanly arranged products with modern design ensure effortless shopping.